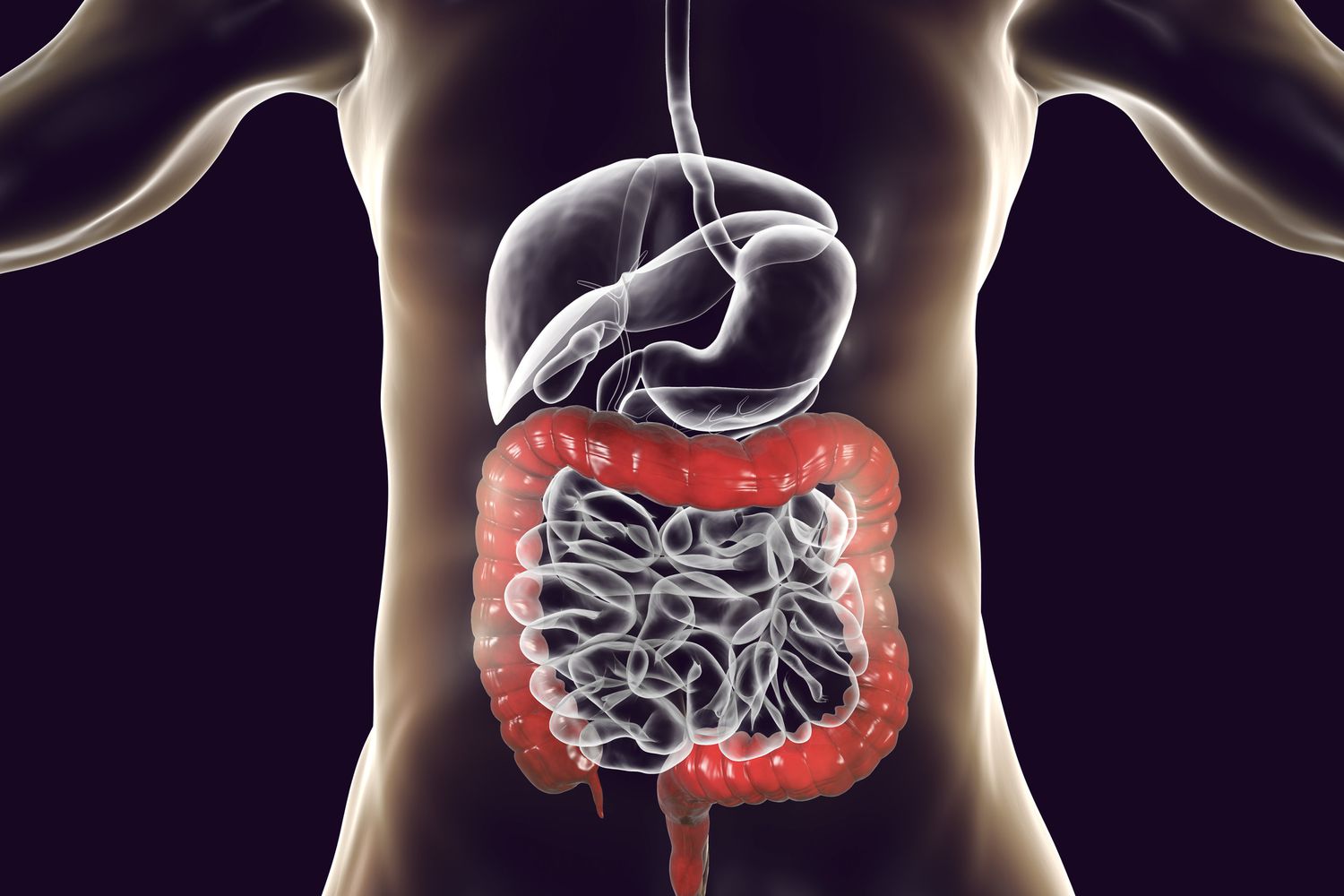
The large intestine, also known as the colon, is a crucial part of the digestive system. While it may not receive as much attention as its counterpart, the small intestine, the large intestine plays a vital role in absorbing water, processing waste, and maintaining overall digestive health.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the large intestine and explore 20 extraordinary facts that will leave you amazed. From its structure and function to its role in gut health, we will uncover the secrets of this often overlooked organ. So, get ready to expand your knowledge of human anatomy and discover the wonders that lie within the large intestine!
Key Takeaways:
- The large intestine, or colon, is a crucial part of the digestive system, responsible for absorbing water, forming feces, and housing helpful bacteria. It’s important to take care of it through a balanced diet and regular check-ups.
- Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, can impact the health of the large intestine. It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle to promote optimal colon health and overall digestive well-being.
The large intestine is the last part of the digestive system.
The large intestine, also known as the colon, is the final portion of the gastrointestinal tract. It plays a crucial role in the absorption of water, electrolytes, and certain vitamins, as well as in the formation and elimination of feces.
The large intestine is approximately 5 feet long.
Measuring around 5 feet in length, the large intestine is wider and shorter than the small intestine. It consists of several sections, including the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum.
The large intestine is responsible for forming and storing feces.
As food travels through the large intestine, water and electrolytes are absorbed, and the remaining residue is formed into feces. These feces are stored in the rectum until they are eliminated from the body through the process of defecation.
The large intestine houses trillions of bacteria.
The large intestine is home to a diverse population of bacteria, known as the gut microbiota. These bacteria aid in the digestion and fermentation of certain carbohydrates, produce vitamins such as vitamin K and biotin, and help maintain a healthy immune system.
The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes.
One of the main functions of the large intestine is the absorption of water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium. This process helps in maintaining the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance.
The large intestine is prone to certain disorders and diseases.
Disorders and diseases that can affect the large intestine include colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis), diverticulitis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Regular screenings and a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of these conditions.
The large intestine helps in the formation of fecal matter.
As the digested food passes through the large intestine, water and electrolytes are absorbed, and the waste products are compacted to form fecal matter. The fecal matter contains undigested food particles, bacteria, and other waste materials.
The large intestine has muscular contractions called peristalsis.
Peristalsis is a series of coordinated muscular contractions that propel the contents through the digestive system. In the large intestine, peristalsis helps to move feces towards the rectum for elimination.
The large intestine helps in the absorption of vitamins.
In addition to water and electrolytes, the large intestine is involved in the absorption of certain vitamins, such as vitamin K and biotin. These vitamins are produced by the gut microbiota and play important roles in various biological processes.
The large intestine has an important role in immune function.
The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) present in the large intestine plays a crucial role in the immune system. It helps in the recognition and elimination of harmful pathogens, while also maintaining tolerance to beneficial bacteria.
The large intestine can be affected by dietary factors.
The large intestine is sensitive to dietary factors, such as the consumption of fiber. Adequate fiber intake can help promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, while a low-fiber diet can increase the risk of various colon-related conditions.
The large intestine can store a significant amount of fecal matter.
The large intestine has the capacity to store a significant amount of fecal matter until it is ready to be eliminated. This storage capacity allows for efficient and controlled passage of feces during bowel movements.
The large intestine has a rich blood supply.
The large intestine receives a rich blood supply through branches of the mesenteric arteries. This ensures an adequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the colon and supports its proper functioning.
The large intestine undergoes rhythmic contractions known as haustral churning.
Haustral churning is a rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscular wall of the large intestine, which helps to mix and propel the contents forward. This process aids in the absorption of water and promotes the formation of well-formed stools.
The large intestine has a unique shape and structure.
The large intestine has a distinct shape characterized by pouches called haustra, which give it a segmented appearance. These haustra allow for the expansion and contraction of the colon, accommodating the passage of feces.
The large intestine has a role in gut-brain communication.
The large intestine communicates with the brain through the gut-brain axis, which involves bidirectional signaling between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system. This communication pathway plays a significant role in regulating appetite, mood, and overall gut health.
The large intestine can be affected by lifestyle choices.
Lifestyle choices such as a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet high in processed foods can negatively impact the health of the large intestine. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help promote optimal colon health.
The large intestine can be examined through a colonoscopy.
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that allows for the examination of the large intestine and rectum using a flexible tube with a camera. This procedure is commonly used for detecting abnormalities, such as polyps or signs of colon cancer.
The large intestine plays a vital role in the elimination of waste.
By consolidating and propelling fecal matter towards the rectum, the large intestine plays a crucial role in the elimination of waste products from the body. This process ensures that the body maintains a healthy digestive system.
The large intestine is essential for overall digestive health.
The large intestine, with its various functions and interactions with other organs, is vital for maintaining overall digestive health. Taking care of the large intestine through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and routine screenings can contribute to a healthy digestive system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the large intestine, also known as the colon, is a truly remarkable organ with many fascinating functions. From its role in absorbing water and electrolytes to its involvement in waste elimination, the large intestine plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being.This article has highlighted 20 extraordinary facts about the large intestine. We have explored its length, structure, and unique features such as the presence of haustra and the vermiform appendix. Additionally, we have discussed its importance in housing trillions of beneficial bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiota.Understanding the functions and characteristics of the large intestine can help us appreciate the intricacies of our digestive system. It also emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support optimal colon health.So, the next time you hear someone talk about the large intestine, you’ll have an array of intriguing facts to share. Let’s continue to nurture and care for this extraordinary organ that contributes so significantly to our overall well-being.
FAQs
1. What is the function of the large intestine?
The large intestine primarily absorbs water, electrolytes, and vitamins. It also helps in the formation and elimination of waste materials.
2. How long is the large intestine?
The average length of the large intestine is approximately 5 feet, but it can vary among individuals.
3. What are haustra?
Haustra are the pouches or sacs present in the large intestine that allow for expansion and contraction, aiding in the movement of stool.
4. What is the role of the gut microbiota in the large intestine?
The large intestine houses trillions of beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion, produce vitamins, and support the immune system.
5. Can problems occur in the large intestine?
Yes, various conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, diverticulitis, and colorectal cancer can affect the large intestine’s normal function.
6. How can I maintain a healthy large intestine?
Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain a healthy large intestine.
7. When should I consult a healthcare professional regarding my large intestine?
If you experience persistent changes in bowel habits, unexplained weight loss, severe abdominal pain, or blood in your stool, it is important to seek medical advice promptly.
Hungry for more intriguing facts about the digestive system? Satisfy your curiosity by exploring additional mind-boggling truths about the large intestine, unraveling the secrets of the cecum, and delving into the astonishing world of the sigmoid colon. These captivating articles will take you on a journey through the wonders of the human body, leaving you amazed and eager to learn more.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
