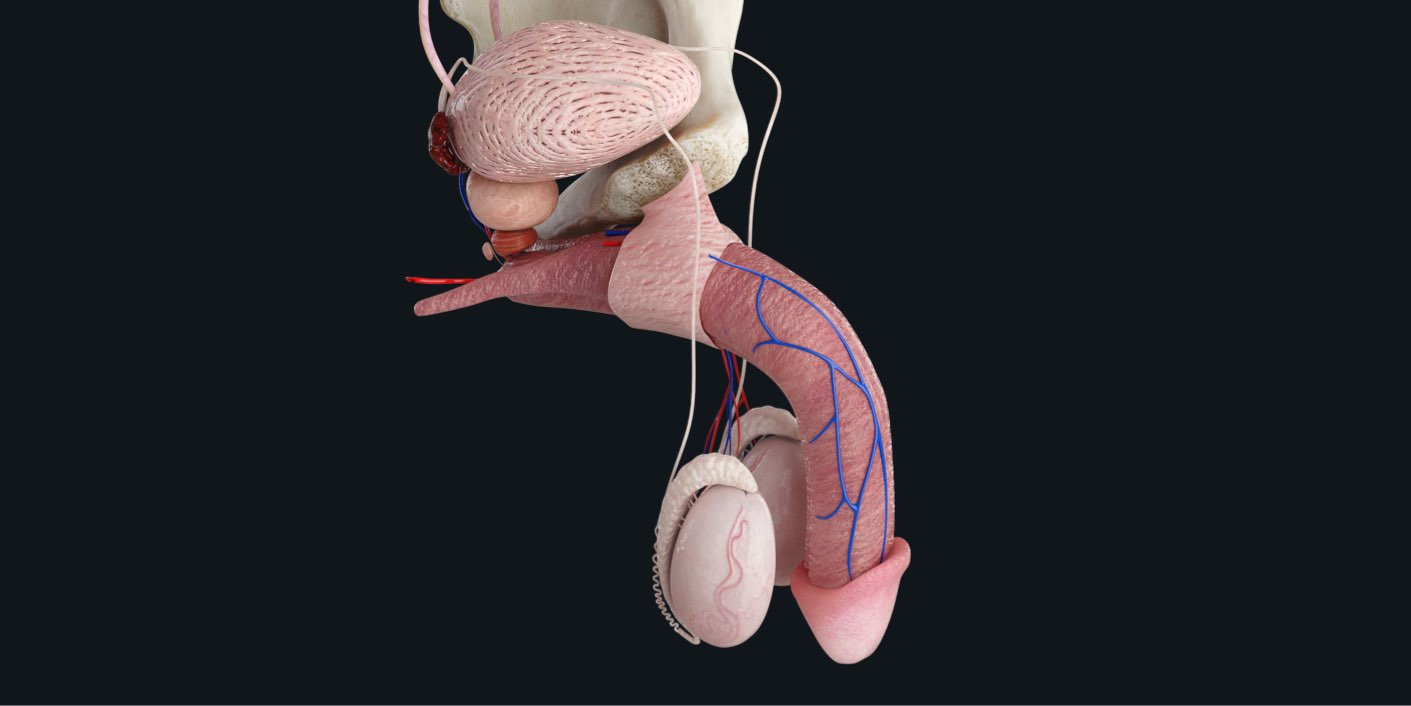
Cowper’s glands, also known as bulbourethral glands, are small glands located in the male reproductive system. Despite their relatively small size, these glands play a crucial role in human anatomy and sexual function. Named after English anatomist William Cowper, who first described them in the 17th century, these glands are an essential part of the male reproductive system.
In this article, we will explore ten fascinating facts about Cowper’s glands. From their anatomical location and structure to their functions and potential health implications, we will delve into the intriguing details of these remarkable glands. So, if you’re curious to learn more about Cowper’s glands and their significance in the male reproductive system, keep reading!
Key Takeaways:
- The Cowper’s glands, also known as bulbourethral glands, produce a fluid that helps prepare the urethra for the passage of sperm, and their size can vary among individuals without affecting their function.
- These fascinating glands play a crucial role in the male reproductive system by producing pre-ejaculate fluid, neutralizing urethral acidity, and working alongside other accessory glands to support semen production.
The Cowper’s glands are also known as the bulbourethral glands.
The bulbourethral glands are small, pea-sized structures located beneath the prostate gland in the male reproductive system.
They are responsible for producing pre-ejaculate fluid.
The Cowper’s glands produce a clear, viscous fluid that is released before ejaculation. This fluid helps to lubricate and cleanse the urethra, preparing it for the passage of sperm.
They are named after the English anatomist, William Cowper.
William Cowper first described these glands in the late 17th century. His detailed anatomical studies helped to advance our understanding of the male reproductive system.
Their secretion contains enzymes and mucus.
The fluid produced by the Cowper’s glands contains enzymes, such as alpha-glucosidase, which helps to break down starches in the urethra. It also contains mucus, which provides additional lubrication.
Their function is regulated by the parasympathetic nervous system.
The Cowper’s glands are controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating sexual arousal and the physiological responses associated with it.
Cowper’s gland fluid may contain sperm.
In some cases, the fluid produced by the Cowper’s glands may contain small amounts of sperm. Although this is rare, it can potentially lead to unintended pregnancy if proper precautions are not taken.
They play a role in neutralizing the acidity of the urethra.
The Cowper’s glands secrete an alkaline fluid that helps to neutralize the acidity of the urethra, creating a more favorable environment for sperm to survive and function.
Cowper’s gland inflammation can cause discomfort and pain.
Inflammation of the Cowper’s glands, known as Cowperitis, can result in pain and discomfort in the genital area. It is typically caused by bacterial infections or sexually transmitted infections.
They are part of the male reproductive system’s accessory glands.
The Cowper’s glands are one of the accessory glands in the male reproductive system, along with the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and epididymis. These glands work together to produce and store semen.
Their size can vary among individuals.
The size of the Cowper’s glands can vary among individuals, with some individuals having larger or smaller glands than others. This natural variation does not affect their function.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cowper’s glands, also known as bulbourethral glands, are a fascinating part of the male reproductive system. These small glands play a crucial role in sexual health and function. They secrete a fluid that helps lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidity caused by urine residue, creating a conducive environment for the sperm to survive.Understanding the functions and importance of Cowper’s glands can contribute to a better comprehension of the male reproductive system as a whole. By producing a clear, lubricating fluid, these glands aid in enhancing sexual pleasure and overall reproductive health.Learning about the fascinating facts surrounding Cowper’s glands highlights the intricate design of the human body and its ability to adapt to the complex functions of reproduction. Further research and study in this field can continue to reveal more insights into the mechanisms and implications of Cowper’s glands, benefiting both scientific knowledge and individual health.
FAQs
Q: What are Cowper’s glands?
A: Cowper’s glands, also known as bulbourethral glands, are small glands located on either side of the male urethra, below the prostate gland. They play a role in secreting a clear, slippery fluid that helps lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidity caused by urine.
Q: What is the function of Cowper’s glands?
A: The main function of Cowper’s glands is to secrete a mucous-like fluid that helps lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidity caused by urine residue. This lubrication aids in facilitating the passage of sperm during ejaculation.
Q: Can problems occur with Cowper’s glands?
A: In some cases, problems can arise with Cowper’s glands. These may include inflammation, infection, or blockage of the glands, leading to difficulties in seminal fluid production or an altered composition of the fluid. It is important to seek medical attention if any issues are suspected.
Q: Do Cowper’s glands contribute to sexual pleasure?
A: Yes, Cowper’s glands do contribute to sexual pleasure. The lubricating fluid secreted by these glands enhances the ease of sexual intercourse and can increase comfort and pleasure during intimacy.
Q: Are Cowper’s glands present in all males?
A: Yes, Cowper’s glands are present in all males. They are a natural part of the male reproductive system and play a vital role in reproductive health and sexual function.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
