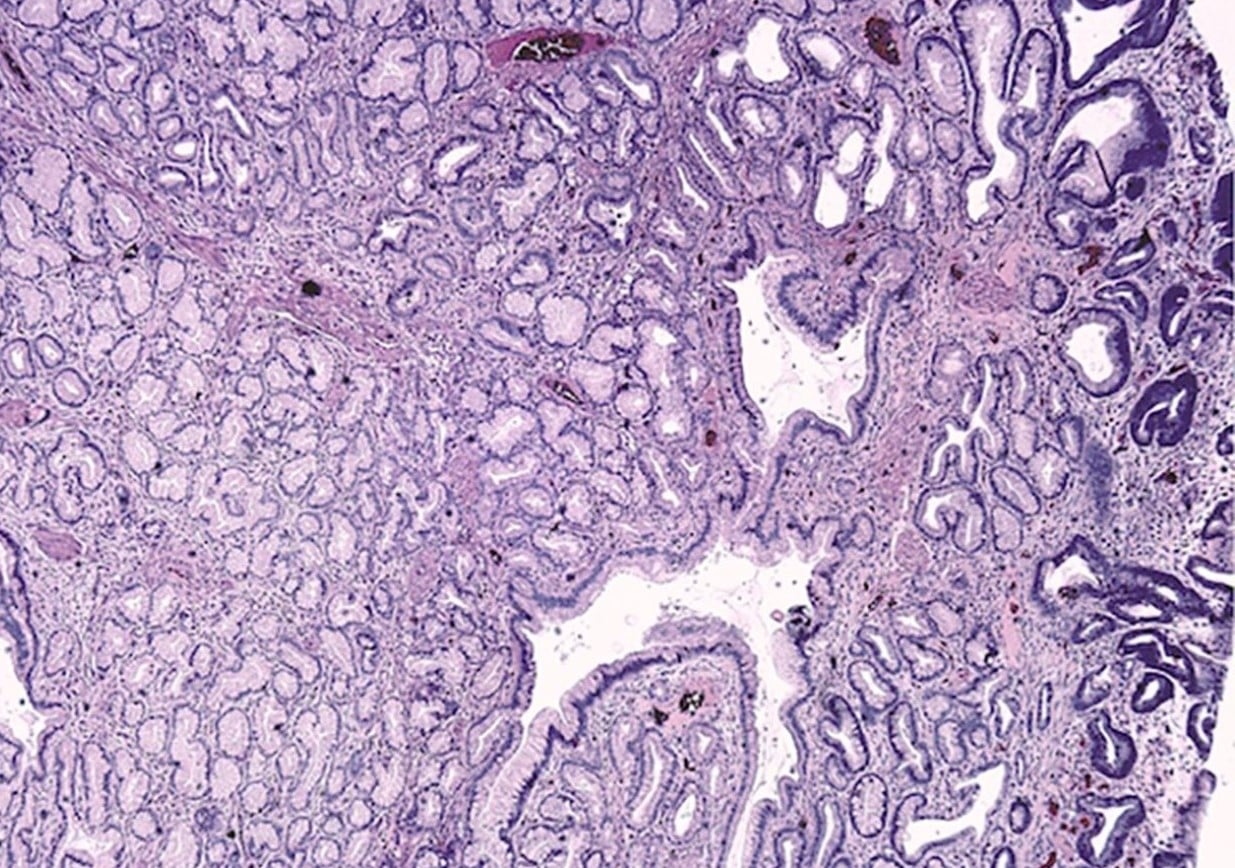
When it comes to the intricate workings of the human body, one of the most fascinating areas to explore is the world of glands. These tiny, yet powerful structures play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. Among the many glands in our body, one that often goes unnoticed is Brunner’s glands.
Brunner’s glands, named after the Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Brunner, are specialized glands found in the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. While they may be small in size, these glands have some mind-blowing secrets waiting to be uncovered. In this article, we will delve into 14 intriguing facts about Brunner’s glands that will leave you in awe of the complexities of the human anatomy.
Key Takeaways:
- Brunner’s glands produce a special fluid that protects the small intestine from stomach acid and helps with digestion by neutralizing acidic contents.
- These unique onion-shaped glands play a vital role in maintaining digestive health and preventing ulcers, showcasing the complexity of the human body.
Unique Structural Features
Brunner’s glands are distinctive due to their onion-shaped appearance, with multiple lobules branching off from a central duct.
Secretory Function
These glands secrete a specialized alkaline fluid that helps neutralize the acidic contents coming from the stomach, creating an optimal pH environment for digestive enzymes.
Mucus Production
Brunner’s glands produce a significant amount of mucus, which helps to protect the duodenum from the damaging effects of stomach acid and aids in the smooth passage of food.
Control of Digestive Enzymes
The alkaline secretions from Brunner’s glands regulate the release of digestive enzymes from the pancreas and contribute to the effective breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
HCO3- Production
The main component of the alkaline fluid secreted by Brunner’s glands is bicarbonate (HCO3-), which assists in neutralizing stomach acid and maintaining the ideal pH for enzymatic activity.
Hormonal Regulation
Brunner’s glands are influenced by various hormones, including secretin and cholecystokinin, which stimulate the secretion of their alkaline fluid in response to the presence of acidic content in the duodenum.
Protection Against Ulcers
The mucus produced by Brunner’s glands acts as a protective barrier, preventing the development of ulcers in the duodenum caused by acid erosion.
Size and Distribution
Brunner’s glands vary in size and distribution within the duodenum, with more abundant glands found in the proximal portion of the small intestine compared to the distal region.
Relation to Peptic Ulcers
Brunner’s glands have been found to play a role in the defense against peptic ulcers, as they secrete substances that inhibit the growth of Helicobacter pylori, the bacteria responsible for many cases of peptic ulcers.
Potential Diagnostic Marker
The examination of Brunner’s gland hyperplasia, an overgrowth of these glands, can serve as a potential diagnostic marker for certain underlying medical conditions, such as duodenitis.
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Brunner’s glands can be visualized during gastrointestinal endoscopy, a procedure commonly used to diagnose and treat various gastrointestinal disorders.
Role in Parietal Cell Stimulation
Brunner’s glands contribute to parietal cell stimulation in the stomach, promoting the release of hydrochloric acid to aid in the digestion of food.
Protection Against Acidic Solvents
The alkaline fluid secreted by Brunner’s glands offers protection against acidic solvents ingested through diet, preventing damage to the intestinal lining.
Important for Digestive Health
Brunner’s glands, with their secretory and protective functions, are vital for maintaining overall digestive health and preventing disturbances in the delicate balance of the gastrointestinal system.
In conclusion, Brunner’s glands serve as an integral part of the human digestive system, playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal pH and protecting the duodenum from acidic damage. Understanding the fascinating facts about Brunner’s glands sheds light on their significance and highlights the complexity of the digestive process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Brunner’s glands are fascinating and vital components of the human digestive system. These small, but powerful glands, located in the duodenum, play a crucial role in protecting the lining of the small intestine and aiding in digestion. The 14 mind-blowing facts about Brunner’s glands that we have explored in this article highlight their unique characteristics and importance.From their ability to secrete mucus to their role in controlling the pH of the intestinal contents, Brunner’s glands contribute significantly to the overall functioning of the digestive system. Moreover, their involvement in the production of digestive enzymes and protection against harmful bacteria further showcases their functionality and significance.Understanding the functions and features of Brunner’s glands can enhance our knowledge of human anatomy and physiology. It is essential to appreciate the complexity and intricacy of these glands and their role in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
FAQs
1. What are Brunner’s glands?
Brunner’s glands are compound tubular glands located in the submucosa layer of the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine.
2. What is the function of Brunner’s glands?
The main function of Brunner’s glands is to secrete mucus, which protects the lining of the duodenum from acidic chyme and other irritants.
3. How do Brunner’s glands contribute to digestion?
Brunner’s glands secrete alkaline mucus, which helps neutralize the acidic chyme coming from the stomach, creating a favorable environment for the digestive enzymes in the small intestine.
4. Can Brunner’s glands get infected or develop diseases?
Yes, Brunner’s glands can become inflamed or infected, resulting in conditions such as Brunner’s gland hyperplasia or Brunner’s gland adenoma.
5. Are there any treatments available for Brunner’s gland disorders?
Treatment options depend on the specific condition. In some cases, medications to reduce stomach acid may be prescribed, while surgical removal of the affected glands may be necessary in more severe cases.
6. Can Brunner’s glands regenerate or repair themselves?
Yes, Brunner’s glands have regenerative capabilities, allowing them to recover and repair damaged tissue.
7. Are Brunner’s glands present in other animals besides humans?
Yes, Brunner’s glands are found in various mammalian species, including dogs, cats, and pigs.
8. Do Brunner’s glands have any role in immune defense?
Brunner’s glands produce lysozyme, an enzyme with antimicrobial properties, which helps in the defense against harmful bacteria in the digestive system.
9. Are there any lifestyle or dietary factors that can affect Brunner’s glands?
Spicy foods and certain medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can potentially affect the function of Brunner’s glands.
10. Can an imbalance in Brunner’s gland secretion lead to digestive disorders?
Yes, an overproduction or underproduction of mucus by Brunner’s glands can disrupt the normal functions of the digestive system and lead to digestive disorders.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
