The reproductive system is a fascinating and vital aspect of our biology. Responsible for the perpetuation of our species, it plays a crucial role in human development and the continuation of life. From the intricate mechanisms of fertilization to the fascinating hormonal processes, the reproductive system is a subject of immense interest and importance.
In this article, we will delve into 14 captivating facts about the reproductive system that will leave you informed and intrigued. From exploring the complex structures involved in reproduction to uncovering the surprising ways our bodies adapt and change during different stages of life, these facts will provide a deeper understanding of this essential biological system. So, let’s embark on this exciting journey into the world of the reproductive system, uncovering its wonders along the way.
Key Takeaways:
- The reproductive system is responsible for creating new life by merging genetic material from two individuals, and it involves organs like the testes, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
- Understanding the complexities of the reproductive system can lead to advancements in reproductive health and fertility treatments, highlighting its significance in human biology and the miraculous journey of life.
The reproductive system is responsible for the creation of new life.
The primary function of the reproductive system is to facilitate the merging of genetic material from two individuals, resulting in the creation of offspring.
The male reproductive system consists of the testes.
The testes are responsible for producing sperm cells and the hormone testosterone, which plays a vital role in male development and fertility.
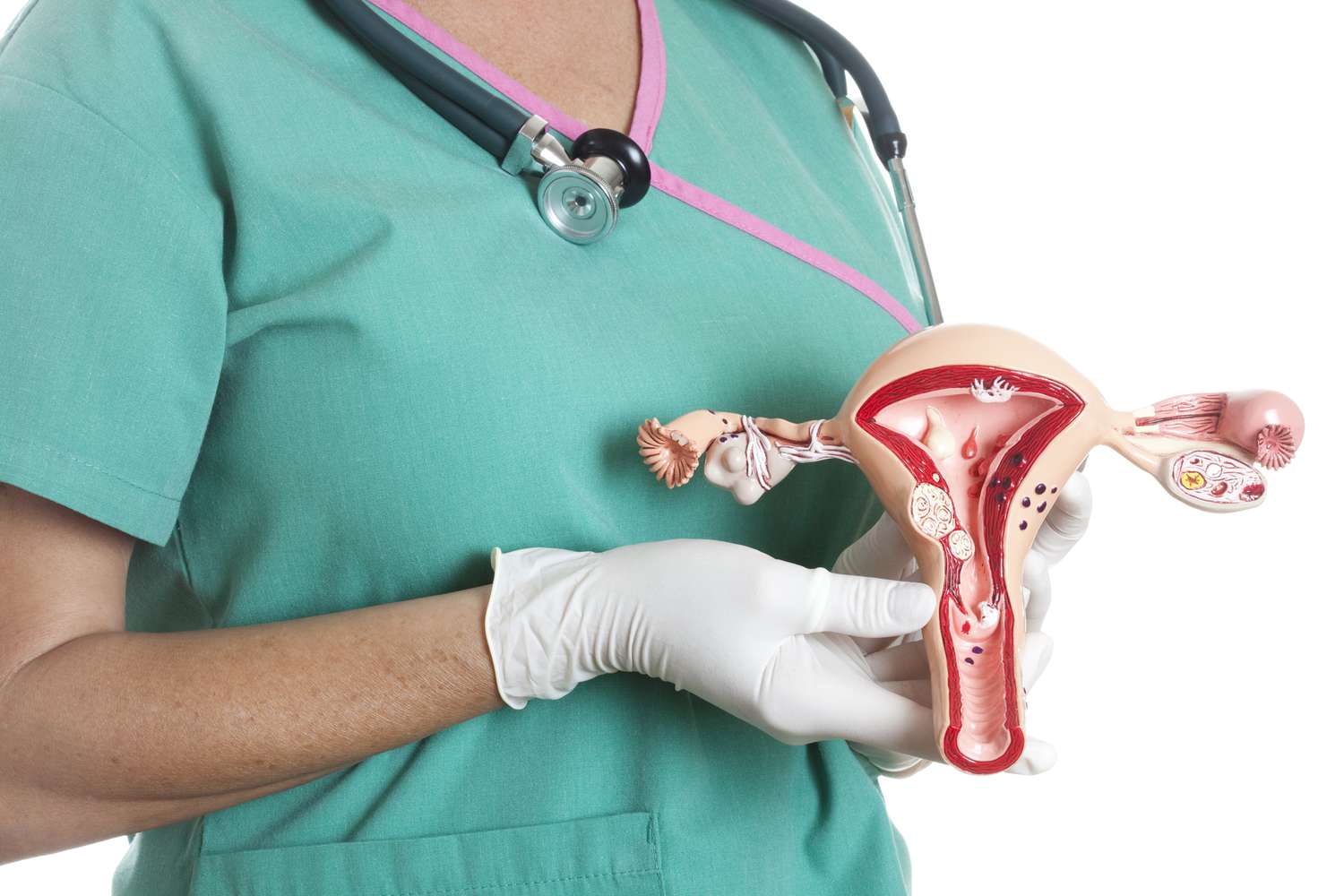
The female reproductive system includes the ovaries.
The ovaries are responsible for producing eggs and the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and support pregnancy.
Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tubes.
After release from the ovary, an egg travels through the fallopian tubes. If it encounters sperm along the way, fertilization can occur.
The uterus is the organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops.
The uterus is a muscular organ that can expand significantly during pregnancy to accommodate the growing fetus.
The menstrual cycle is a monthly hormonal process in females.
During the menstrual cycle, the uterus undergoes changes in preparation for the potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
Sperm can survive in the female reproductive system for up to five days.
This is advantageous for couples trying to conceive, as it allows for a wider window of opportunity for fertilization.
The clitoris is a highly sensitive organ in females.
It contains a dense concentration of nerve endings and plays a key role in sexual pleasure.
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition in males.
It refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection, often resulting in difficulties with sexual intercourse.
Ovarian cancer is a serious health concern for women.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes and survival rates.
The placenta serves as a lifeline between mother and baby.
This temporary organ provides oxygen, nutrients, and waste removal for the developing fetus.
The human reproductive system undergoes changes with age.
Both males and females experience hormonal shifts and a decline in fertility as they get older.
Sperm production takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
It involves the continuous production and maturation of sperm throughout a male’s life.
Women are born with all the eggs they will ever have.
Unlike men who constantly produce new sperm, women have a finite number of eggs, which gradually diminish as they age.
These captivating facts about the reproductive system highlight its significance in human biology and the complexities involved in the creation of new life. Understanding this intricate system can pave the way for advancements in reproductive health and fertility treatments. So the next time you think about the miraculous journey of life, take a moment to appreciate the wonders of the reproductive system!
Conclusion
The reproductive system is a remarkable and fascinating aspect of human biology. From the intricate processes of fertilization to the development of a new life, every step is finely tuned to ensure the continuation of our species. As we have explored in this article, the reproductive system is not only essential for procreation but also plays a significant role in overall health and well-being. By understanding the complexities of our reproductive system, we can make informed decisions about our sexual and reproductive health.
FAQs
Q: What is the primary function of the reproductive system?
A: The primary function of the reproductive system is to produce and deliver sperm in males and to produce eggs and provide the environment for fetal development in females.
Q: How does fertilization occur?
A: Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell, forming a zygote. This usually takes place in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system.
Q: Can infertility affect both men and women?
A: Yes, infertility can affect both men and women. Factors such as hormonal imbalances, reproductive organ abnormalities, and certain medical conditions can contribute to infertility in either sex.
Q: What are some common disorders of the reproductive system?
A: Some common disorders of the reproductive system include endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), erectile dysfunction, and prostate cancer.
Q: Does age affect fertility?
A: Yes, age can affect fertility. In women, fertility declines with age, particularly after the age of 35. In men, although fertility declines with age, it is less pronounced compared to women.
Q: Are there any natural methods of contraception?
A: Yes, natural methods of contraception include tracking menstrual cycles, using fertility awareness methods, and practicing abstinence during fertile periods.
Q: Can sexually transmitted infections (STIs) affect the reproductive system?
A: Yes, sexually transmitted infections can affect the reproductive system. Untreated STIs can lead to complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Q: What are the benefits of regular gynecological exams?
A: Regular gynecological exams can detect early signs of reproductive health issues, including cervical cancer and sexually transmitted infections. They also provide an opportunity for discussions about contraception and menstrual health.
Q: How can I maintain a healthy reproductive system?
A: Maintaining a healthy reproductive system includes practicing safe sex, getting regular check-ups, maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
