DNA replication is a fundamental process that allows cells to duplicate their genetic material in order to pass on accurate genetic information to the next generation. It is a complex and fascinating process that is essential for the growth, development, and survival of all living organisms. Understanding the intricacies of DNA replication has been a major focus of scientific research, resulting in several astonishing discoveries.
In this article, we will delve into 8 astonishing facts about DNA replication that showcase the incredible mechanisms and intricacies behind this essential biological process. From the high fidelity of DNA replication to the role of enzymes and proteins, these facts highlight the remarkable nature of DNA replication and its significance in maintaining the integrity of our genetic information.
Key Takeaways:
- DNA replication is a crucial process for making new cells and passing on genetic information. It’s like making a perfect copy of a recipe to share with friends.
- DNA replication is like a well-choreographed dance involving many enzymes and proteins. It’s a complex but highly organized process that ensures the faithful transmission of genetic information.
DNA replication is an essential process for cellular growth and reproduction.
DNA replication is the process by which a cell’s DNA is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. This allows for the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division and ensures the continuity of life.
DNA replication is a highly accurate process.
The accuracy of DNA replication is essential for maintaining the integrity of genetic information. The replication machinery in cells has built-in proofreading mechanisms, such as DNA polymerase enzymes, which correct any errors that may occur during the replication process.
DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle.
The cell cycle consists of a series of stages that a cell goes through to divide and reproduce. DNA replication specifically takes place during the synthesis (S) phase of the cell cycle, where the cell prepares for division by duplicating its genetic material.
DNA replication involves the unwinding of the double helix structure.
DNA is composed of two strands that are intertwined in a double helix structure. During replication, enzymes called DNA helicases unwind and separate the two strands, creating a replication fork where new DNA strands can be synthesized.
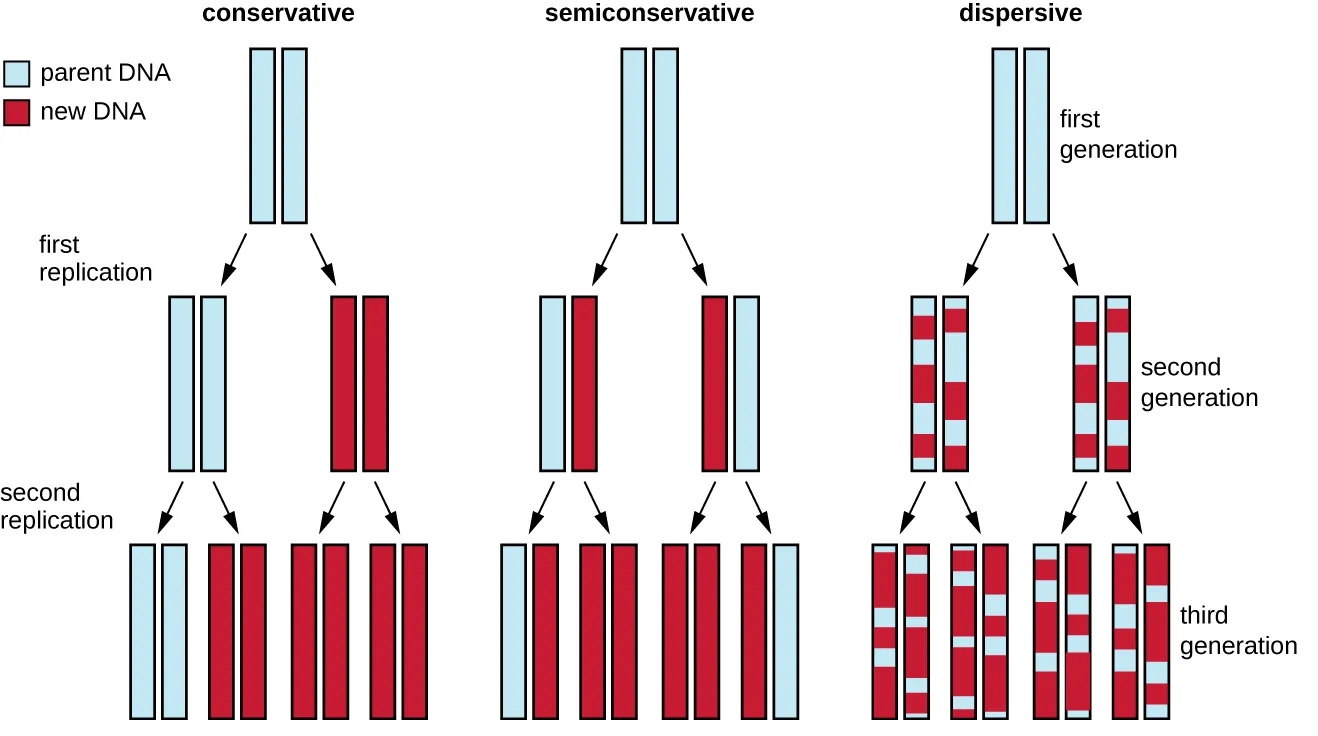
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process.
In semi-conservative DNA replication, each of the new DNA molecules synthesized contains one original parental strand and one newly synthesized daughter strand. This ensures that the genetic information is retained and passed on to the next generation of cells.
DNA replication is a complex and coordinated process.
Multiple enzymes and proteins work together in a highly orchestrated manner to ensure the successful replication of DNA. These include DNA polymerases, DNA ligases, primases, and helicases, among others.
DNA replication can occur at multiple replication forks simultaneously.
In eukaryotic cells, DNA replication occurs at multiple sites along each chromosome, known as replication forks. This allows for efficient and rapid duplication of the entire genome.
DNA replication can be affected by external factors.
Various factors such as radiation, chemicals, and environmental conditions can interfere with DNA replication and lead to errors or DNA damage. Cells have repair mechanisms to fix these errors, but if left uncorrected, they can contribute to genetic mutations and diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNA replication is a truly fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the perpetuation of life. Through the precise and intricate mechanisms involved, our genetic information is faithfully duplicated, ensuring that each new generation inherits the necessary instructions for their development and survival.Understanding the intricacies of DNA replication has not only deepened our knowledge of genetics but has also paved the way for advancements in various fields including medicine, biotechnology, and forensic science. From unraveling the mysteries of inherited diseases to creating genetically modified crops, the study of DNA replication continues to shape the world we live in.As we delve further into the complexities of DNA replication, it is clear that there is still much more to uncover. Ongoing research in this field holds promise for unraveling the mysteries of evolution, aging, and disease. With each new discovery, we come closer to unlocking the secrets of life itself.
FAQs
1. What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division occurs. It ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information.
2. Why is DNA replication important?
DNA replication is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. Without accurate replication, errors can occur, leading to genetic mutations and potentially harmful consequences.
3. How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication involves several steps, including unwinding the DNA double helix, separating the DNA strands, and synthesizing new complementary strands using existing DNA as a template. It requires the action of enzymes and other proteins to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
4. What are the key players in DNA replication?
The key players in DNA replication include DNA polymerase, which synthesizes the new DNA strands, and various proteins, such as helicase, primase, and ligase, which assist in unwinding the DNA, creating RNA primers, and joining the newly synthesized DNA fragments, respectively.
5. Can DNA replication go wrong?
Although DNA replication is highly accurate, errors can occasionally occur due to environmental factors, genetic mutations, or problems with the replication machinery. These errors can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
6. Are there any regulatory mechanisms in DNA replication?
Yes, there are several regulatory mechanisms in place to control the timing and accuracy of DNA replication. These include checkpoints that ensure the DNA is properly replicated and repaired before cell division proceeds.
7. Can DNA replication be influenced by external factors?
Yes, external factors such as UV radiation, chemicals, and certain drugs can affect DNA replication. Exposure to these factors can lead to DNA damage and mutations, which can have serious consequences for an organism.
8. How does DNA replication relate to genetic diversity?
DNA replication is essential for preserving the genetic information within a species. However, it is through genetic mutations that diversity arises. While DNA replication maintains the integrity of genetic information, mutations during replication introduce genetic variations, leading to genetic diversity among individuals in a population.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
