Welcome to an intriguing journey into the world of hepatic lobules – the remarkable structures that play a vital role in our liver’s functioning. Hepatic lobules are microscopic units within the liver that are responsible for the crucial processes of detoxification, metabolism, and nutrient storage.
In this article, we will uncover 18 astonishing facts about hepatic lobules that will leave you amazed at the incredible complexity and efficiency of our body’s internal systems. From their unique architecture to their remarkable regenerative abilities, hepatic lobules are truly fascinating entities that deserve our attention and appreciation.
So, buckle up and get ready to dive deep into the world of hepatic lobules as we explore the extraordinary features and functions that make them an essential component of our overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- Hepatic lobules are like tiny building blocks in the liver, with a unique hexagonal shape and a vital role in detoxification, metabolism, and even recycling old red blood cells.
- These incredible structures have a three-dimensional organization, support the immune system, and communicate with each other, showcasing the liver’s amazing abilities and resilience.
What are Hepatic Lobules?
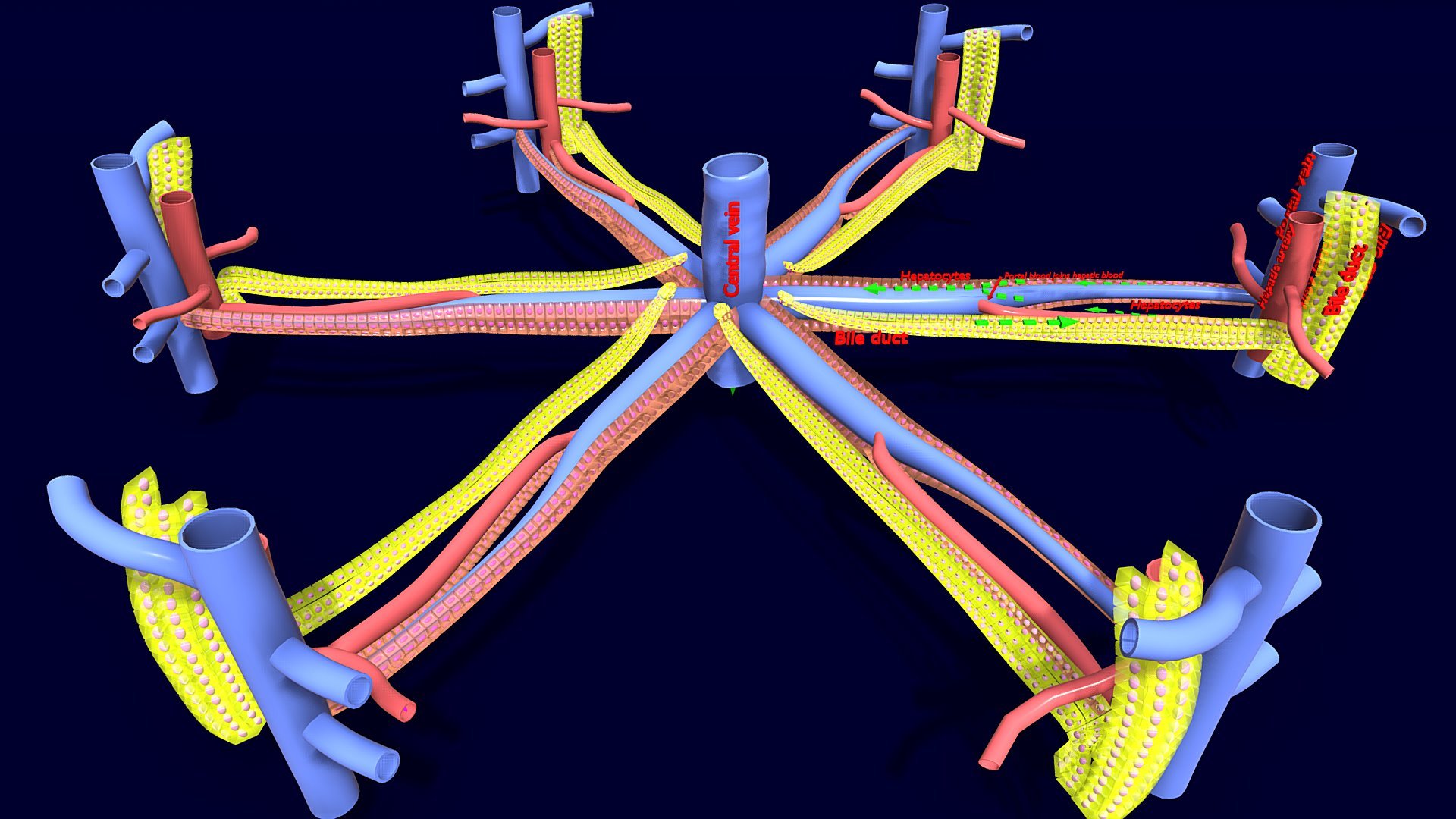
Hepatic lobules are small, functional units that make up the liver. These structures are like building blocks, responsible for the liver’s unique architecture and function.
Hexagonal Shape
One fascinating aspect of hepatic lobules is their hexagonal shape. Each lobule has six sides and is arranged in a pattern resembling a honeycomb. This formation contributes to the efficiency of the liver’s metabolic activities.
Portal Triad
Within each lobule, you will find a unique arrangement known as the portal triad. This triad consists of three essential components – a branch of the hepatic artery, a branch of the hepatic portal vein, and a bile duct. These structures work together to ensure proper blood supply and bile drainage within the liver.
Blood Flow
Hepatic lobules are at the center of the liver’s circulatory system. Blood flows through specialized blood vessels called sinusoids, which connect the portal triads within each lobule.
Oxygen and Nutrient Exchange
As blood flows through the sinusoids, there is a crucial exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the blood and the hepatocytes, the liver’s functional cells. This exchange is vital for the liver’s metabolic processes.
Lobule Zones
Each hepatic lobule can be divided into zones based on the distribution of blood and metabolic activities. These zones, known as zone 1, zone 2, and zone 3, have varying oxygen and nutrient levels, which influence their specific functions.
Detoxification Powerhouse
Hepatic lobules are the liver’s detoxification powerhouses. Within these structures, toxic substances are filtered, metabolized, and eliminated from the body, ensuring our overall health and well-being.
Metabolic Functions
The liver, with the help of hepatic lobules, performs various metabolic functions. These include carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism, as well as vitamin and mineral storage.
Recycling of Red Blood Cells
The liver’s remarkable ability to recycle old and damaged red blood cells is made possible by the intricate workings of hepatic lobules. These structures break down and remove components from red blood cells, allowing for the synthesis of new blood cells.
Hepatic Lobules and Bile Production
Bile, a crucial substance for digestion, is produced within the hepatic lobules. The hepatocytes within the lobules synthesize and secrete bile, which is then transported to the gallbladder for storage.
Regeneration Potential
Incredible as it may seem, hepatic lobules have a remarkable ability to regenerate. Even if a portion of the liver is damaged, these structures can regenerate and restore the liver’s functionality.
Three-Dimensional Organization
Hepatic lobules are not just flat structures; they have a three-dimensional organization. This intricate arrangement allows for efficient interactions between hepatocytes and other liver cells.
Hepatic Lobules and the Immune System
The liver plays a crucial role in our immune system, and hepatic lobules are key players in this defense mechanism. Within these structures, immune cells called Kupffer cells are present, helping to protect the liver from pathogens and foreign substances.
Liver Diseases and Hepatic Lobules
Many liver diseases, such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, can directly impact the structure and function of hepatic lobules. Understanding these structures can help researchers and medical professionals in diagnosing and treating such conditions.
Lobule Architecture in Laboratory Research
Hepatic lobules have been extensively studied in laboratory research to understand liver function and develop new therapies for liver diseases. The detailed knowledge of these structures aids in advancing medical science.
Unique Microenvironment
Each hepatic lobule has a unique microenvironment that supports the metabolic activities of the liver. This specialized environment ensures optimal functioning and facilitates the intricate processes that occur within the lobules.
Communication Between Lobules
Hepatic lobules communicate and interact with each other through various signaling pathways. This inter-lobular communication allows for coordinated functioning and ensures the overall effectiveness of the liver.
Hepatocytes – The Stars of Lobules
Hepatocytes, the main cells within hepatic lobules, are the true stars of the show. These remarkable cells carry out the majority of the liver’s functions and are vital for its overall health and well-being.
The world of hepatic lobules is truly remarkable, and these 18 unbelievable facts only scratch the surface of their complexity. Understanding the intricacies of these structures deepens our appreciation for the liver’s remarkable abilities and highlights the vital role it plays in maintaining our overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the hepatic lobules are truly fascinating structures within the liver. These small units play a crucial role in the liver’s functions and are responsible for processes like detoxification, metabolism, and nutrient storage. Understanding the anatomy and functions of hepatic lobules is essential for comprehending the liver’s overall functionality and its impact on overall health.Learning about hepatic lobules can also help in diagnosing and treating various liver diseases and conditions. By examining the arrangement and characteristics of these lobules, medical professionals can gain valuable insights into the liver’s health and assess any abnormalities or disorders.Furthermore, the remarkable regeneration capability of hepatic lobules underscores the liver’s resilience. This regenerative capacity allows the liver to repair and restore its function, making it a vital organ for overall well-being.In essence, hepatic lobules are incredible structures that contribute significantly to the liver’s critical functions. Appreciating their complexity and significance can deepen our understanding of the human body and its intricate mechanisms.
FAQs
1. What is the primary function of hepatic lobules?
The primary function of hepatic lobules is to facilitate the metabolic processes of the liver, such as detoxification, synthesis of proteins, and storage of nutrients.
2. How do hepatic lobules contribute to liver regeneration?
Hepatic lobules play a crucial role in liver regeneration by containing specialized cells known as hepatocytes, which have the ability to divide and multiply to restore liver function after damage or injury.
3. Are hepatic lobules present in all vertebrates?
Yes, hepatic lobules are present in all vertebrates, and they vary in size and complexity depending on the species.
4. Can liver diseases affect the structure of hepatic lobules?
Yes, liver diseases such as cirrhosis or hepatitis can cause structural changes in hepatic lobules, disrupting their normal functioning and leading to impaired liver function.
5. How do hepatic lobules contribute to nutrient storage?
Hepatic lobules contain specialized cells called hepatocytes that store various nutrients like glycogen, vitamins, and minerals, which can be released into the bloodstream as needed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


