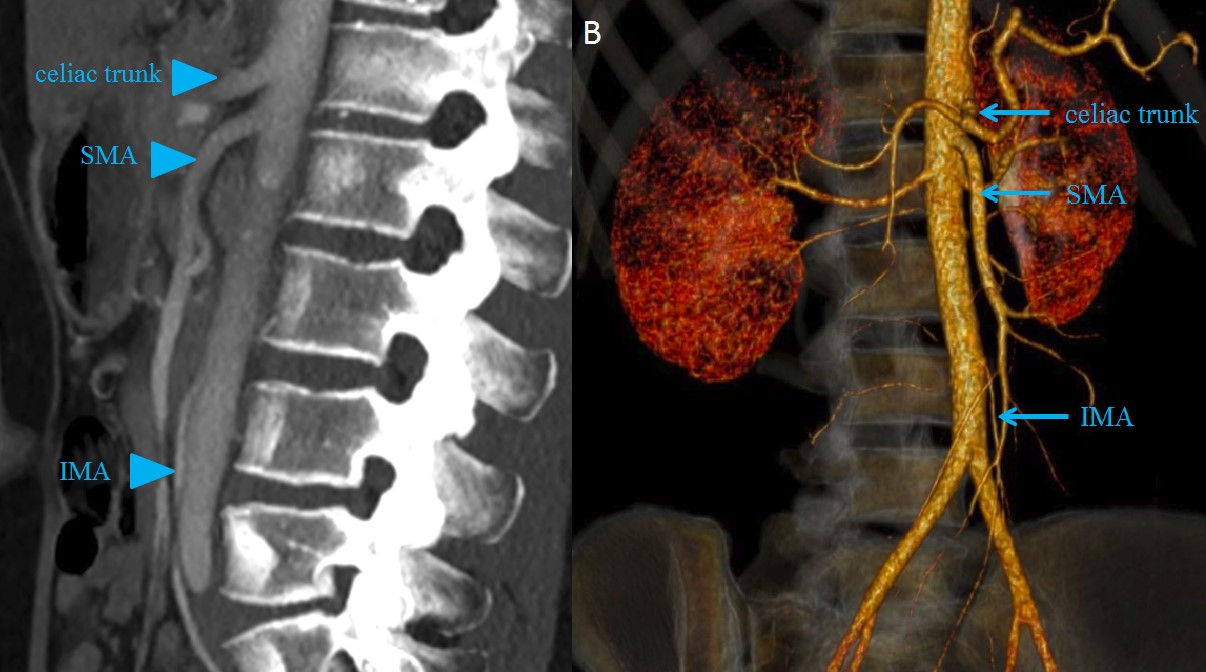
The Inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is an important blood vessel located in the abdomen. It plays a vital role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to various organs such as the large intestine, rectum, and part of the descending colon. Despite its relatively small size compared to other arteries, the IMA carries out essential functions that contribute to the overall well-being of the body.
In this article, we are going to explore 16 intriguing facts about the Inferior mesenteric artery. From its anatomical features to its clinical significance, understanding these facts will give you a deeper insight into the role that the IMA plays within the human body. So, let’s dive in and discover the fascinating world of the Inferior mesenteric artery.
Key Takeaways:
- The inferior mesenteric artery supplies blood to the lower intestines and rectum, playing a crucial role in maintaining their health and proper functioning.
- Understanding the anatomy and functions of the inferior mesenteric artery is essential for medical professionals involved in colorectal surgery and patient care.
Origin and Location
The inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is a major blood vessel that arises from the abdominal aorta. It is located in the lower abdominal region, supplying blood to the intestines.
Branches
The IMA has several branches, including the left colic artery, sigmoid arteries, and superior rectal artery. These branches provide vital blood supply to different sections of the large intestine.
Blood Supply
The IMA plays a crucial role in supplying oxygenated blood to the lower part of the colon, the rectum, and parts of the anal canal. It ensures proper functioning of these regions.
Collateral Circulation
In case of blockage or occlusion of the IMA, collateral circulation can occur. This means that other arteries can compensate by providing alternative routes for blood flow to the affected areas.
Size and Diameter
The IMA typically measures around 1.5 to 2 centimeters in diameter. However, the size can vary among individuals depending on their anatomical characteristics.
Role in Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
The IMA supplies blood to the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and proper functioning of these parts of the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Surgical Implications
The IMA is an important structure in surgical procedures involving the colon and rectum. Surgeons must carefully consider its location and blood supply to ensure successful outcomes.
Mesenteric Ischemia
Blockage or insufficient blood flow through the IMA can lead to a condition called mesenteric ischemia. This condition can cause severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even bowel ischemia if left untreated.
Diagnostic Imaging
Medical professionals often use imaging techniques such as angiography or CT scans to assess the condition of the IMA and identify any abnormalities or blockages.
Importance in Colorectal Cancer
The IMA is involved in the blood supply to the colon and rectum, making it relevant in the context of colorectal cancer. Treatment options may consider the IMA and its branches.
Impact of Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise can influence the health of the IMA and overall vascular system. Maintaining a balanced diet and an active lifestyle can promote proper blood flow.
Developmental Variations
The IMA’s location and branching pattern can vary among individuals. These anatomical variations should be considered during surgical procedures or diagnostic evaluations.
Collaboration with the Superior Mesenteric Artery
The IMA works in conjunction with the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) to ensure adequate blood supply to the intestines and maintain their proper functioning.
Role in Hemorrhoids
The IMA supplies blood to the rectal region, making it relevant in the context of hemorrhoid development and management. Proper blood flow is essential for preventing this condition.
Clinical Relevance
Understanding the anatomy and functioning of the IMA is crucial for medical professionals, particularly in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research continues to explore the role of the IMA in various conditions and the development of new treatment approaches to improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the inferior mesenteric artery is a vital blood vessel with essential functions in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Understanding its anatomy and clinical implications is crucial for medical professionals involved in colorectal surgery, diagnostic imaging, and overall patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the inferior mesenteric artery is a fascinating part of the human anatomy with a variety of important functions. Understanding its role in the circulatory system and its connections to surrounding organs is crucial for medical professionals and individuals interested in their health. The 16 intriguing facts discussed in this article shed light on the significance of the inferior mesenteric artery. From its origin and course to its branches and clinical implications, this artery plays a vital role in maintaining the well-being of the digestive system. Further research and exploration into the complexities of the inferior mesenteric artery will continue to enhance our understanding of human anatomy and pave the way for advancements in medical treatments and interventions.
FAQs
1. What is the inferior mesenteric artery?
The inferior mesenteric artery is a major blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the lower part of the large intestine, including the rectum and sigmoid colon.
2. Where does the inferior mesenteric artery originate from?
The inferior mesenteric artery typically arises from the abdominal aorta, just below the level of the renal arteries.
3. What are the main branches of the inferior mesenteric artery?
The main branches of the inferior mesenteric artery include the left colic artery, sigmoid arteries, and superior rectal artery.
4. What functions does the inferior mesenteric artery serve?
The inferior mesenteric artery supplies oxygenated blood to the lower part of the large intestine, helps regulate bowel movements, and aids in the removal of waste products from the body.
5. Are there any clinical conditions associated with the inferior mesenteric artery?
Yes, conditions such as mesenteric ischemia, aneurysm, and embolism can affect the inferior mesenteric artery and lead to severe abdominal pain and digestive disturbances.
6. How is a blockage or narrowing of the inferior mesenteric artery diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests such as angiography, ultrasound, and CT scans can be used to detect blockages or narrowing of the inferior mesenteric artery.
7. Can the inferior mesenteric artery be treated if it becomes diseased?
Treatment options for diseases of the inferior mesenteric artery may include medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical intervention, such as bypass surgery or angioplasty.
8. Can regular exercise and a healthy diet help maintain the health of the inferior mesenteric artery?
Yes, a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet can promote overall cardiovascular health, including the health of the inferior mesenteric artery.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
