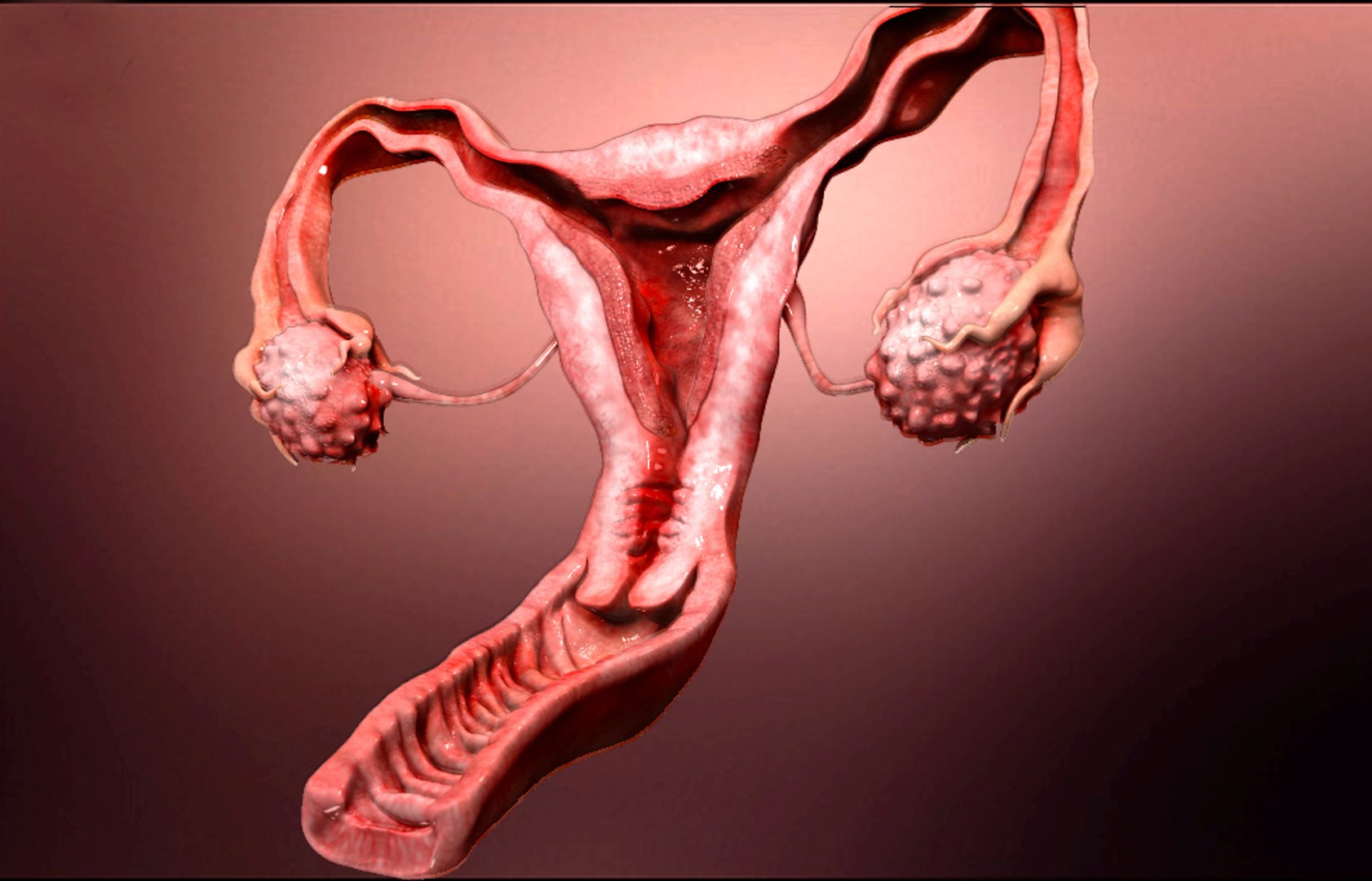
The endometrium is a crucial component of the female reproductive system. This remarkable tissue lines the uterus and plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. While it may seem like a simple layer, the endometrium holds many astonishing facts that highlight its complexity and significance.
In this article, we will delve into 18 astonishing facts about the endometrium that will broaden your understanding of this remarkable tissue. From its unique structure and function to its remarkable ability to undergo monthly changes, the endometrium is truly a marvel of the human body. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of the endometrium!
Key Takeaways:
- The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus that thickens and sheds during the menstrual cycle, playing a vital role in pregnancy preparation and immune defense.
- Hormonal changes, fertility assessments, and conditions like endometriosis can impact the endometrium, affecting women’s reproductive health and overall well-being.
The endometrium is the innermost lining of the uterus.
The endometrium is a remarkable tissue that lines the inside of the uterus. It undergoes dynamic changes throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle, preparing the uterus for possible pregnancy.
The endometrium is composed of two layers.
The endometrium consists of two layers: the functional layer and the basal layer. The functional layer is shed during menstruation, while the basal layer serves as the regenerative base for the new functional layer.
Endometrial tissue is highly responsive to hormonal changes.
The endometrium is sensitive to hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the growth and shedding of the endometrial lining during the menstrual cycle.
The endometrium thickens in preparation for pregnancy.
In response to hormonal signals, the endometrium thickens to create a nourishing environment for a potential embryo. This process, known as the proliferative phase, occurs during the first half of the menstrual cycle.
If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the endometrium sheds.
If fertilization doesn’t take place, the endometrium undergoes a process called menstruation. The shedding of the functional layer results in menstrual bleeding, which typically lasts for a few days.
The endometrium can repair and regenerate itself.
The basal layer of the endometrium is capable of regenerating the functional layer after menstruation. This remarkable ability allows the endometrium to continuously repair and renew itself throughout a woman’s reproductive years.
The endometrium is essential for implantation.
During the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle, the endometrium becomes more vascular and glandular, preparing for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. It creates an optimal environment for the embryo to attach and establish a pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalances can affect the endometrium.
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or anovulation, can result in abnormal thickening or thinning of the endometrial lining. These imbalances can impact fertility and menstrual regularity.
Endometrial cancer can develop in the endometrium.
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the cells of the endometrium. It is often detected early due to symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain, allowing for timely treatment.
Endometriosis is a condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus.
In endometriosis, the endometrial tissue grows in areas outside the uterus, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or pelvic cavity. This condition can cause pelvic pain, fertility issues, and other complications.
The endometrium plays a role in the immune response.
The endometrium is involved in immunological processes, helping to defend the uterus against potential infections. It contains specialized immune cells that contribute to maintaining a healthy environment for reproductive functions.
The thickness of the endometrium is measured during fertility assessments.
Doctors may perform an ultrasound to measure the thickness of the endometrium as part of fertility evaluations. The thickness is an important factor in determining the chances of successful embryo implantation.
The endometrium undergoes angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels. The endometrium undergoes angiogenesis during the menstrual cycle to ensure proper blood supply to support potential pregnancy.
The endometrium has a rich blood supply.
The endometrium has an extensive network of blood vessels, providing the necessary nutrients and oxygen to support the growth and development of the endometrial lining.
The endometrium can be affected by hormonal contraceptives.
Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, can impact the thickness and characteristics of the endometrium. These contraceptives work by altering hormone levels and preventing ovulation.
Disorders like endometritis can cause inflammation of the endometrium.
Endometritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the endometrium, usually caused by infection. It can lead to symptoms like pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, and fever.
The endometrium changes during menopause.
During menopause, the endometrium undergoes significant changes. The hormonal fluctuations and decrease in estrogen levels lead to a thinning of the endometrial lining and the cessation of menstrual cycles.
The endometrium has the ability to support embryo implantation.
The endometrium provides a nurturing environment for the embryo during the implantation process. It secretes various substances that support the attachment and growth of the fertilized egg.
These 18 astonishing facts about the endometrium highlight its remarkable functions, complexities, and its crucial role in reproduction. Understanding the intricacies of the endometrium not only enhances our knowledge of the female reproductive system but also sheds light on various conditions and disorders that can affect women’s health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the endometrium is a remarkable tissue within the female reproductive system. Its function extends beyond providing a supportive environment for embryo implantation. It undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle and plays a critical role in pregnancy. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the endometrium is vital for women’s health, fertility, and management of various conditions such as endometriosis and abnormal uterine bleeding. By exploring the astonishing facts about the endometrium, we can deepen our knowledge and appreciation for this intricate structure and its significant role in reproductive health.
FAQs
Q: What is the endometrium?
A: The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, characterized by its ability to grow and shed every menstrual cycle.
Q: How does the endometrium change during the menstrual cycle?
A: The endometrium thickens and becomes more vascularized in preparation for potential pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, it sheds during menstruation.
Q: Can the endometrium be affected by hormonal imbalances?
A: Yes, hormonal imbalances can result in abnormal growth of the endometrium, leading to conditions such as endometriosis and abnormal uterine bleeding.
Q: Can the endometrium regenerate after miscarriage or childbirth?
A: Yes, the endometrium has the ability to regenerate and repair itself after miscarriage or childbirth to prepare for future pregnancies.
Q: Can endometrial thickness affect fertility?
A: Yes, an optimal endometrial thickness is crucial for embryo implantation and successful pregnancy. An inadequate or excessive endometrial thickness can impact fertility.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
