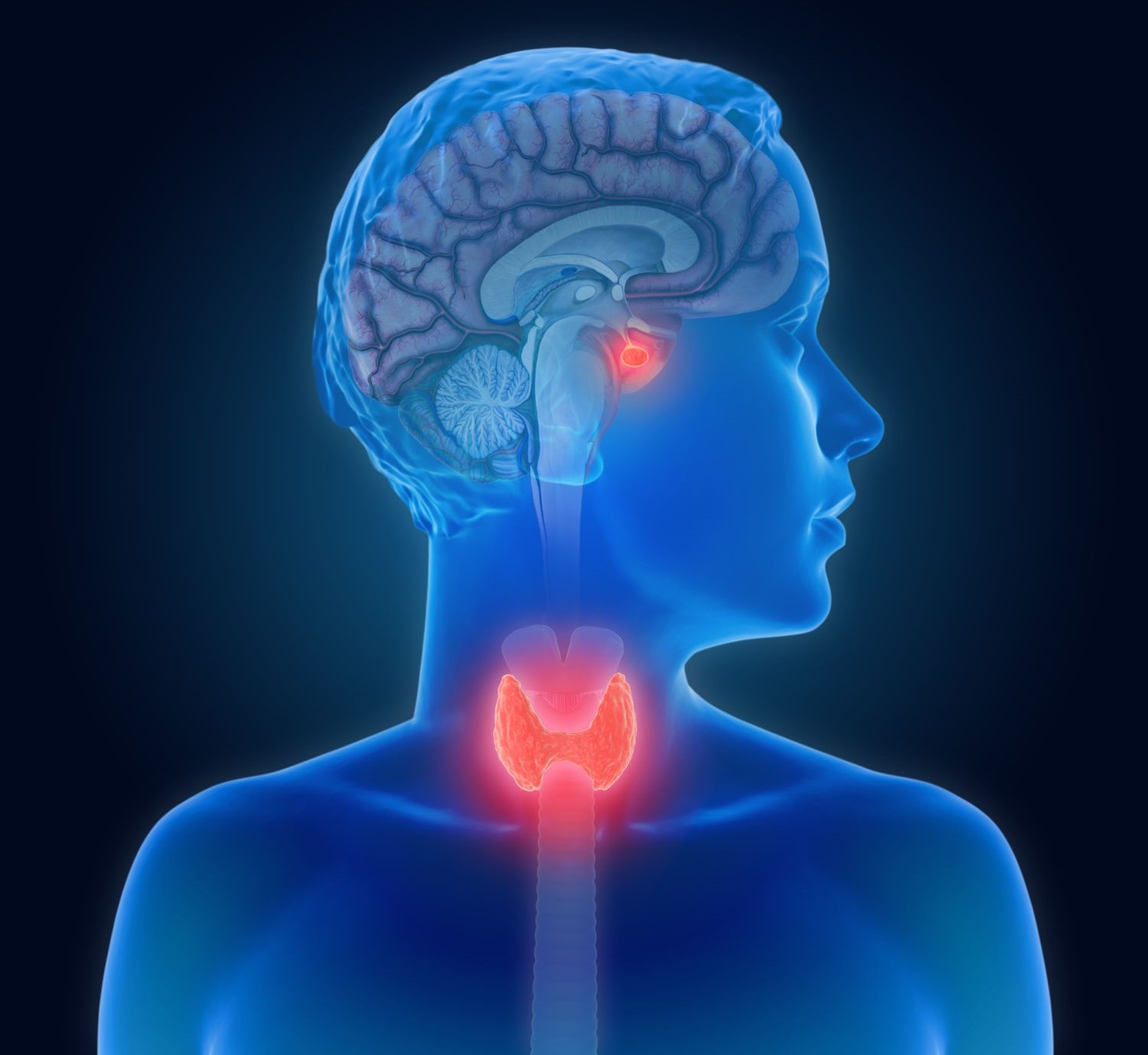
The Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) plays a crucial role in regulating the function of the thyroid gland, which is responsible for the production of hormones that control energy levels, metabolism, and growth. TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. While TSH may seem like a straightforward hormone, there are many fascinating facts about it that are worth exploring. In this article, we will delve into 20 astonishing facts about TSH that will leave you amazed and give you a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of the human body. So, let’s dive in and uncover the remarkable world of TSH!
Key Takeaways:
- TSH, produced by the pituitary gland, regulates thyroid hormones, affecting metabolism and body temperature. Fluctuating TSH levels can indicate thyroid disorders, which can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
- TSH plays a vital role in growth, development, and maintaining body temperature. It can be influenced by stress, pregnancy, and medications. Monitoring TSH levels through blood tests helps diagnose and manage thyroid disorders.
TSH is produced by the pituitary gland.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone, also known as TSH, is a hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland located in the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating the function of the thyroid gland.
TSH stimulates the production of thyroid hormones.
TSH acts on the thyroid gland to stimulate the production and release of thyroid hormones, specifically thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are essential for regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
TSH levels fluctuate throughout the day.
TSH levels in the body can vary throughout the day, with the highest levels seen during the early morning hours and the lowest levels occurring in the evening. This natural fluctuation helps to maintain a balance in thyroid hormone production.
High TSH levels indicate an underactive thyroid.
Elevated levels of TSH in the blood often indicate an underactive thyroid, a condition known as hypothyroidism. This means that the thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs.
Low TSH levels indicate an overactive thyroid.
On the other hand, low levels of TSH can indicate an overactive thyroid, also known as hyperthyroidism. In this condition, the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones, disrupting the body’s normal function.
TSH levels can be affected by certain medications.
Some medications, such as glucocorticoids and dopamine agonists, can influence TSH levels in the body. It is important for healthcare providers to consider these factors when interpreting TSH test results.
TSH levels can fluctuate during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, TSH levels can change due to hormonal fluctuations. It is not uncommon for TSH levels to decrease in the first trimester and gradually increase later in pregnancy. This is considered a normal physiological response.
TSH plays a role in maintaining body temperature.
TSH influences the body’s thermoregulatory system, helping to maintain stable body temperature. Imbalances in TSH levels can affect this regulation and lead to temperature abnormalities.
TSH receptors are present in other organs besides the thyroid.
Although TSH primarily acts on the thyroid gland, TSH receptors are also found in other organs, including the heart, liver, and kidneys. This suggests that TSH may have additional functions beyond regulating thyroid hormone production.
TSH levels can be affected by stress.
High levels of stress can impact the release of TSH, leading to changes in thyroid hormone production. Chronic stress may contribute to thyroid disorders and alterations in TSH levels.
TSH is essential for normal growth and development.
TSH is particularly important during infancy and childhood, as it is necessary for normal growth and development. Insufficient TSH levels can negatively impact physical and cognitive development in children.
TSH levels can be affected by certain medical conditions.
Various medical conditions, such as pituitary disorders and thyroid abnormalities, can influence TSH levels. An accurate diagnosis often requires a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
TSH levels may be monitored in patients taking thyroid medication.
Patients who are prescribed thyroid medication, such as levothyroxine, may have their TSH levels regularly monitored to ensure that the dosage is appropriate and to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
TSH levels can be influenced by nutritional deficiencies.
Deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as iodine and selenium, can impact TSH levels and thyroid function. Adequate nutrition is crucial for maintaining optimal TSH levels and overall thyroid health.
TSH testing is commonly used to diagnose thyroid disorders.
Measuring TSH levels through a blood test is a standard procedure for the diagnosis of thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. TSH levels help healthcare providers evaluate the overall function of the thyroid gland.
TSH levels can vary based on age and gender.
TSH levels can differ based on age and gender, with older individuals generally having higher TSH levels. Women may also experience fluctuations in TSH levels during different stages of their menstrual cycle.
TSH levels are regulated by a negative feedback loop.
The release of TSH is regulated by a negative feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to produce TSH.
TSH can be measured using highly sensitive assays.
Advancements in laboratory technology have led to the development of highly sensitive TSH assays, allowing for accurate measurement of TSH levels even in small concentrations.
TSH levels can be influenced by sleep patterns.
Disruptions in sleep patterns, such as sleep deprivation, can affect TSH levels. It is important to prioritize quality sleep to maintain optimal TSH function and overall hormonal balance.
Abnormal TSH levels can be managed with appropriate treatment.
Depending on the underlying cause, abnormal TSH levels can be managed effectively with medications, lifestyle modifications, or surgical interventions. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Conclusion
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) plays a crucial role in regulating the function of the thyroid gland and maintaining overall health. Understanding the fascinating facts about TSH can help us comprehend its importance and impact on our bodies.
From its role in the regulation of metabolism to its involvement in the development of thyroid disorders, TSH is a hormone that should not be overlooked. Its connection to energy levels, weight management, and even mental health emphasizes the significance of monitoring TSH levels.
By staying informed about TSH and its effects, we can take proactive steps towards maintaining the health of our thyroid gland and overall well-being. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in ensuring optimal TSH levels and preventing any complications.
FAQs
1. What is the function of TSH?
TSH plays a vital role in stimulating the thyroid gland to produce and release hormones. It helps regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
2. How do TSH levels affect weight?
Abnormal TSH levels can impact metabolism and lead to weight gain or loss. Maintaining balanced TSH levels is essential for healthy weight management.
3. How often should TSH levels be checked?
It is recommended to have TSH levels checked regularly, especially if you have symptoms of thyroid dysfunction or a family history of thyroid disorders.
4. Can stress affect TSH levels?
Yes, stress can influence TSH levels. Chronic stress may disrupt the function of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis, leading to TSH imbalances.
5. What are the symptoms of TSH imbalances?
Common symptoms of TSH imbalances include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, hair loss, and changes in body temperature.
6. Can TSH levels impact fertility?
Yes, abnormal TSH levels can affect fertility in both men and women. Maintaining optimal TSH levels is important for reproductive health.
7. How can TSH imbalances be treated?
TSH imbalances are usually treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy or medications that help regulate thyroid function.
8. Can diet affect TSH levels?
Diet can have a minor impact on TSH levels, but it is not a primary factor. However, consuming a balanced diet with adequate iodine is important for overall thyroid health.
9. Can TSH levels fluctuate during pregnancy?
Yes, TSH levels can fluctuate during pregnancy. Regular monitoring of TSH levels is crucial for the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
10. Is TSH testing the only way to diagnose thyroid disorders?
No, TSH testing is the initial step in diagnosing thyroid disorders, but other tests, such as T3 and T4 levels, may also be required for a comprehensive evaluation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
