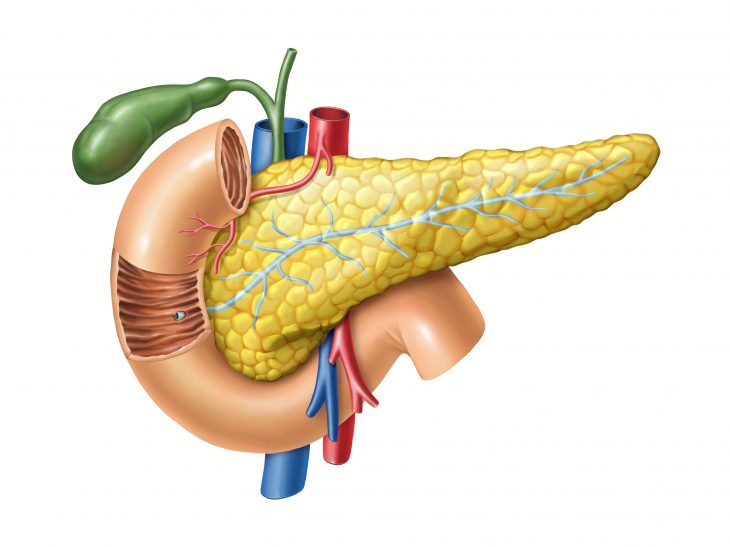
The pancreas is an essential organ in the human body, playing a vital role in digestion and hormone regulation. Despite its relatively small size, this gland holds significant importance in maintaining overall health and well-being. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the intriguing world of the pancreas, uncovering interesting facts about its structure, functions, and the role it plays in our daily lives. Join us on this journey as we delve into the fascinating world of the pancreas.
An Integral Organ
The pancreas is a long, flat gland located deep in the abdomen, behind the stomach. It is part of the digestive system and the endocrine system. This dual functionality makes it a truly remarkable organ in the human body.
Size and Shape
The pancreas measures approximately 6 to 8 inches in length and weighs around 70 to 100 grams. It has a unique elongated, tadpole-like shape, with a broader head on the right side and a narrower tail on the left side.
Anatomy and Structure
The pancreas is made up of two main types of tissue: exocrine tissue and endocrine tissue. The exocrine tissue consists of acinar cells that produce and secrete digestive enzymes into the pancreatic ducts. The endocrine tissue consists of clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans, which secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
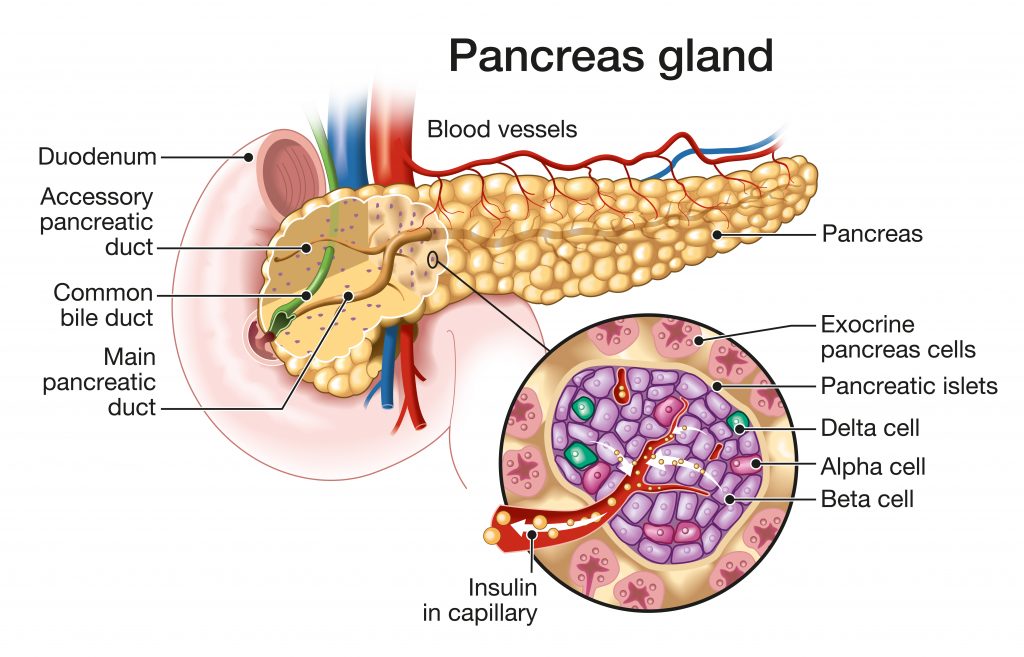
Digestive Function
The exocrine function of the pancreas is crucial for digestion. It produces digestive enzymes, including amylase, lipase, and proteases, which are released into the small intestine. These enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, facilitating their absorption and utilization by the body.
Hormone Regulation
The endocrine function of the pancreas involves the production and secretion of hormones, including insulin and glucagon. These hormones play a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin helps lower blood sugar by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar levels by promoting the release of stored glucose from the liver.
Hidden Location
The pancreas is located deep within the abdomen, making it difficult to palpate or feel during a physical examination. This hidden location protects it from external trauma, but it also makes it challenging to diagnose pancreatic disorders at early stages.
Regenerative Abilities
Unlike many other organs in the human body, the pancreas has remarkable regenerative capabilities. It can regenerate and repair damaged tissue, especially in response to mild injuries or specific diseases. This regenerative capacity provides hope for potential treatments of pancreatic diseases in the future.
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive and deadly forms of cancer. It is often challenging to detect in its early stages due to the pancreas’s deep location and the lack of specific symptoms. Early diagnosis is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and increasing the chances of survival.
Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT)
Individuals with certain pancreatic disorders, such as chronic pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis, may require pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT). This therapy involves taking oral pancreatic enzyme supplements to aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, as the pancreas is unable to produce sufficient enzymes.
Pancreatic Islet Transplantation
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, pancreatic islet transplantation can be a potential treatment option. This procedure involves transferring islet cells from a donor pancreas into the recipient’s pancreas. The transplanted islet cells can then produce insulin, helping regulate blood sugar levels.
Balanced Diet
Eat a well-balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats, as they can put strain on the pancreas.
Moderate Alcohol Intake
Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to chronic pancreatitis, a condition characterized by inflammation and irreversible damage to the pancreas.
Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting is highly recommended to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer and other associated health complications. Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing pancreatic diseases.

Regular Check-ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your pancreatic health and address any concerns or symptoms promptly. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
The pancreas is a fascinating and important organ. It plays a vital role in our digestive system and overall health. There are many interesting facts about the pancreas, and it is important to be aware of the symptoms of pancreatic problems so that they can be treated early.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the symptoms of pancreatic problems?
The symptoms of pancreatic problems can vary depending on the type of problem. However, some common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, weight loss, diarrhea, jaundice, and fatigue.
What are the causes of pancreatic problems?
The causes of pancreatic problems can vary depending on the type of problem. However, some common causes include gallstones, alcohol abuse, smoking, diabetes, chronic pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
How is pancreatic cancer treated?
The treatment for pancreatic cancer depends on the stage of the cancer. However, some common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
How can I prevent pancreatic problems?
There is no sure way to prevent pancreatic problems, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, not smoking, and limiting your alcohol intake.
What are the long-term effects of pancreatic problems?
The long-term effects of pancreatic problems can vary depending on the type of problem and the severity of the damage. However, some possible long-term effects include malabsorption, indigestion, pain, and fatigue.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
