The ulnar artery is a crucial blood vessel located in the forearm and hand. It plays a vital role in supplying oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and tissues in this region. While it may not be as well-known as some of the other blood vessels in the body, the ulnar artery has several astonishing facts that make it truly fascinating. In this article, we will explore eight of these intriguing facts about the ulnar artery, shedding light on its importance and the incredible functions it performs. From its unique course to the connection with important structures in the hand, the ulnar artery is a true wonder of human anatomy. So, let’s dive in and discover the astonishing facts about the ulnar artery!
Key Takeaways:
- The Ulnar Artery is a major blood vessel that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the lower arm and hand, playing a crucial role in hand strength and coordination for tasks like writing and gripping objects.
- Despite carrying deoxygenated blood, the Ulnar Artery is vital for the proper functioning of the hand, branching out into smaller blood vessels and exhibiting a unique anatomical pathway.
The Ulnar Artery is one of the major blood vessels in the human body.
The Ulnar Artery is a vital component of the circulatory system, responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the lower arm and hand. This artery runs parallel to the ulna bone in the forearm, and its function is crucial for proper blood circulation to these areas.
The Ulnar Artery contributes to the blood supply of the hand.
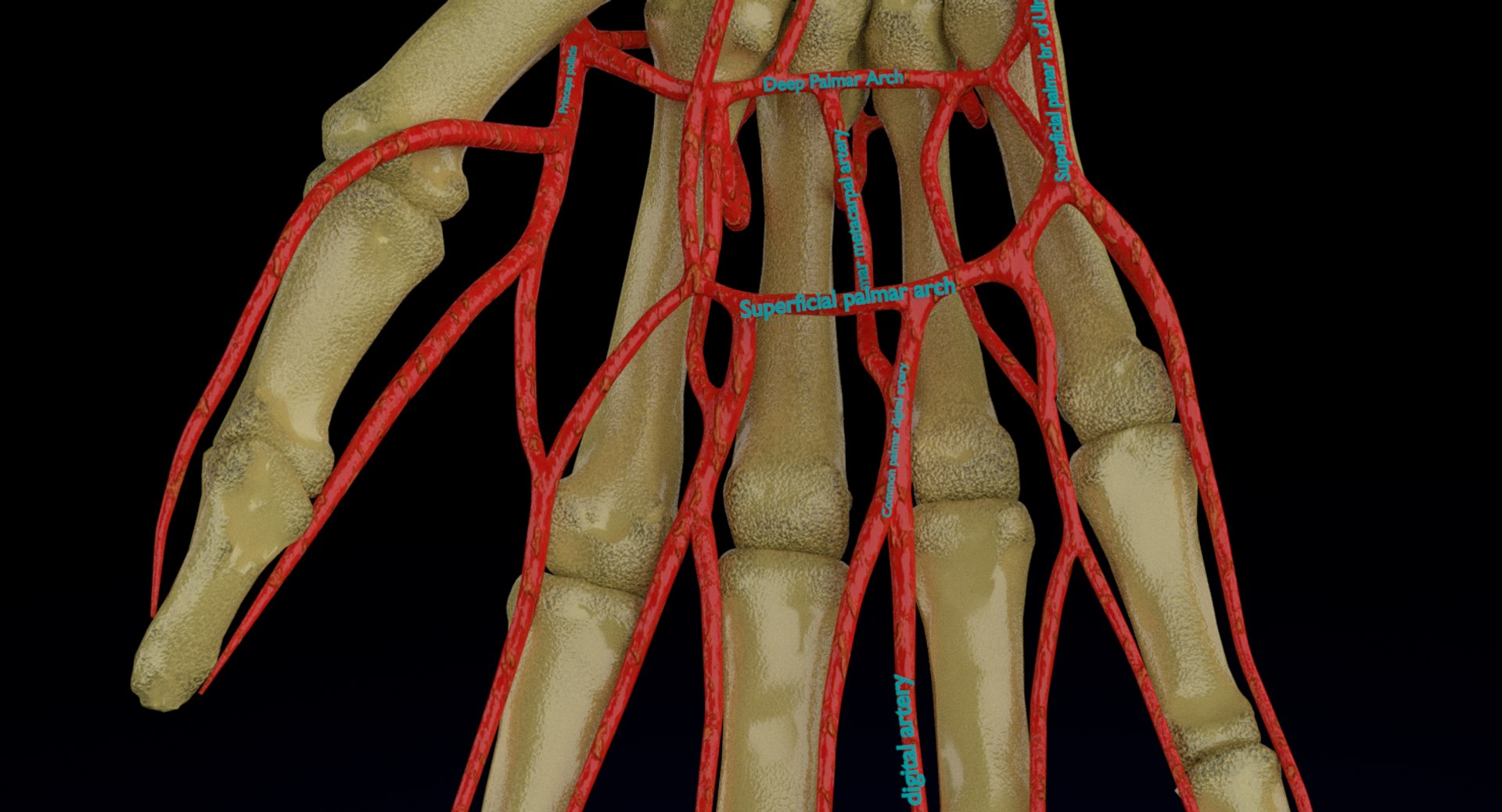
The Ulnar Artery branches out into smaller blood vessels within the hand, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the various structures, including muscles, tendons, and nerves. Without the proper blood supply from the ulnar artery, the hand would not be able to function optimally.
The Ulnar Artery exhibits a unique anatomical pathway.
The Ulnar Artery starts at the brachial artery near the elbow, travels down the forearm along the ulna bone, and terminates at the superficial palmar arterial arch in the palm of the hand. Its distinctive route allows it to provide specialized blood flow to the structures of the lower arm and hand.
The Ulnar Artery is susceptible to certain medical conditions.
Due to its location and role in blood circulation, the ulnar artery can be affected by various conditions such as arterial occlusion, thrombosis, and aneurysm. These conditions can lead to restricted blood flow, pain, and potential complications if left untreated.
The Ulnar Artery can be used for medical procedures.
In certain medical interventions, the ulnar artery can be utilized as an access point for procedures such as arterial catheterization, arterial blood gas sampling, and even arterial grafting. Its accessibility and reliability make it a valuable resource for healthcare professionals.
The Ulnar Artery has important clinical implications.
Impairment or damage to the ulnar artery can result in medical conditions known as ulnar artery disease or ulnar artery syndrome. These conditions can cause symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower arm and hand.
Ulnar Artery carries deoxygenated blood.
Contrary to popular belief, the ulnar artery carries deoxygenated blood, which is then oxygenated by the surrounding tissues of the hand and lower arm. Once oxygenated, the blood is then collected by the veins and returned to the heart for reoxygenation.
The Ulnar Artery has significant functional significance in hand strength and coordination.
The Ulnar Artery plays a crucial role in supplying oxygen and nutrients to the muscles responsible for hand strength and precision. Its proper functioning is essential for tasks requiring fine motor skills, such as writing, gripping objects, and performing delicate movements.
Conclusion
The ulnar artery is a vital blood vessel in the human body that plays a crucial role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to the forearm and hand. Understanding the anatomy and function of the ulnar artery can provide valuable insights into various medical conditions and procedures. From its origin to its branches, the ulnar artery is a fascinating part of human anatomy.In conclusion, the ulnar artery is a remarkable blood vessel that deserves our attention and appreciation. Its intricate network ensures adequate blood flow to the forearm and hand, enabling us to perform daily tasks. Whether you are a medical professional or simply curious about the human body, exploring the astonishing facts about the ulnar artery can deepen our understanding of the incredible complexities of human anatomy.
FAQs
1. What is the role of the ulnar artery?
The ulnar artery plays a vital role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to the forearm muscles and hand. It is responsible for nourishing the tissues and maintaining their functionality.
2. How does the ulnar artery differ from other arteries?
The ulnar artery runs along the ulna bone in the forearm and is one of the two main arteries responsible for blood supply to the hand, the other being the radial artery. Unlike the radial artery, the ulnar artery supplies blood to a larger portion of the hand.
3. Can the ulnar artery be affected by diseases?
Yes, the ulnar artery can be affected by various conditions such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, or aneurysms. These conditions can lead to decreased blood flow, causing pain, numbness, and other complications in the forearm and hand.
4. Are there any treatments available for ulnar artery disorders?
Yes, treatment options for ulnar artery disorders depend on the specific condition. They can include lifestyle changes, medication, surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass grafting, or in severe cases, amputation. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
5. Can the ulnar artery regenerate if damaged?
While the ulnar artery has some regenerative capabilities, the extent of regeneration depends on the severity and location of the damage. In some cases, medical intervention may be required to restore optimal blood flow to the affected area.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
