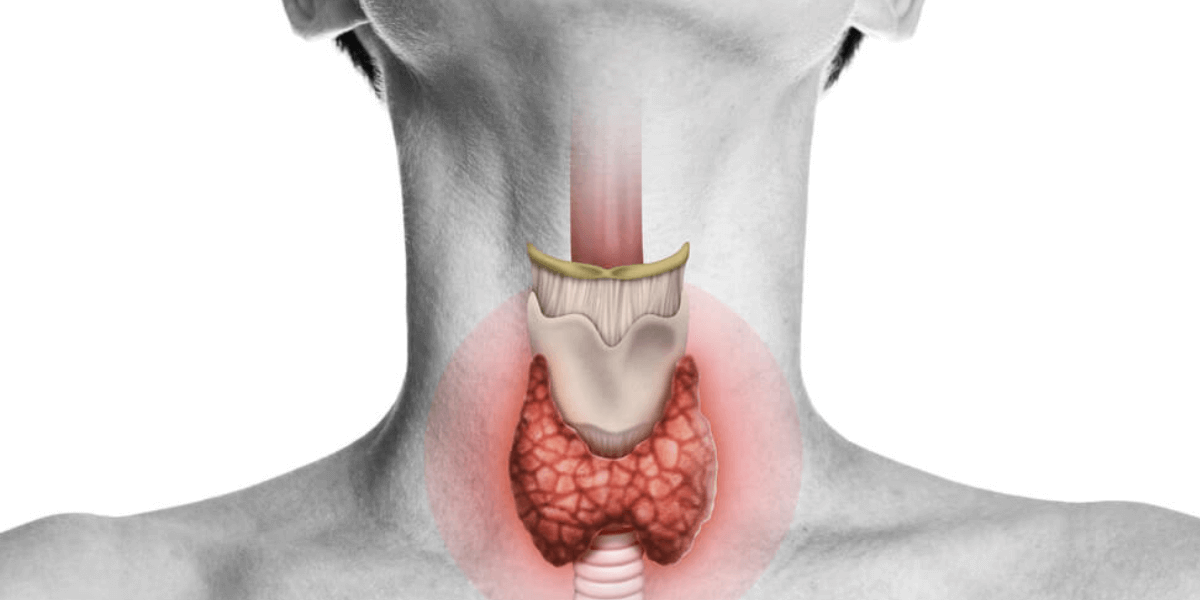
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is a small but powerful organ that plays a vital role in the functioning of our bodies. Despite its small size, the thyroid gland has a profound impact on our overall health and well-being. From regulating metabolism to controlling hormone levels, the thyroid gland has a multitude of functions that are crucial for our body’s functioning.
In this article, we will explore 20 mind-blowing facts about the thyroid gland that will not only expand your knowledge, but also give you a deeper understanding of this remarkable organ. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of the thyroid gland, and discover the incredible facts that make it so intriguing!
Key Takeaways:
- The thyroid gland, shaped like a butterfly, controls metabolism, brain development, and heart rate. It can be affected by disorders and requires iodine for hormone production. Women are more prone to thyroid issues.
- Thyroid imbalances can impact mental health, fertility, and bone health. Stress and iodine deficiency can disrupt thyroid function, leading to weight fluctuations and hair/skin changes. Regular check-ups are crucial for early detection.
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front part of the neck.
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland situated in the lower front of the neck. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions through the production of thyroid hormones.
The thyroid gland produces and releases hormones that control metabolism.
The thyroid gland produces two main hormones, known as triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which are responsible for regulating the body’s metabolic rate. These hormones influence processes such as growth, development, temperature regulation, and energy levels.
Thyroid hormones are essential for brain development in infants and children.
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in the development and maturation of the brain in infants and children. Insufficient levels of thyroid hormones during this period can lead to cognitive and developmental delays.
The thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” controls the function of the thyroid gland by producing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones.
The thyroid gland can be affected by various disorders and conditions.
Thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiter, and thyroid cancer can affect the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. These conditions may require medical intervention and treatment.
The thyroid gland regulates body temperature.
Thyroid hormones help regulate body temperature by affecting the metabolic rate and heat production within the body. Imbalances in thyroid function can lead to temperature sensitivity and intolerance.
Thyroid hormones impact heart rate and cardiovascular health.
Thyroid hormones influence the heart rate and rhythm, ensuring proper functioning of the cardiovascular system. Abnormal thyroid levels can lead to heart-related complications such as palpitations and high blood pressure.
The thyroid gland stores excess hormones.
The thyroid gland has the ability to store excess thyroid hormones for later use. This storage mechanism helps maintain a balance of hormones in the body and ensures a steady supply of thyroid hormones even during periods of stress or illness.
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones.
Iodine is a vital mineral required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. A deficiency in iodine can lead to thyroid dysfunction and can be prevented by consuming iodized salt or foods rich in iodine.
Thyroid disorders are more common in women than in men.
Women are more prone to developing thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and Hashimoto’s disease, than men. Fluctuations in hormone levels during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause are some of the factors contributing to this increased risk.
Emotional and mental health can be affected by thyroid imbalances.
Thyroid hormone imbalances can have a significant impact on mental and emotional well-being. Hypothyroidism is often associated with symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
Thyroid hormones influence fertility and reproductive health.
Imbalances in thyroid hormone levels can affect fertility in both men and women. Hypothyroidism can cause irregular menstruation and difficulty conceiving, while hyperthyroidism can disrupt sperm production in men.
The thyroid gland can enlarge and form a goiter.
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, often caused by an iodine deficiency or certain thyroid disorders. Goiters can lead to difficulty swallowing, breathing, and speaking.
Thyroid nodules are common but are usually noncancerous.
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths or lumps that form within the thyroid gland. While most nodules are benign, some may require further investigation to rule out the presence of thyroid cancer.
Autoimmune diseases can affect the thyroid gland.
Autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto’s disease and Graves’ disease, can cause the immune system to attack the thyroid gland. These conditions can result in an underactive or overactive thyroid, respectively.
The thyroid gland plays a role in bone health.
Thyroid hormones are essential for bone growth and development. Imbalances in thyroid function can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Stress can impact thyroid function.
Chronic stress can disrupt the normal functioning of the thyroid gland and lead to imbalances in hormone levels. Stress management techniques and a healthy lifestyle can help support proper thyroid function.
Thyroid hormones affect hair and skin health.
Thyroid imbalances can cause changes in hair and skin quality. Dry, brittle hair and changes in skin texture are common symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
Thyroid hormone imbalances can result in weight fluctuations.
Hypothyroidism can lead to weight gain, while hyperthyroidism may cause weight loss. Balancing thyroid hormone levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
Regular check-ups and blood tests can detect thyroid disorders.
Regular monitoring of thyroid function through blood tests can help detect thyroid disorders early on. This allows for timely intervention and treatment to manage the condition effectively.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland is a fascinating organ that plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions. From controlling metabolism to maintaining body temperature, this little butterfly-shaped gland has a profound impact on our overall health. Understanding the thyroid gland can help us recognize the signs of dysfunction and seek appropriate treatment.
By exploring these mind-blowing facts about the thyroid gland, we gain deeper insight into its importance and complexity. From its intricate hormonal system to its connection with the immune system, the thyroid gland continues to captivate researchers and medical professionals alike.
So next time you hear the word “thyroid,” remember that it’s not just a small gland in your neck—it’s a powerhouse that influences numerous physiological processes and deserves our attention.
FAQs
1. What is the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development in the body.
2. What are common thyroid disorders?
Common thyroid disorders include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
3. How do I know if I have a thyroid problem?
Symptoms of thyroid dysfunction may include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and changes in heart rate.
4. Can thyroid disorders be treated?
Yes, thyroid disorders can often be effectively managed with medication, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery.
5. Can stress affect the thyroid gland?
Yes, chronic stress can impact thyroid function and contribute to thyroid disorders.
6. Are there risk factors for developing thyroid disorders?
Yes, risk factors for thyroid disorders include family history, age, gender, and certain autoimmune diseases.
7. Can a healthy lifestyle support thyroid health?
Yes, maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can support thyroid health.
8. How often should I have my thyroid checked?
It is recommended to have your thyroid levels checked regularly, especially if you have a family history of thyroid disorders or experience symptoms.
9. Can pregnancy affect the thyroid gland?
Yes, pregnancy can cause changes in thyroid function, and it is essential to monitor thyroid health during and after pregnancy.
10. Can I live a normal life with a thyroid disorder?
Yes, with proper management and treatment, individuals with thyroid disorders can lead normal, healthy lives.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
