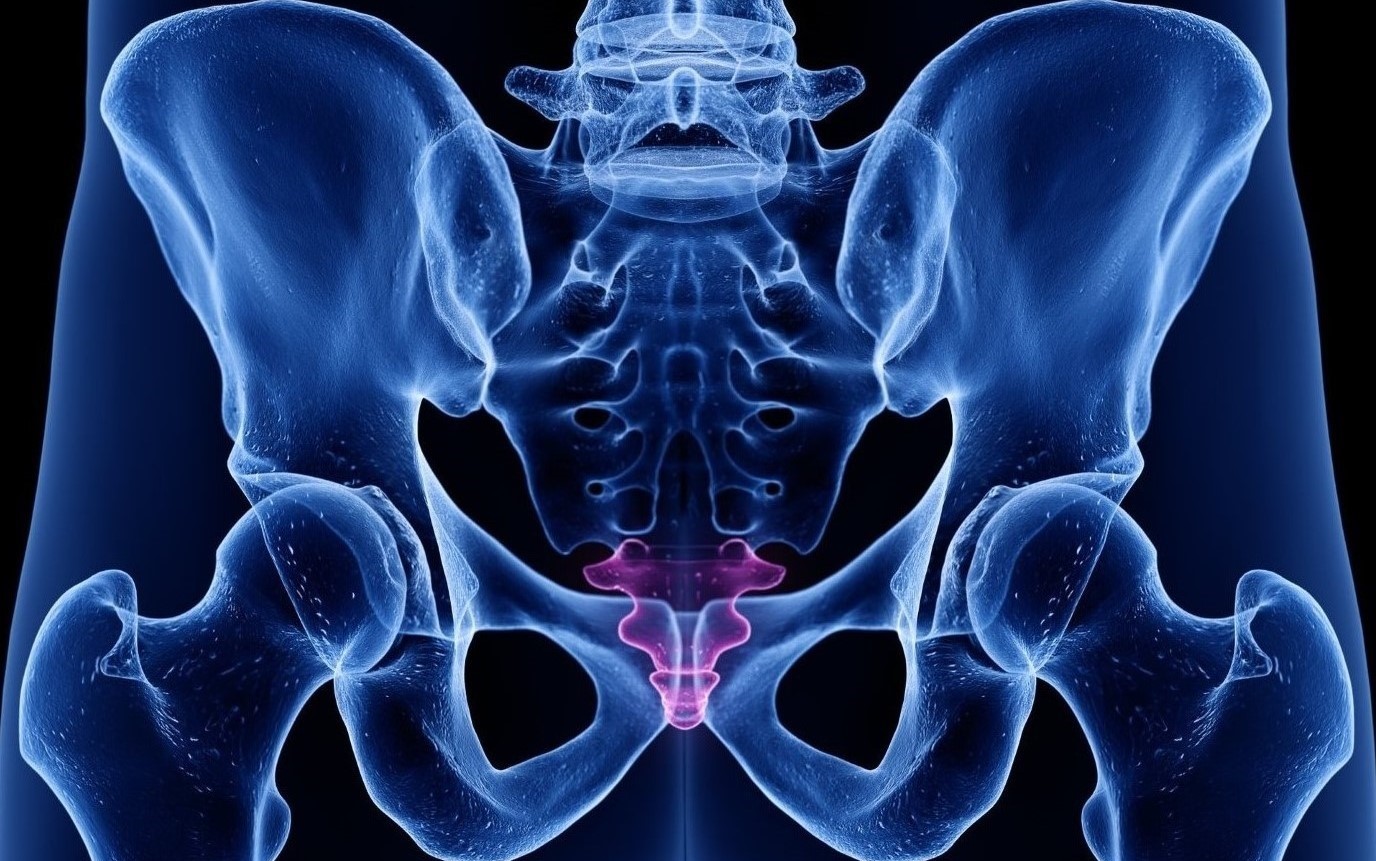
The coccyx, commonly referred to as the tailbone, is a small triangular bone located at the bottom of the vertebral column in humans. Despite its seemingly insignificant size, the coccyx plays a crucial role in providing support and stability to the body, and it also serves as an attachment point for various muscles and ligaments.
While many people are familiar with the basic function of the coccyx, there are several fascinating facts about this unique bone that are lesser known. In this article, we will explore 15 extraordinary facts about the coccyx, shedding light on its development, structure, and potential health issues. So, whether you’re a medical professional, anatomy enthusiast, or simply curious about the wonders of the human body, read on to discover some intriguing information about the coccyx.
Key Takeaways:
- The coccyx, or tailbone, is a small but mighty bone that supports our body, protects our organs, and provides a glimpse into our evolutionary past. It’s like a hidden superhero at the base of our spine!
- Just like a fingerprint, everyone’s coccyx is unique in shape and size. It’s not just a leftover tailbone from our ancestors, but also a helpful tool for forensic scientists to uncover important clues about a person’s identity.
The Coccyx is the Tail End
The coccyx, commonly known as the tailbone, is a small triangular bone located at the base of the spine. It consists of three to five fused vertebrae and is the vestigial remnant of a tail that our ancestors once had.
Provides Support and Stability
The coccyx plays a crucial role in supporting and stabilizing the body when sitting or standing. It helps to distribute the weight of the upper body and provides attachment points for various muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Can Vary in Shape and Size
The size and shape of the coccyx can vary among individuals. In some cases, it may be curved or bent, while others have a straight or slightly tilted coccyx. These variations can impact comfort and mobility in certain individuals.
Sensitive to Injury and Pain
The coccyx is highly sensitive and can be prone to injury, especially from direct trauma such as falls or childbirth. This can result in coccydynia, a condition characterized by pain and discomfort in the tailbone area.
Aid in Balance and Stability
Although its main function is to support the body, the coccyx also plays a role in balance and stability. It helps to anchor and stabilize the pelvis, allowing for smooth movements and proper alignment during activities.
Protection for Internal Organs
The coccyx acts as a protective barrier for the internal organs located within the pelvic cavity, including the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and part of the large intestine. It helps to cushion these organs and prevent injury.
Developmental Remnant
The coccyx is considered a developmental remnant as it is a leftover structure from our evolutionary past. It is believed to be the remnant of the tail that our primate ancestors used for balancing and communication.
Attached to Muscles and Ligaments
The coccyx is connected to various muscles and ligaments, including the gluteus maximus, coccygeus, and sacrococcygeal ligaments. These attachments aid in providing stability, movement, and support to the tailbone region.
Canine Coccyx Variations
Interestingly, humans aren’t the only ones with a coccyx. Dogs also have a tailbone, though the number of vertebrae can vary significantly among different breeds and species.
May Cause Discomfort During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the coccyx may be susceptible to additional pressure and discomfort due to hormonal changes and the growing uterus. This can lead to tailbone pain in pregnant women, especially during the third trimester.
Coccyx as an Attachment Point for Muscles
The coccyx serves as an attachment point for several muscles involved in posture, locomotion, and pelvic floor support. These muscles include the levator ani and various gluteal muscles.
The Coccyx is Not Always Fused
While it is common for the coccyx to be composed of fused vertebrae, some individuals may have a partially or completely unfused coccyx. This condition is known as coccygeal cornua and is usually asymptomatic.
Evolutionary Significance
The presence of the coccyx provides an insight into our evolutionary history. It serves as a reminder of our shared ancestry with other mammals and our adaptation from a tailed form to a tailless one over millions of years.
Can be Altered by Injury or Surgery
In cases of severe coccyx pain or injury that doesn’t respond to conservative treatments, surgical interventions, such as coccygectomy, may be considered. This procedure involves partial or complete removal of the coccyx to alleviate symptoms.
Informative Tool in Forensic Science
The coccyx can serve as a useful tool in forensic science for estimating the age, sex, and overall size of an individual. Its shape and development can provide important clues for forensic anthropologists during investigations.
Conclusion
The coccyx, also known as the tailbone, may be a small and often overlooked part of the human body, but it holds remarkable significance. From providing support and stability to improving posture and balance, the coccyx plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common disorders can help us appreciate its importance and take better care of it.In this article, we explored 15 extraordinary facts about the coccyx. We learned about its structure, consisting of three to five fused vertebrae, and its attachment to various important ligaments and muscles in the pelvic region. We discovered its purpose in providing support to the lower spine and acting as an anchor point for the surrounding structures.Additionally, we discussed the coccyx’s role in facilitating childbirth and absorbing impact during sitting or falling. We examined the potential causes and symptoms of coccydynia, a condition characterized by pain in the coccyx region, and explored treatment options, ranging from conservative measures to surgical interventions.By delving into these fascinating facts about the coccyx, we gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for this small yet essential part of our anatomy. Taking care of our tailbone through proper posture, regular movement, and seeking medical attention when needed ensures a healthier and more comfortable life.
FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of the coccyx?
A: The coccyx provides support and stability to the lower spine and acts as an anchor point for the surrounding muscles and ligaments.
Q: How many vertebrae make up the coccyx?
A: The coccyx is made up of three to five fused vertebrae.
Q: Can the coccyx move?
A: While the coccyx is relatively immobile, it does have some limited movement.
Q: What is coccydynia?
A: Coccydynia is a condition characterized by pain in the coccyx region. It can be caused by various factors such as trauma, childbirth, or prolonged sitting.
Q: How is coccydynia treated?
A: Treatment for coccydynia may include pain medication, physical therapy, using cushions designed for coccyx support, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Q: Can childbirth affect the coccyx?
A: Yes, the coccyx can be affected during childbirth due to the pressure applied during delivery. This can lead to temporary or long-lasting pain.
Q: How can I prevent coccyx pain?
A: Maintaining good posture, avoiding prolonged sitting, using proper ergonomics, and practicing exercises that strengthen the pelvic area can help prevent coccyx pain.
Q: Is surgery always required for coccydynia?
A: No, surgery is typically reserved for severe cases of coccydynia that do not respond to conservative treatments. Most cases can be managed with non-invasive measures.
Q: Can sitting on a cushion help with coccyx pain?
A: Yes, using cushions specifically designed to relieve pressure from the coccyx can alleviate pain and provide comfort during prolonged sitting.
Q: Can trauma to the coccyx cause long-term damage?
A: In some cases, severe trauma to the coccyx can cause long-term damage or lead to chronic pain. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent coccyx pain following an injury.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
