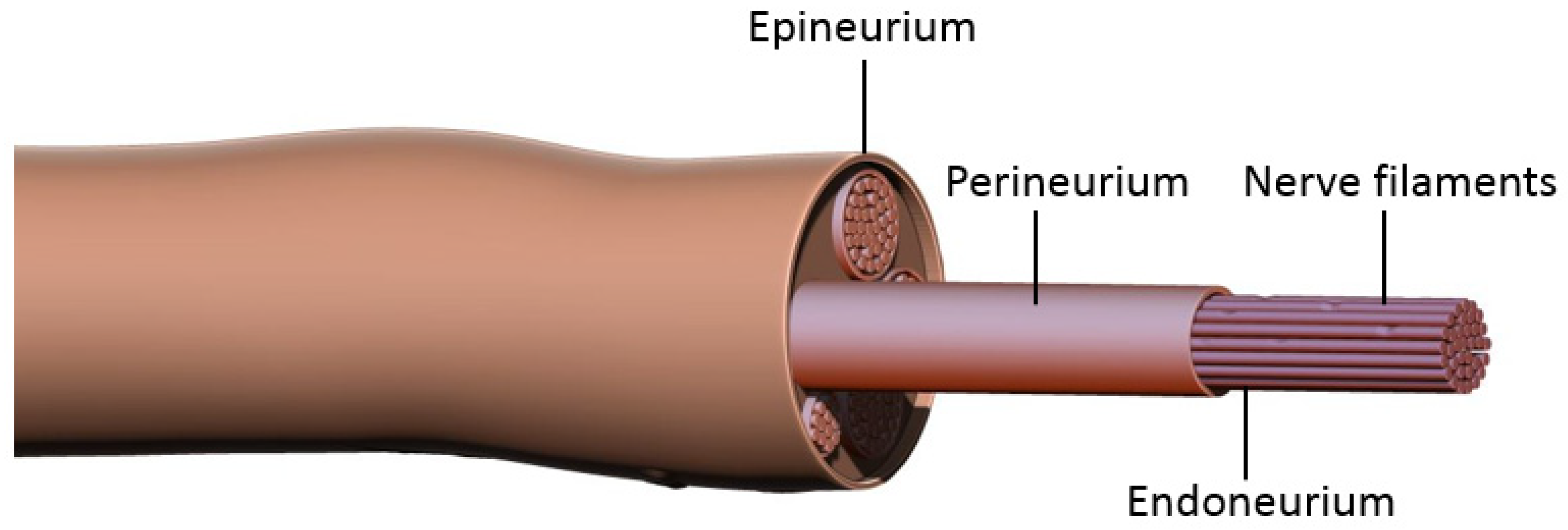
The human body is an incredible and complex machine, and perhaps no system showcases this better than the nervous system. From the brain to the spinal cord, every component plays a vital role in allowing us to move, think, and experience the world around us. One fascinating aspect of the nervous system is the presence of different layers that protect and support the delicate nerve fibers. One such layer is the endoneurium.
The endoneurium is a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds individual nerve fibers within a nerve. Although it may seem small and insignificant, the endoneurium has a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of our nervous system. In this article, we will delve into 14 mind-blowing facts about the endoneurium that will increase your understanding of this essential component of human anatomy. Get ready to be amazed by the fascinating intricacies of the endoneurium!
Key Takeaways:
- The endoneurium is like a superhero for our nerves, protecting and supporting them so they can send messages throughout our body without any interference or damage.
- Just like a bodyguard, the endoneurium keeps our nerves safe and healthy, making sure they have everything they need to work properly and repair themselves when needed.
The Endoneurium is a Vital Component of the Nervous System
The endoneurium is a crucial element of the nervous system. It plays a significant role in supporting and protecting the delicate nerve fibers found within the peripheral nerves.
Endoneurium Consists of Connective Tissue
The endoneurium is composed of a specialized type of connective tissue called endoneurial connective tissue. This tissue surrounds individual nerve fibers, providing structural support.
The Endoneurium is Rich in Capillaries
Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels in the body, are abundant within the endoneurium. These capillaries supply nutrients and oxygen to the nerve fibers, ensuring their proper functioning.
It Functions as an Insulator
The endoneurium acts as an insulator by providing a protective layer around the nerve fibers. This insulation helps to maintain the electrical signals transmitted by the nerves, allowing for efficient communication within the nervous system.
Endoneurium Facilitates Nerve Regeneration
Following injury or damage to the nerves, the endoneurium plays a vital role in the regeneration process. It provides a supportive environment for the regrowth of nerve fibers, aiding in the restoration of proper nerve function.
The Composition of Endoneurium Influences Nerve Impulse Transmission
The specific composition of the endoneurium, including its extracellular matrix and associated molecules, can affect the transmission of nerve impulses. A healthy endoneurial environment is crucial for efficient nerve signal transmission.
Endoneurium Helps Maintain Nerve Fiber Alignment
The endoneurium assists in keeping nerve fibers properly aligned within the peripheral nerves. This alignment ensures the efficient transmission of nerve signals and helps prevent tangling or excessive stress on the nerve fibers.
It Contains Cells Important for Nerve Repair
Specialized cells, such as fibroblasts and Schwann cells, are present in the endoneurium. These cells play critical roles in repairing and supporting damaged nerve tissue, aiding in the recovery process after injury.
The Endoneurium Supports Nerve Metabolism
Metabolic processes within the nerves require a steady supply of nutrients and oxygen, which are provided by the endoneurium. This support ensures the proper functioning and maintenance of nerve cells.
Endoneurium Plays a Role in Immune Responses
The endoneurium is involved in immune responses within the nervous system. It hosts immune cells that help defend against potential threats, contributing to the protection and healing of the nerves.
It Helps Prevent Cross-Talk Between Nerve Fibers
The endoneurium acts as a barrier, preventing cross-talk or interference between adjacent nerve fibers. This selective boundary ensures the integrity of individual nerve impulses and their targeted destinations.
Endoneurium Isolates Nerve Fibers
Isolation and separation of nerve fibers are crucial for their proper functioning. The endoneurium provides this isolation, preventing unwanted electrical interactions and enhancing the precision of nerve transmissions.
The Structure of the Endoneurium Varies Throughout the Body
The endoneurium differs in thickness and composition depending on the location within the body. This variation reflects the specialized functions and requirements of different peripheral nerves throughout the body.
Endoneurium Supports Optimal Performance of the Nervous System
By providing structural support, insulation, and necessary nutrients, the endoneurium plays a vital role in maintaining the optimal performance of the nervous system. It ensures the smooth transmission of nerve signals and supports overall nerve health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the endoneurium is a crucial component of the nervous system, providing essential support and protection to nerve fibers. It is a connective tissue layer that surrounds individual nerve fibers, allowing for proper transmission of electrical signals. Understanding the functions and characteristics of the endoneurium is essential for gaining a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy.Through this article, we have explored 14 mind-blowing facts about the endoneurium that shed light on its importance and intricate nature. From its role in maintaining the structural integrity of nerve fibers to its involvement in the regeneration process, the endoneurium plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of our nervous system.We hope that this article has deepened your knowledge and appreciation for the intricacies of the endoneurium. By understanding the significance of this connective tissue layer, we can better comprehend the complexities of the human body and its remarkable ability to transmit and process information.
FAQs
1. What is the endoneurium?
The endoneurium is a connective tissue layer that surrounds individual nerve fibers within a peripheral nerve.
2. What is the function of the endoneurium?
The main function of the endoneurium is to provide support and protection to nerve fibers, allowing for the proper transmission of electrical signals.
3. How does the endoneurium differ from other layers of the peripheral nerve?
The endoneurium is the innermost layer of the peripheral nerve and directly surrounds individual nerve fibers, while the perineurium and epineurium are outer layers that provide additional support and protection.
4. Can the endoneurium regenerate?
Yes, the endoneurium has the capability to regenerate following nerve injury, contributing to the overall regeneration process of damaged nerve fibers.
5. Are there any diseases or conditions related to the endoneurium?
Several disorders, such as peripheral neuropathy, can affect the endoneurium, leading to impaired nerve function and various symptoms.
6. How can I keep my endoneurium healthy?
Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding habits that may damage nerves, such as excessive alcohol consumption, can help promote the health of the endoneurium.
7. Can the endoneurium be visualized through medical imaging?
While it is challenging to visualize the endoneurium directly through medical imaging techniques, advanced imaging methods, such as high-resolution ultrasound, can provide detailed insights into peripheral nerve structures.
8. Does the endoneurium play a role in pain perception?
While the endoneurium itself does not directly contribute to pain sensation, damage or inflammation in the endoneurium can result in nerve pain.
9. Is the endoneurium present in the central nervous system?
No, the endoneurium is exclusive to the peripheral nervous system, which includes the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
10. Can endoneurium abnormalities lead to neurological disorders?
Endoneurium abnormalities, such as fibrosis or inflammation, can contribute to the development of certain neurological disorders, warranting further research and medical intervention.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
