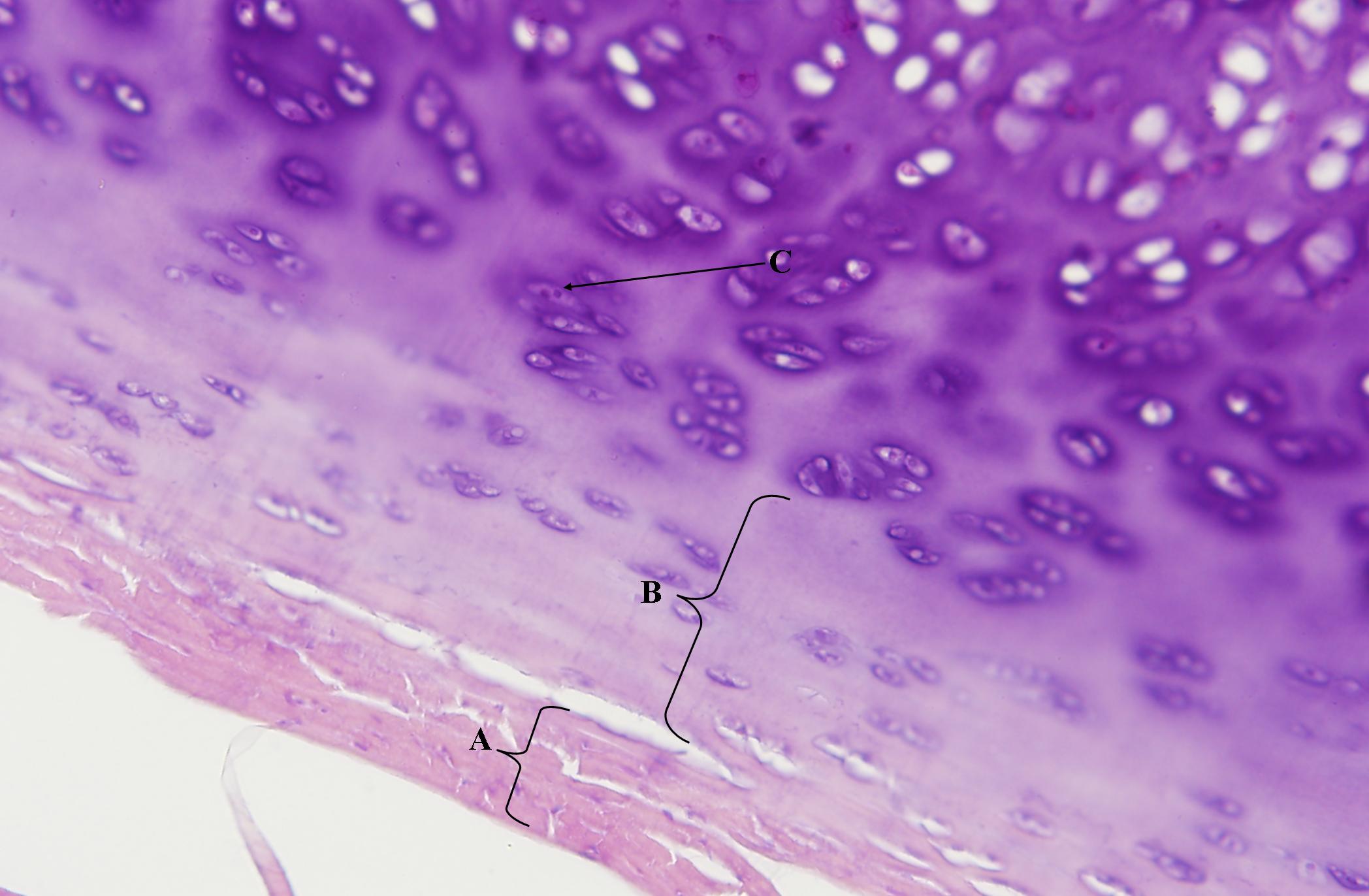
Hyaline cartilage is a crucial component of our body’s skeletal system, providing cushioning and support to various joints and structures. This smooth, pearly white tissue is found in areas such as the nose, trachea, and ends of long bones, playing a vital role in maintaining flexibility and stability. But did you know that hyaline cartilage holds some truly fascinating secrets? In this article, we will uncover 15 intriguing facts about this remarkable tissue. From its unique composition to its regenerative abilities, hyaline cartilage proves to be an extraordinary feature of the human anatomy. So, let’s dive into the world of hyaline cartilage and explore its astonishing properties!
Key Takeaways:
- Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in the body, providing support, flexibility, and protection to our joints and vital body structures.
- Its smooth, glass-like appearance and high water content make hyaline cartilage a crucial shock absorber and essential for bone development and respiratory function.
The Most Common Type of Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in the human body. It is found in various locations, including the joints, rib cage, nose, and trachea.
Smooth and Glass-like Appearance
Hyaline cartilage derives its name from its smooth and glass-like appearance. Under a microscope, it appears transparent and has a bluish-white color.
Provides Support and Flexibility
Hyaline cartilage plays a crucial role in providing support to the body while maintaining flexibility. It acts as a cushion between bones, reducing friction during movements.
Contains High Water Content
Hyaline cartilage contains a high percentage of water, which contributes to its ability to absorb shock and distribute pressure evenly across the joint surfaces.
Limited Healing Capacity
Unlike other tissues, hyaline cartilage has limited healing capacity due to its avascular nature. Injuries to hyaline cartilage can be slow to heal and may require medical intervention.
Vulnerable to Degeneration
Hyaline cartilage is vulnerable to degeneration and can be affected by conditions such as osteoarthritis. The gradual loss of cartilage can lead to joint pain and stiffness.
Important in Bone Development
Hyaline cartilage plays a vital role in the development and growth of bones. It serves as a template for bone formation during embryonic development and early childhood.
Helps Maintain Joint Range of Motion
Hyaline cartilage contributes to the smooth gliding motion of joints, allowing for maximum range of motion. It helps reduce friction and wear on joint surfaces.
Regenerative Potential in Some Areas
Although hyaline cartilage’s regenerative capacity is limited, certain areas such as the nasal septum and ear can regenerate small amounts of hyaline cartilage.
Composed of Specialized Cells
Hyaline cartilage is composed of chondrocytes, which are specialized cells responsible for the production and maintenance of the extracellular matrix.
Low Friction Surface
The smooth surface of hyaline cartilage reduces friction, allowing effortless joint movement. This is especially beneficial in weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips.
Protects Against Compression Forces
Hyaline cartilage’s ability to resist compression forces makes it an ideal shock absorber, protecting the underlying bones from excessive pressure and damage.
Important for Respiratory Function
Hyaline cartilage forms the rings of the trachea and bronchi, providing structure and support to the airways, ensuring unobstructed airflow during respiration.
Vital for Rib Cage Function
The hyaline cartilage in the rib cage allows for the expansion and contraction of the chest during breathing, facilitating the intake and release of air.
Utilized in Medical Procedures
Due to its unique properties, hyaline cartilage is used in various medical procedures, including cartilage repair surgeries and the development of tissue-engineered constructs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyaline cartilage is a remarkable tissue that plays a crucial role in the human body. Its unique structure and properties make it a vital component of the skeletal system. From providing support and cushioning to facilitating smooth joint movement, hyaline cartilage is essential for maintaining overall joint health. Its ability to repair and regenerate gives hope for potential treatments in the future. By understanding the fascinating facts about hyaline cartilage, we can appreciate the intricacies of our body’s anatomy and the incredible complexity that allows us to move and function.
FAQs
1. What is hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is translucent, flexible, and made up of collagen fibers. It is found in various parts of the body, including the nose, trachea, and the articulating surfaces of joints.
2. What are the functions of hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage provides structural support, helps reduce friction between bones in joints, aids in shock absorption, and allows for smooth joint movement.
3. How does hyaline cartilage repair itself?
Hyaline cartilage has limited ability to repair itself due to its avascular nature. However, when damage occurs, cells called chondrocytes can attempt to repair the tissue by producing new collagen fibers and proteoglycans.
4. Can hyaline cartilage be replaced in case of severe damage?
In cases of severe damage, the body’s natural healing processes may not be sufficient. However, medical advancements, such as tissue engineering and cartilage transplantation, offer potential options for cartilage replacement.
5. Can hyaline cartilage degenerate with age?
Yes, hyaline cartilage can degenerate with age due to wear and tear, leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help preserve joint health and delay degeneration.
6. How can we take care of hyaline cartilage?
Proper joint care involves maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive impact on joints, engaging in regular low-impact exercise, and ensuring proper nutrition to support cartilage health.
7. Can hyaline cartilage injuries be prevented?
While some injuries may be unavoidable, certain precautions can help reduce the risk. These include using proper protective equipment during physical activities, practicing correct technique, and avoiding repetitive stress on joints.
8. Are there any medical treatments available for hyaline cartilage injuries?
Yes, there are several medical treatments available for hyaline cartilage injuries, including arthroscopic procedures, cartilage transplantation, and regenerative therapies.
9. Can hyaline cartilage be found in all joints?
No, hyaline cartilage is not found in all joints. While it is present in major joints such as the knee, it may be absent or present in smaller amounts in other joints where different types of cartilage, such as fibrocartilage, are more prevalent.
10. Can hyaline cartilage undergo excessive calcification?
Excessive calcification is not a characteristic of hyaline cartilage. However, other types of cartilage, such as elastic cartilage, can undergo calcification under certain pathological conditions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
