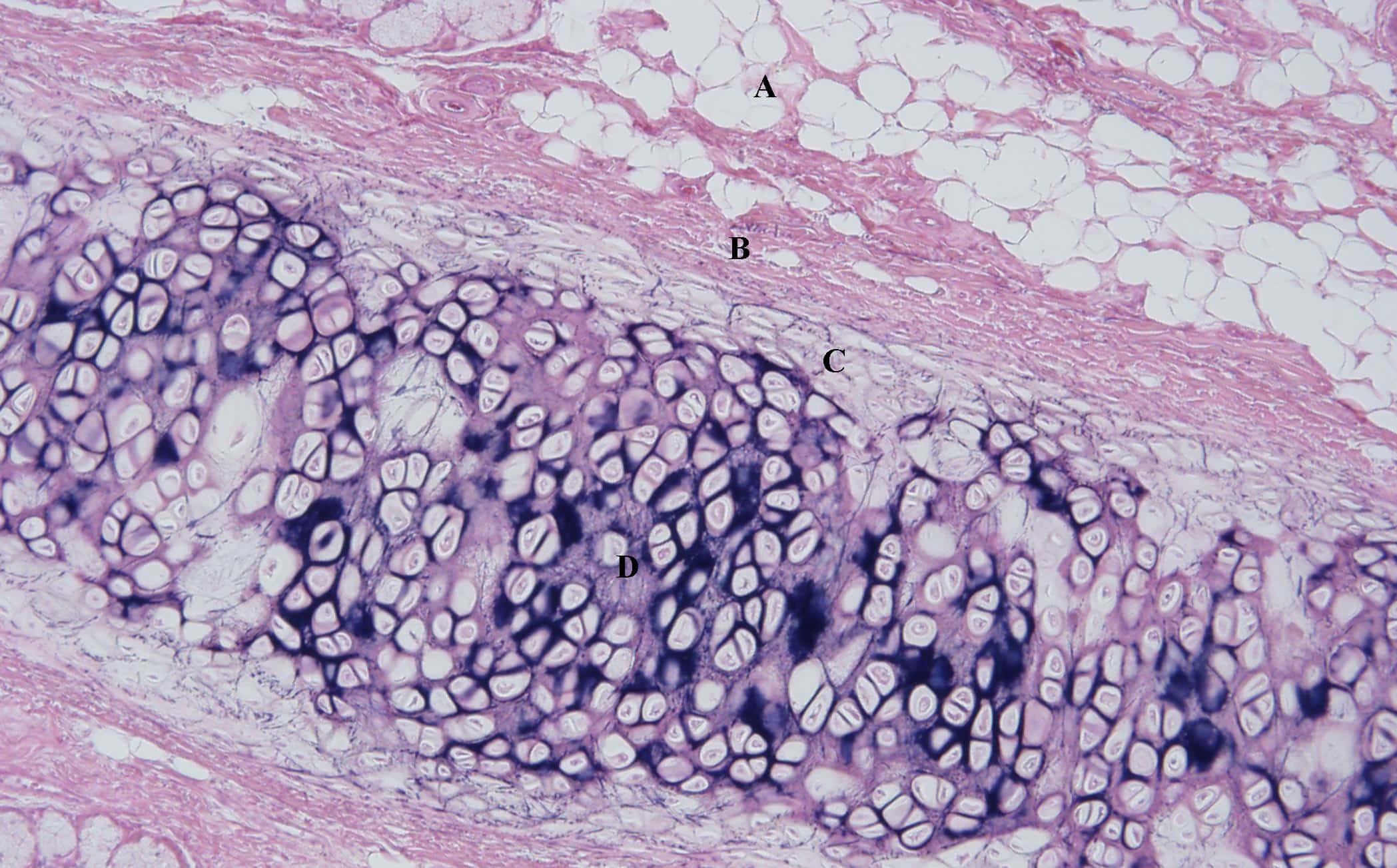
Elastic cartilage is a fascinating type of connective tissue that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of various organs in the human body. It is found in specific regions where flexibility and resilience are essential, such as the outer ear, the epiglottis, and the larynx. Composed of a unique matrix of collagen fibers and elastin, elastic cartilage provides both strength and elasticity.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of elastic cartilage, exploring its characteristics, functions, and the unique facts that make it stand out. From its role in maintaining the shape of the outer ear to its ability to withstand repeated stress, we will uncover twelve intriguing facts about this remarkable type of cartilage. So, let’s dive in and discover the wonders of elastic cartilage!
Key Takeaways:
- Elastic cartilage is like the superhero of the human body, found in the ears, throat, and more. It’s super flexible, shock-absorbing, and helps us stay balanced. It’s a true body marvel!
- With its unique properties, elastic cartilage supports our ears, maintains shape, and even helps us keep our balance. It’s like the secret ingredient that makes our bodies work like magic!
Elastic cartilage is found in various parts of the human body.
One of the remarkable features of the human body is the presence of elastic cartilage, a specialized type of connective tissue. It can be found in the external ear, the epiglottis (a structure that covers the windpipe during swallowing), and the Eustachian tube, which helps equalize pressure between the middle ear and the throat.
Elastic cartilage is flexible and highly resilient.
Elastic cartilage owes its unique properties to the presence of abundant elastic fibers within its matrix. These elastic fibers allow the cartilage to stretch and recoil, making it highly flexible and resilient. This characteristic enables the external ear to withstand deformation and regain its shape.
Elastic cartilage provides support and maintains shape.
While elastic cartilage is flexible, it also plays a crucial role in providing support and maintaining the shape of specific body structures. It gives structure to the external ear, keeping it upright and enhancing sound reception. Similarly, the epiglottis remains in position to protect the airway during swallowing.
Elastic cartilage consists of chondrocytes and extracellular matrix.
Elastic cartilage comprises specialized cells, known as chondrocytes, embedded within an extracellular matrix. The chondrocytes produce and maintain the elastic fibers that give the cartilage its unique properties. This matrix also contains proteins, such as collagen, that provide additional strength and support.
Elastic cartilage has excellent shock-absorbing capabilities.
Due to its elastic fibers and flexible nature, elastic cartilage is excellent at absorbing and cushioning shocks and impacts. This is particularly important in structures like the external ear, which are exposed to various forces in daily activities.
Elastic cartilage has a lower cell density compared to other types of cartilage.
In contrast to hyaline cartilage, which has a higher cell density, elastic cartilage has a lower number of chondrocytes per unit volume. This lower cell density allows for greater interstitial space within the tissue and contributes to its unique properties.
Elastic cartilage can undergo age-related changes.
As with other tissues in the body, elastic cartilage can undergo changes with aging. The elastic fibers may become less abundant and more fragmented, leading to a decrease in elasticity and resilience. This can contribute to age-related changes in the shape and function of structures like the external ear.
Elastic cartilage has a rich blood supply compared to other cartilage types.
Unlike hyaline cartilage, which has a limited blood supply, elastic cartilage is well-vascularized. This rich blood supply ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the chondrocytes, supporting their metabolic activities and overall cartilage health.
Elastic cartilage allows for rapid cellular turnover.
The presence of a robust blood supply in elastic cartilage promotes a higher rate of cellular turnover compared to other types of cartilage. This allows for efficient repair and maintenance of the cartilage tissue, ensuring its functionality and integrity.
Elastic cartilage can be affected by certain medical conditions.
Although elastic cartilage is resilient, it can be susceptible to certain medical conditions. For example, the external ear may be affected by conditions such as cauliflower ear, in which repeated trauma can lead to deformity and disfigurement.
Elastic cartilage can be a target for regenerative medicine research.
The unique properties of elastic cartilage make it an intriguing target for regenerative medicine research. Scientists are exploring ways to harness the regenerative potential of stem cells to restore or replace damaged elastic cartilage, opening up new possibilities for medical interventions.
Elastic cartilage plays a vital role in maintaining body balance.
The presence of elastic cartilage in the semicircular canals of the inner ear contributes to our sense of balance and spatial orientation. These structures detect head movements and relay information to the brain, allowing us to maintain equilibrium and navigate our surroundings.
As we have discovered, elastic cartilage is a fascinating component of the human body. Its unique properties enable flexibility, resilience, and support in various structures. Understanding the intricacies of elastic cartilage not only deepens our knowledge of human anatomy but also highlights its importance in maintaining our overall well-being.
In conclusion, these 12 intriguing facts about elastic cartilage shed light on its significance and multifaceted role in the human body. From providing support and maintaining shape to its flexible nature and shock-absorbing capabilities, elastic cartilage is truly a remarkable tissue. So the next time you marvel at the flexibility of your ears or appreciate your sense of balance, remember the intricate workings of elastic cartilage that make it all possible.
Conclusion
In conclusion, elastic cartilage is a fascinating component of the human body that plays a crucial role in maintaining structure and flexibility. Its unique properties allow it to withstand repeated bending and stretching without permanent deformation. Understanding the intricacies of elastic cartilage can help us appreciate its importance in various anatomical structures such as the outer ear, epiglottis, and the larynx. Whether it’s providing structural support, protecting delicate organs, or allowing for smooth movement, elastic cartilage is an essential part of our physiological makeup.By delving into the intriguing facts about elastic cartilage, we gain a deeper understanding of its function and significance. From its composition to its role in the body, elastic cartilage proves to be a remarkable tissue worthy of exploration and admiration.
FAQs
1. What is elastic cartilage?
Elastic cartilage is a type of cartilage that contains elastic fibers, allowing it to be more flexible and resilient compared to other types of cartilage.
2. Where is elastic cartilage found in the body?
Elastic cartilage is primarily found in external ear (pinna), epiglottis, and the larynx. These structures require flexibility and elasticity for their proper function.
3. How does elastic cartilage differ from other types of cartilage?
Elastic cartilage contains more elastic fibers, which give it the ability to bend and recoil. In contrast, hyaline cartilage is more rigid, while fibrocartilage is suited for strength and is found in areas that require shock absorption.
4. What is the function of elastic cartilage in the body?
Elastic cartilage provides support and maintains the shape of certain anatomical structures, while also allowing for flexibility and accommodation of movement.
5. Can elastic cartilage be damaged or degenerate?
Yes, like other cartilaginous tissues, elastic cartilage can undergo degeneration or damage due to aging, trauma, or various medical conditions. This can lead to functional impairment and potential complications.
6. Is there any treatment or therapy for elastic cartilage damage?
Treatment options for elastic cartilage damage depend on the severity and location of the damage. Conservative approaches, such as medication and physiotherapy, may be effective in some cases. However, in more severe instances, surgical interventions like cartilage grafting or implantation may be necessary.
7. Can elastic cartilage regenerate?
Elastic cartilage has limited regenerative capacity. However, it can undergo repair to some extent with the help of specialized cells called chondrocytes. Stimulating chondrocyte activity and promoting tissue healing may aid in the regeneration process.
8. How does aging affect elastic cartilage?
Aging can lead to deterioration of elastic cartilage, contributing to a loss of elasticity and increased stiffness. This can impact the function of elastic cartilage-containing structures.
9. Can lifestyle choices affect the health of elastic cartilage?
Yes, certain lifestyle choices such as regular exercise and maintaining a balanced diet can promote the health of elastic cartilage. On the other hand, factors such as obesity, poor nutrition, and smoking can negatively affect the integrity and function of cartilage.
10. Are there any conditions associated with elastic cartilage dysfunction?
Yes, conditions like elastic cartilage disorders, such as elastic ear syndrome and elastic cartilage-related genetic disorders, can cause abnormalities in the structure and function of elastic cartilage.
Elastic cartilage's unique properties make it a fascinating subject, but there's so much more to explore in the world of human anatomy. Delving into the intricacies of connective tissue reveals a complex network that holds our bodies together. Discover how the epiglottis, a small flap of elastic cartilage, plays a crucial role in protecting our airways. And if you're curious about elasticity in everyday objects, take a look at the surprising science behind rubber bands.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


