The Bayer Process is a crucial chemical process that plays a significant role in the production of alumina, a key ingredient in the manufacturing of aluminum. Developed by Karl Josef Bayer in the late 19th century, this process revolutionized the aluminum industry and continues to be widely used today. The Bayer Process involves extracting alumina from bauxite ore through a series of chemical reactions and purification steps. It is a fascinating and complex process that combines chemistry, engineering, and environmental considerations. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of the Bayer Process and explore nine astonishing facts that highlight its importance and impact on our everyday lives. From its origins to its applications, get ready to be amazed by the wonders of this chemical process.
Key Takeaways:
- The Bayer Process, developed in the late 19th century, revolutionized the aluminum industry by extracting alumina from bauxite ore, making aluminum widely accessible for various industries.
- The Bayer Process not only produces alumina but also generates red mud as a byproduct, prompting efforts to find sustainable uses for this waste material to minimize environmental impact.
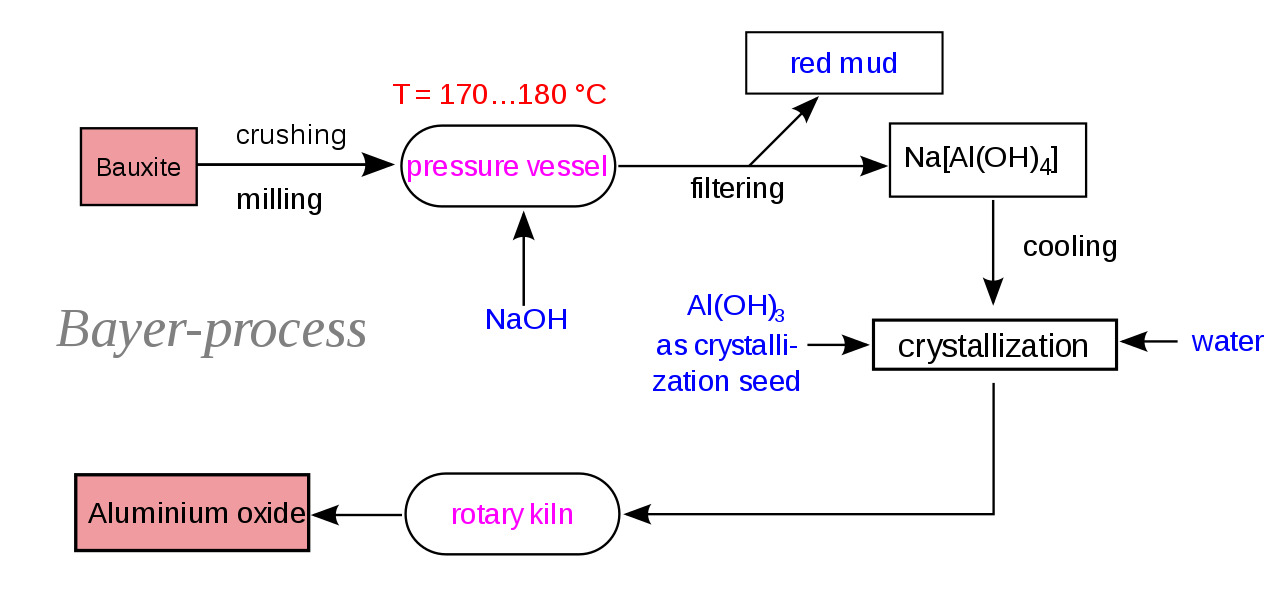
The Bayer Process is a widely used method for extracting alumina from bauxite ore.
The Bayer Process, named after its inventor Karl Bayer, revolutionized the aluminum industry by allowing for the large-scale production of alumina, which is the precursor for aluminum.
The Bayer Process was developed in the late 19th century.
In 1887, Karl Bayer, a German chemist, discovered the process for extracting alumina from bauxite ore. His groundbreaking work laid the foundation for the modern aluminum industry.
The Bayer Process involves several steps.
The process begins with the grinding of bauxite ore into a fine powder. The powder is then mixed with caustic soda, which dissolves the alumina from the bauxite. The resulting solution is clarified, and impurities are removed. Finally, the clarified solution is cooled and seeded to promote the growth of pure alumina crystals.
The Bayer Process requires large amounts of energy and water.
Due to the high energy demand, the Bayer Process is typically conducted near a reliable source of electricity. Additionally, large quantities of water are needed for the dissolution and separation of the alumina from the bauxite.
The Bayer Process produces red mud as a byproduct.
Red mud, also known as bauxite residue, is a highly alkaline waste material that is generated during the Bayer Process. Efforts are being made to find sustainable uses for red mud to minimize its environmental impact.
The Bayer Process is used globally to produce alumina.
The process is employed in numerous countries around the world, including Australia, China, Brazil, and Guinea. These countries are rich in bauxite deposits and have the necessary infrastructure for large-scale alumina production.
The Bayer Process has undergone continuous improvements and optimizations.
Since its development, the Bayer Process has been refined through technological advancements and innovations. These improvements have resulted in increased efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced product quality.
The Bayer Process has made aluminum a widely accessible and versatile material.
Aluminum, derived from the alumina produced through the Bayer Process, is used in various industries, including automotive, construction, packaging, and aerospace. Its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties have made it a preferred choice in many applications.
The Bayer Process plays a crucial role in the circular economy of aluminum.
Through recycling and the use of sustainable practices, the Bayer Process contributes to the circular economy by minimizing waste and conserving resources. It enables the recovery of valuable materials from scrap aluminum and promotes a more sustainable aluminum industry.
Conclusion
The Bayer Process is undoubtedly a captivating chemical process that plays a significant role in the production of alumina. Its revolutionary impact on the industry cannot be overlooked, and it continues to be an essential part of modern-day aluminum production. From its inception to the various stages involved, the Bayer Process has proven to be a remarkable scientific achievement.By extracting alumina from bauxite ore and transforming it into aluminum oxide, this process has enabled the production of aluminum on a large scale. The utilization of sodium hydroxide and various innovative techniques ensures the efficient extraction and purification of alumina, making it an indispensable process for the aluminum industry.Furthermore, the environmentally conscious practices employed in the Bayer Process demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. The recycling and reuse of valuable chemicals significantly reduce waste and minimize the ecological impact of the production process.Overall, the Bayer Process stands as a testament to the ingenuity of chemical engineering and its contributions to modern society.
FAQs
1. What is the Bayer Process?
The Bayer Process is a chemical process used to extract alumina from bauxite ore, which is then refined into aluminum oxide.
2. How does the Bayer Process work?
The process involves grinding bauxite into a fine powder and mixing it with sodium hydroxide, which dissolves the alumina. The resulting solution undergoes precipitation, filtration, and calcination to produce pure aluminum oxide.
3. What is the purpose of the Bayer Process?
The Bayer Process is crucial in the production of alumina, a key ingredient in the manufacturing of aluminum. It enables the extraction and purification of alumina from bauxite ore.
4. Are there any environmental considerations in the Bayer Process?
Yes, the Bayer Process incorporates sustainability measures, such as recycling and reusing chemicals, to minimize waste and reduce the environmental impact of the production process.
5. What industries rely on the Bayer Process?
The primary industry that benefits from the Bayer Process is the aluminum industry. It is used to produce aluminum oxide, which is further processed to manufacture aluminum products.
6. Are there any alternatives to the Bayer Process?
While there are alternative methods for extracting alumina from bauxite, the Bayer Process remains the most widely used due to its efficiency and effectiveness.
7. Is the Bayer Process economically viable?
Yes, the Bayer Process is economically viable as it provides a cost-effective means of extracting alumina, which is a vital component in the production of aluminum.
8. Can the Bayer Process be conducted on a small scale?
While the Bayer Process is predominantly used on an industrial scale, it is theoretically possible to perform it on a smaller scale, albeit with some modifications.
9. What are the future prospects of the Bayer Process?
The Bayer Process is likely to continue being a significant part of aluminum production in the foreseeable future. Ongoing research and development aim to further enhance its efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
