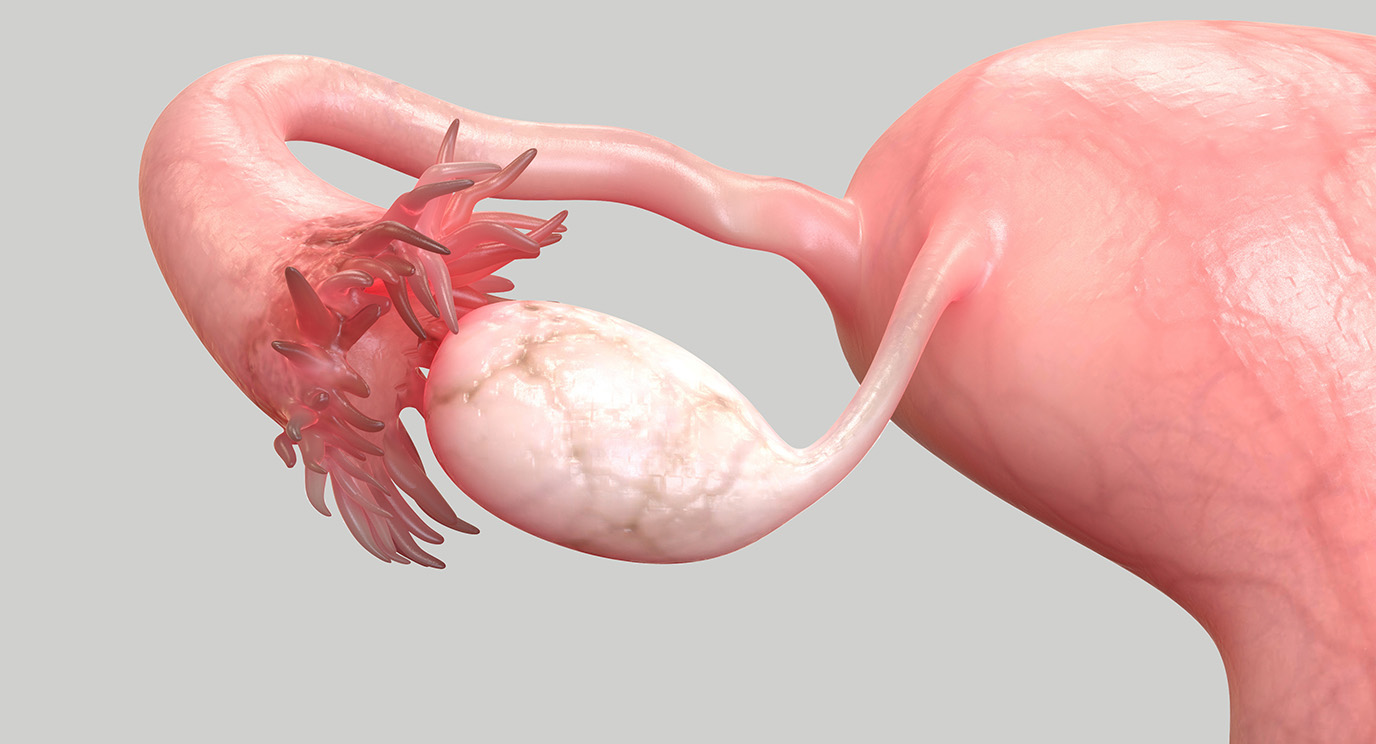
The uterine tubes, also known as Fallopian tubes, play a crucial role in the female reproductive system. These delicate and intricate structures are responsible for transporting the egg from the ovary to the uterus, where fertilization takes place. While most people have a basic understanding of the uterine tubes and their function, there are several surprising facts that are lesser known.
In this article, we will explore 11 intriguing and eye-opening facts about uterine tubes that will give you a deeper insight into their importance and marvel at the complexity of the female reproductive system. From their unique structure to their role in fertility and contraception, these facts will leave you amazed and appreciating the wonders of the human body.
Key Takeaways:
- Uterine tubes, also known as Fallopian tubes, are not directly connected to the uterus. They play a crucial role in fertility by providing a pathway for the sperm to reach the egg for fertilization.
- The Uterine tubes have finger-like projections called fimbriae that help capture the released egg from the ovary during ovulation and guide it into the Uterine tube for fertilization.
The Uterine tubes are not actually connected to the uterus?
Contrary to popular belief, the Uterine tubes, also known as Fallopian tubes, are not directly connected to the uterus. Instead, they are attached to the top corners of the uterus, allowing them to serve as a pathway for the eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus.
The Uterine tubes play a vital role in fertility.
The Uterine tubes are an essential part of the female reproductive system and play a crucial role in fertility. They provide a pathway for the sperm to reach the egg for fertilization, and they also transport the fertilized egg from the ovaries to the uterus for implantation and development.
Each Uterine tube has finger-like projections called fimbriae.
The Uterine tubes have finger-like projections called fimbriae at their distal ends. These fimbriae help to capture the released egg from the ovary during ovulation and guide it into the Uterine tube for fertilization.
The Uterine tubes have muscles that help move the egg.
The walls of the Uterine tubes are lined with smooth muscles that contract in a coordinated manner to help move the egg towards the uterus. These muscular contractions, along with the beating cilia on the inner lining, create a gentle current that propels the egg along the tube.
The Uterine tubes can increase the chances of ectopic pregnancy.
If the Uterine tubes become blocked or damaged, they can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus, typically in the Uterine tube. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Some women have a condition called tubal factor infertility.
Tubal factor infertility refers to a condition where the Uterine tubes are blocked or damaged, making it difficult for the sperm to reach the egg or for the fertilized egg to travel to the uterus. This condition is one of the common causes of female infertility.
The Uterine tubes are named after the Italian anatomist Gabriello Fallopio.
The term “Fallopian tubes” was named after Gabriello Fallopio, an Italian anatomist from the 16th century who first described the anatomy of the female reproductive system, including the Uterine tubes.
Uterine tubes vary in length and diameter.
The length and diameter of the Uterine tubes can vary among individuals. On average, they measure about 10-13 cm in length and 1-4 mm in diameter. However, these measurements can vary based on factors such as age, hormonal changes, and individual anatomical differences.
The Uterine tubes can be affected by infections.
Infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can affect the Uterine tubes and lead to inflammation and scarring. This can cause blockages and impair their ability to function properly, resulting in fertility problems.
The Uterine tubes have different regions.
The Uterine tubes can be divided into different regions, including the infundibulum, ampulla, and isthmus. Each region has unique characteristics and plays a specific role in the reproductive process.
The Uterine tubes can be visualized using medical imaging techniques.
Medical imaging techniques such as hysterosalpingography, ultrasound, and laparoscopy can be used to visualize the Uterine tubes and evaluate their structure and function. These imaging techniques are commonly employed in diagnosing conditions related to the Uterine tubes.
Conclusion
Uterine tubes, also known as Fallopian tubes, are fascinating and essential organs in the female reproductive system. These slender tubes play a critical role in fertilization, as they transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus. While they may seem like simple structures, there are several surprising facts about uterine tubes that you may not be aware of.
Firstly, did you know that the uterine tubes are not directly connected to the ovaries? Instead, they have funnel-shaped openings called fimbriae that sweep over the ovaries to collect the released egg. Additionally, these tubes are lined with cilia, small hair-like structures that help propel the fertilized egg towards the uterus.
Another intriguing fact is that fertilization often occurs in the uterine tubes. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, and the journey through the tube provides an opportunity for the sperm to meet and fertilize the egg.
Furthermore, uterine tubes can be affected by various conditions such as blockages, infections, or even ectopic pregnancies. Understanding the structure and function of these tubes is crucial for identifying and treating any potential issues.
In conclusion, uterine tubes are remarkable organs that play a vital role in the journey of the egg and the process of fertilization. Appreciating the complexity and importance of these tubes enhances our understanding of the female reproductive system.
FAQs
1. What are the uterine tubes?
The uterine tubes, also known as Fallopian tubes, are slender tubes in the female reproductive system that transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
2. How do the uterine tubes collect the eggs?
The uterine tubes have funnel-shaped openings called fimbriae that sweep over the ovaries to collect the released egg.
3. Can fertilization occur in the uterine tubes?
Yes, fertilization often occurs in the uterine tubes. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, providing an opportunity to meet and fertilize the egg.
4. What are some conditions that can affect the uterine tubes?
Blockages, infections, and ectopic pregnancies are some conditions that can affect the uterine tubes.
5. Why is understanding the structure and function of uterine tubes important?
Understanding the structure and function of uterine tubes is crucial for identifying and treating conditions that may arise, ensuring proper reproductive health.
Uterine tubes play a crucial role in reproductive health, but there's more to learn. Curious about factors affecting fertility rates? We've got 17 surprising facts that shed light on this topic. Gynecology is a complex field, and our article on 11 ob gyn facts provides valuable insights. Lastly, understanding reproductive health drugs is essential for making informed decisions, so check out our piece on 6 must-know facts.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


