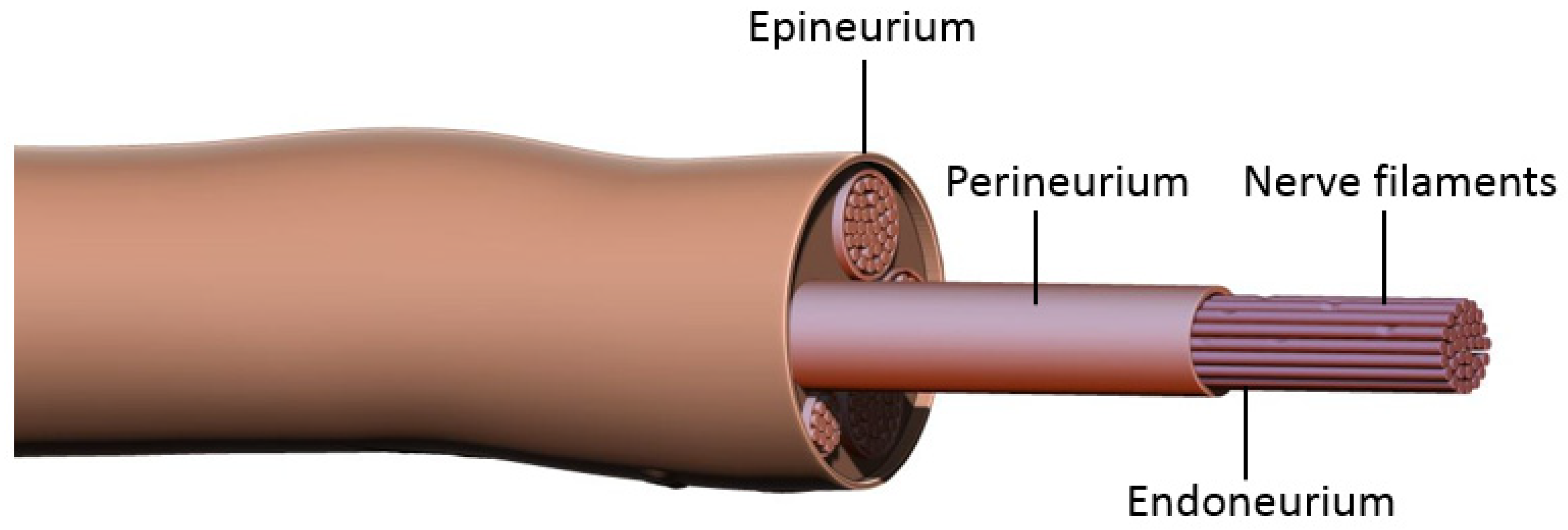
The human body is a remarkable and complex system, and one of its most intriguing components is the nervous system. Within this intricate network of neurons and nerve fibers lies the epineurium, a vital protective covering that plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of our nerves. The epineurium, a dense layer of connective tissue, surrounds the entire peripheral nerve and acts as a shield against external trauma and injury.
In this article, we will delve into the depths of knowledge about the epineurium and explore 20 extraordinary facts that highlight its significance. From its unique composition to its ability to regenerate, the epineurium holds many secrets waiting to be unraveled. So, let’s embark on this journey to uncover fascinating details about the epineurium and gain a deeper understanding of its role in our bodies.
Key Takeaways:
- Epineurium is like a superhero cape for nerves, protecting and supporting them from injury, infection, and mechanical stress, while also helping them regenerate after injury.
- It’s like a nerve bodyguard, regulating temperature, providing cushioning, and ensuring a constant blood supply, all to keep our nerves healthy and functioning at their best.
The epineurium is the outermost layer of the peripheral nerves.
The epineurium encases and protects the entire nerve bundle, ensuring its integrity and shielding it from external damage.
It consists of dense irregular connective tissue.
This strong and resilient tissue helps maintain the shape and structure of the nerves, providing stability and protection.
The epineurium plays a crucial role in nerve regeneration.
Following nerve injury, the epineurium aids in the healing process by providing a supportive environment for nerve cell regrowth.
It contains an extensive network of blood vessels.
The epineurium ensures a constant blood supply to the nerves, delivering oxygen and nutrients essential for their proper functioning.
The epineurium is composed of collagen fibers.
These fibers provide strength and flexibility to the epineurium, allowing it to withstand various mechanical stresses and strains.
Epineurium acts as a barrier against infection.
It prevents pathogens from entering the nerve fibers, safeguarding the peripheral nervous system against potential infections.
The epineurium assists in the conduction of nerve impulses.
By providing structural support to the nerve fibers, it facilitates the efficient transmission of electrical signals throughout the body.
It helps regulate the temperature of the nerves.
The epineurium aids in maintaining optimal temperature conditions for the nerves to function optimally.
Epineurium is a continuous structure along the length of the nerve.
It creates a seamless covering that ensures the entire nerve is protected and supported.
The epineurium contains numerous nerve endings.
These nerve endings within the tissue contribute to proprioception, allowing us to have a sense of the position and movement of our body parts.
It can vary in thickness.
The thickness of the epineurium may differ depending on the location and size of the nerve it surrounds.
Epineurium provides cushioning for the nerves.
This protective layer helps absorb shock and vibrations, preventing damage to the delicate nerve fibers.
The epineurium is rich in elastin fibers.
These elastic fibers enable the tissues to stretch and recoil, allowing for movement and flexibility of the nerves.
It plays a role in lymphatic drainage.
The epineurium helps remove waste products and excess fluid from the nerves, maintaining their optimal environment.
The epineurium undergoes remodeling during nerve development.
During embryonic growth, the epineurium adapts and changes to accommodate the developing nerves.
Epineurium can thicken in response to chronic nerve compression.
This adaptation helps protect the nerve from further injury and damage.
The epineurium has a protective role against mechanical stress.
It acts as a buffer, guarding the nerves against excessive tension and compression.
Epineurium contains fibroblasts.
These cells produce collagen and other components of the extracellular matrix, contributing to the maintenance and repair of the epineurium.
The epineurium can become inflamed in certain conditions.
Inflammatory responses in the epineurium can result in conditions such as neuritis or peripheral neuropathy.
Epineurium is an essential component for nerve grafting procedures.
During nerve grafting surgeries, the epineurium facilitates the successful integration of the graft into the recipient nerve.
The epineurium is an extraordinary anatomical feature that ensures the proper functioning and protection of our nerves. Understanding its role and significance provides invaluable insights into the intricate workings of the peripheral nervous system.
Conclusion
The epineurium is a remarkable component of the peripheral nerves that plays a crucial role in protecting and supporting the delicate nerve fibers. Understanding the anatomy and function of the epineurium can help us appreciate the complex nature of the human body. From its composition to its role in nerve regeneration, the epineurium is an extraordinary structure that deserves recognition. So next time you think about the nerves in your body, take a moment to appreciate the incredible role played by the epineurium in keeping them safe and functioning properly.
FAQs
1. What is the epineurium?
The epineurium is the outermost layer of connective tissue that covers peripheral nerves. It surrounds and protects the nerve fibers, providing strength and support.
2. What is the composition of the epineurium?
The epineurium is composed of dense irregular connective tissue, mainly collagen fibers, along with fibroblasts, blood vessels, and adipose tissue.
3. What is the function of the epineurium?
The primary function of the epineurium is to protect the underlying nerve fibers from external forces and injuries. It also maintains the structural integrity of the nerve and provides a pathway for blood vessels to supply nutrients and oxygen to the nerves.
4. Can the epineurium regenerate?
Although the epineurium does not regenerate independently, it plays a critical role in supporting nerve regeneration. It creates a favorable environment for the regrowing nerve fibers and helps guide their direction during the healing process.
5. Can the epineurium be affected by diseases?
Yes, various conditions can affect the epineurium, including autoimmune diseases, infections, and nerve compressions. These conditions can lead to inflammation, scarring, and nerve damage.
6. Can the epineurium be surgically repaired?
In cases of severe nerve injury or trauma, surgical intervention may be required to repair the epineurium and restore nerve function. Surgeons can use techniques such as nerve grafting or nerve transfers to reconnect the damaged nerve segments.
Epineurium's extraordinary qualities fascinate scientists and medical professionals alike. Dive deeper into the world of neuroscience with our enigmatic facts about Dr. May-Britt Moser, a pioneering researcher in the field. Explore the unbelievable facts about connective tissue, epineurium's close relative, and gain a comprehensive understanding of its functions. Don't miss our collection of enigmatic facts about anatomy, shedding light on the intricate workings of the human body.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
