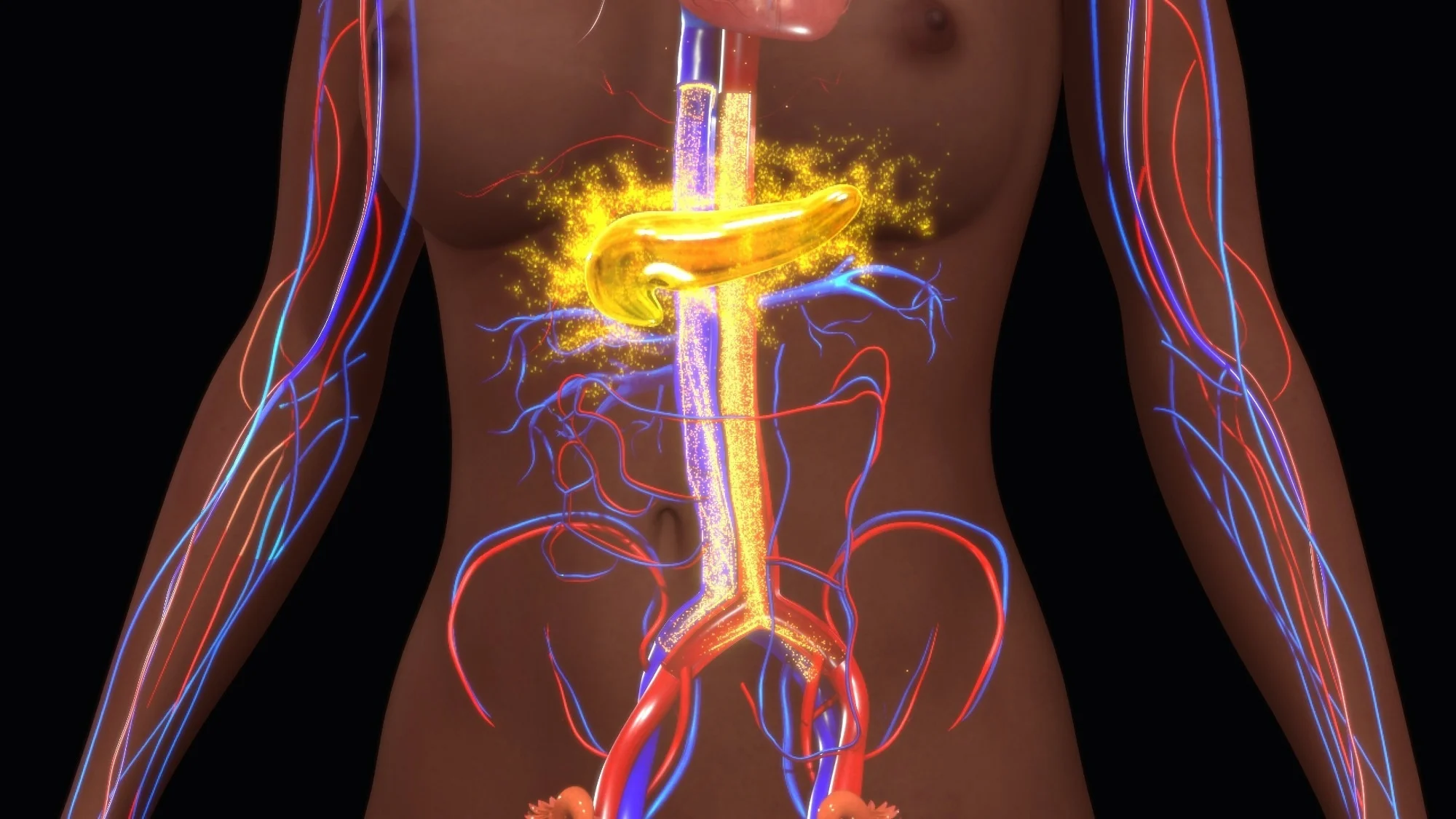
Insulin is a hormone that plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It is primarily known for its role in regulating blood sugar levels, but its impact goes far beyond that. This remarkable hormone is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas and is essential for the proper functioning of our body.
In this article, we will explore 18 astonishing facts about insulin that will not only deepen your understanding of its importance but also leave you amazed at its incredible versatility. From the history of its discovery to its association with diabetes and its potential therapeutic applications, these facts will give you a comprehensive insight into the wonders of insulin.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of insulin and uncover some intriguing facts that will surely blow your mind!
Key Takeaways:
- Insulin is a vital hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels and allows cells to use glucose for energy. It’s crucial for managing diabetes and has revolutionized treatment, enabling people to live longer and healthier lives.
- Insulin can be administered through various methods, including injections, pumps, and even inhaled options. It’s important to store insulin properly, monitor blood sugar levels, and work with healthcare providers to ensure effective and safe treatment.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas.
Insulin is a crucial hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in the body. It allows cells to take in glucose and use it as energy.
Insulin was first discovered in 1921 by Frederick Banting and Charles Best.
These two Canadian scientists made a breakthrough in the field of medicine by isolating and extracting insulin from the pancreas of dogs.
Insulin plays a vital role in the treatment of diabetes.
People with type 1 diabetes do not produce enough insulin, while those with type 2 diabetes have developed insulin resistance. Insulin injections or insulin pumps are used to manage blood sugar levels.
Insulin is not only involved in glucose metabolism.
It also plays a crucial role in promoting the storage of glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscles, as well as in regulating fatty acid synthesis and protein metabolism.
Insulin levels vary throughout the day.
The body releases insulin in response to elevated blood sugar levels after meals, and its secretion decreases during periods of fasting or physical activity.
Insulin resistance is a condition where cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin.
It is often associated with obesity and is a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity and a healthy diet can help improve insulin sensitivity.
Insulin can be administered through various routes.
It can be injected subcutaneously using a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. There are also inhaled insulin options available for some patients.
Insulin pumps provide a continuous supply of insulin.
These small devices are worn on the body and deliver insulin through a small tube inserted under the skin. They can be programmed to release different amounts of insulin throughout the day.
Insulin has evolved over the years.
Since its discovery, different forms of insulin have been developed, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting varieties to meet the specific needs of individuals with diabetes.
Insulin is not just for humans.
Animals such as dogs and cats can also suffer from diabetes and may require insulin treatment under veterinary supervision.
Insulin overdose can lead to hypoglycemia.
Excessive insulin administration can cause blood sugar levels to drop dangerously low, resulting in symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
Insulin has side effects.
Some common side effects of insulin include weight gain, hypoglycemia, injection site reactions, and allergic reactions. Close monitoring and adherence to the prescribed dosage are essential.
Insulin therapy requires proper storage.
Insulin should be stored in a refrigerator at temperatures between 36°F and 46°F (2°C to 8°C). It should not be frozen and should be protected from direct sunlight.
Insulin pumps offer more flexibility with meal planning.
Unlike multiple daily injections, insulin pumps allow for more precise insulin delivery, making it easier to adjust doses during meals and snacks.
The discovery of insulin revolutionized diabetes treatment.
Before insulin, diabetes was often a fatal condition. The availability of insulin has enabled individuals with diabetes to live longer and healthier lives.
Insulin can be expensive.
The cost of insulin varies depending on factors such as brand, type, and insurance coverage. Access to affordable insulin is a critical issue for many people with diabetes.
Insulin therapy requires regular monitoring.
Regular blood sugar testing is essential to adjust insulin doses and ensure optimal management of diabetes. Continuous glucose monitors can provide real-time data to assist with insulin therapy decisions.
Research continues to advance insulin therapy.
Scientists are constantly working on improving insulin formulations and delivery methods. There is ongoing research to develop more efficient and convenient ways to administer insulin.
Conclusion
In conclusion, insulin is a truly remarkable hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating our blood sugar levels and maintaining overall health. From its discovery to its life-saving benefits, the journey of insulin has had a profound impact on the field of medicine. Understanding the astonishing facts about insulin not only enhances our knowledge of human anatomy but also highlights the importance of this hormone in the management of diabetes. As ongoing research continues to unravel more about insulin and its functions, it is clear that this hormone is a vital component of our body’s intricate systems. Appreciating the significance of insulin can lead to better understanding, treatment, and prevention of diabetes and related conditions.
FAQs
1. What is the function of insulin in the body?
Insulin is responsible for regulating the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the body. It helps to control blood sugar levels by allowing cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream to use as energy or store as glycogen.
2. Why is insulin important in diabetes treatment?
In diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or does not use it effectively (Type 2 diabetes). Insulin therapy is vital for managing blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes and preventing complications that can arise from uncontrolled diabetes.
3. How does insulin differ from other hormones?
Insulin is unique in its role as a key regulator of blood sugar levels. It works in opposition to hormones like glucagon, which raise blood sugar levels, to maintain a delicate balance. Unlike some hormones that act on specific organs or tissues, insulin affects numerous cells throughout the body.
4. Can insulin be used to treat conditions other than diabetes?
While insulin therapy is predominantly used for diabetes treatment, it can also be prescribed for other medical conditions such as gestational diabetes, prediabetes, and certain hormonal disorders. Additionally, insulin may be administered in emergency situations to help correct severe imbalances in blood sugar levels.
5. Are there any side effects of insulin injections?
Like any medication, insulin injections can carry potential side effects. Common side effects include injection site reactions, weight gain, and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor and adjust insulin dosages as needed.
Insulin's remarkable journey continues to shape modern medicine. Beyond diabetes, exploring additional facts about this life-saving hormone unveils its multifaceted nature. Diabetic supplies play a crucial role in managing insulin therapy effectively. Hypoglycemics also warrant attention, as they form an integral part of the diabetes management puzzle. Delving deeper into these interconnected topics empowers individuals to navigate their health with confidence and understanding.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
