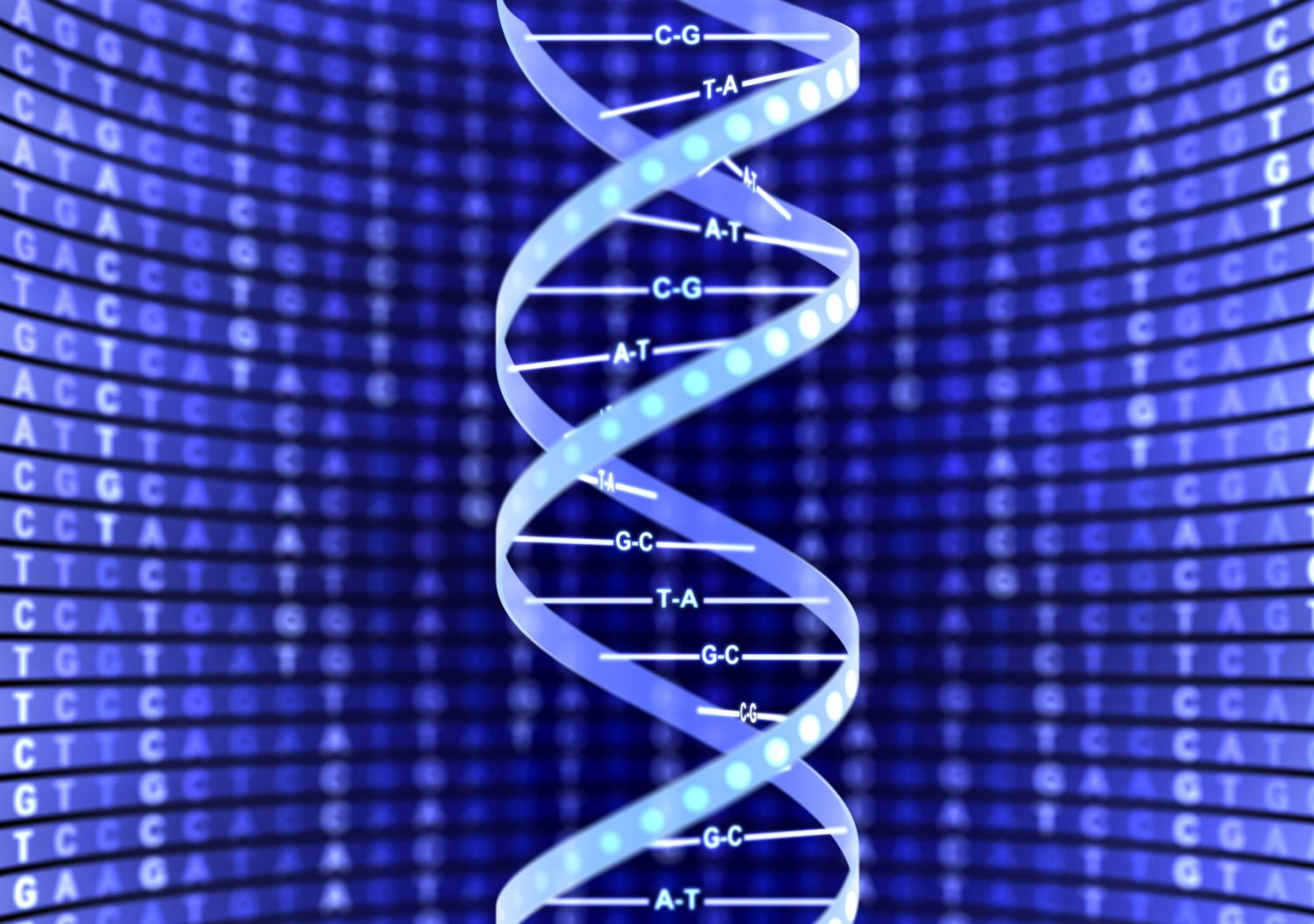
When it comes to understanding the structure of DNA, one cannot ignore the significance of the double helix. Discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, the double helix is the twisted ladder-like structure that serves as the blueprint of life. It is not just a mere configuration, but a complex and fascinating arrangement that holds the genetic information in every living organism. In this article, we delve into the realm of the double helix and bring you 20 mind-blowing facts about its intricacies. From its discovery to its role in inheritance, replication, and evolution, we uncover the secrets within the double-helical structure of DNA that continue to captivate scientists and researchers to this day. So buckle up and prepare to be amazed as we journey into the marvelous world of the double helix!
Key Takeaways:
- The double helix, discovered in 1953, is the iconic structure of DNA and holds over 3 billion base pairs, determining our physical traits and playing a crucial role in genetic inheritance.
- Understanding the double helix’s complexity unlocks the mysteries of life, paving the way for advancements in medicine, genetics, and DNA-based technologies, offering exciting possibilities for the future.
The Double Helix is the Iconic Structure of DNA
Discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, the double helix is the legendary structure that defines the blueprint of life. Composed of two intertwined strands of DNA, the double helix is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Human DNA Unraveled Would Stretch to the Sun and Back
If we were to unwind the DNA contained in just one human cell and lay it out in a straight line, it would stretch a staggering 38 million miles, which is equivalent to approximately 150 round trips to the moon or reaching the sun and back!
The Double Helix Contains Over 3 Billion Base Pairs
Within the double helix structure, there are over 3 billion base pairs that make up the human genome. These base pairs consist of adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C), which form the genetic code that determines our physical characteristics and traits.
Each Double Helix Strand Contains a Range of Genes
The double helix strands are loaded with a multitude of genes. Genes are sections of DNA that contain the instructions for building proteins, which are essential for the functioning and development of our bodies.
The Double Helix Undergoes Replication during Cell Division
One of the most remarkable features of the double helix is its ability to undergo replication. During cell division, the double helix unravels and each strand serves as a template for the creation of new DNA, leading to the formation of identical copies.
The Discovery of the Double Helix Revolutionized Biology
When James Watson and Francis Crick unveiled the double helix structure of DNA, it transformed the field of biology overnight. Their groundbreaking discovery paved the way for significant advancements in genetics, molecular biology, and medicine.
The Double Helix Has a Unique Twisted Shape
Visualize the double helix as a twisted ladder or spiral staircase. The shape arises from the way the two strands wrap around each other, forming a helical structure that is key to its stability and function.
Errors in Double Helix Replication Can Lead to Genetic Mutations
Although the double helix replication process is remarkably accurate, occasional errors can occur. These errors, known as mutations, can lead to genetic variations and may have significant implications for an individual’s health and well-being.
The Double Helix Can Unzip and Re-zip at Specific Locations
During processes such as DNA replication and gene expression, the double helix can unzip and re-zip at specific locations. This allows access to the underlying genetic information and enables the proper functioning of various cellular processes.
The Double Helix Contains Telomeres at the Ends
At the ends of the double helix strands, there are protective structures called telomeres. These specialized regions prevent the DNA from unraveling and provide stability during cell division, helping to maintain the integrity of our genetic material.
The Double Helix Can Form Supercoils
Under certain conditions, the double helix can twist upon itself, forming supercoils. These coiled structures play a vital role in compacting the DNA and ensuring its efficient packaging within the cell nucleus.
Chromosomes Are Composed of Double Helices
Our genetic material is organized into structures known as chromosomes, which are made up of condensed double helices. These chromosomes contain the DNA sequences that comprise our genes and determine our inherited traits.
Scientists Can Manipulate the Double Helix for Genetic Engineering
By understanding the structure and function of the double helix, scientists have gained the ability to manipulate DNA for genetic engineering purposes. This has opened up new avenues for research and potential breakthroughs in areas such as agriculture and medicine.
Chemical Modifications Can Influence Double Helix Functionality
Chemical modifications to the DNA can impact its functionality and gene expression. Processes such as DNA methylation can alter the activity of genes, affecting various cellular processes and contributing to the regulation of gene expression.
The Double Helix Can Be Visualized Using X-ray Crystallography
The structure of the double helix was determined using a technique called X-ray crystallography. This method involves analyzing the diffraction patterns produced by X-rays passing through crystalized DNA, providing insights into its intricate structure.
The Double Helix Can Form Secondary Structures
In addition to the classic double helix, DNA can also adopt secondary structures such as hairpins and cruciforms. These alternative structures play important roles in processes such as DNA repair and have implications for genetic stability and functionality.
The Double Helix Can Store Massive Amounts of Information
The double helix is an exceptionally efficient information storage system. It can pack an incredible amount of genetic information into its compact structure, enabling the encoding of all the instructions necessary for the development and functioning of complex organisms.
Studies on the Double Helix Unveil Insights into Evolution
Investigations into the double helix and its variations across different species provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of evolution. By comparing DNA sequences, scientists can trace the evolutionary relationships between organisms and uncover clues about our shared ancestry.
The Double Helix Offers Potential for DNA-Based Technologies
Advances in understanding the double helix structure have opened up exciting possibilities in the field of DNA-based technologies. From genetic testing to personalized medicine, the double helix serves as the foundation for numerous innovative applications.
The Double Helix is a Testament to the Complexity of Life
The intricate structure of the double helix stands as a testament to the extraordinary complexity of life itself. Its elegant design and essential role in heredity highlight the marvels of nature and the wonders that can be unraveled through scientific exploration.
Conclusion:
These mind-blowing facts about the double helix provide a glimpse into the fascinating world of DNA and its pivotal role in shaping life as we know it. From its iconic structure to its implications for genetic inheritance, the double helix continues to captivate scientists and researchers worldwide. Understanding the intricate complexities of the double helix brings us closer to unlocking the mysteries of life and opens up exciting possibilities for advancements in medicine, genetics, and beyond.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the double helix structure of DNA is truly a fascinating marvel of nature. Its discovery revolutionized the field of genetics and has paved the way for countless advancements in science and medicine. From its elegant symmetry to the intricate pairing of nucleotides, the double helix continues to captivate scientists and researchers around the world.Understanding the structure and function of DNA is crucial in unraveling the mysteries of life itself. The 20 mind-blowing facts about the double helix presented in this article only scratch the surface of its complexity. As scientists continue to delve deeper into the intricacies of DNA, we can expect even more astonishing discoveries in the future.Whether it’s decoding the human genome, developing personalized medicine, or exploring the origins of life, the double helix remains at the forefront of scientific inquiry. Its significance cannot be overstated, and its impact on our understanding of biology is immeasurable. The double helix truly stands as one of the greatest scientific breakthroughs of all time.
FAQs
1. What is the double helix structure of DNA?
The double helix structure refers to the twisted ladder-like arrangement of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. It consists of two strands that are connected by complementary base pairs.
2. Who discovered the double helix?
The double helix structure of DNA was first discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. Their groundbreaking discovery earned them the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962.
3. How does the double helix store genetic information?
The double helix stores genetic information through the sequence of nucleotides that make up its structure. These nucleotides, adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C), form base pairs and create the genetic code.
4. Can the double helix structure be altered?
Yes, the double helix structure can be altered through processes such as mutation or genetic recombination. These alterations can result in genetic variations and contribute to the diversity of life.
5. What are the applications of understanding the double helix structure?
Understanding the double helix structure of DNA has several practical applications. It has paved the way for advancements in genetics, genetic testing, gene therapy, and forensic science, among others.
6. Are there any other structures similar to the double helix?
Yes, the double helix is not unique to DNA. Some RNA molecules can also exhibit a double helix structure, although the specific arrangement and base pairs may differ.
Unraveling the secrets of the double helix is just the beginning. Explore the intriguing world of RNA nucleotides, where four letters hold the key to life's diversity. Marvel at the power of DNA helicase, nature's tireless workhorse in the replication process. Join the celebration of National DNA Day on April 25th, honoring the groundbreaking discoveries that have shaped our understanding of the genetic code.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.