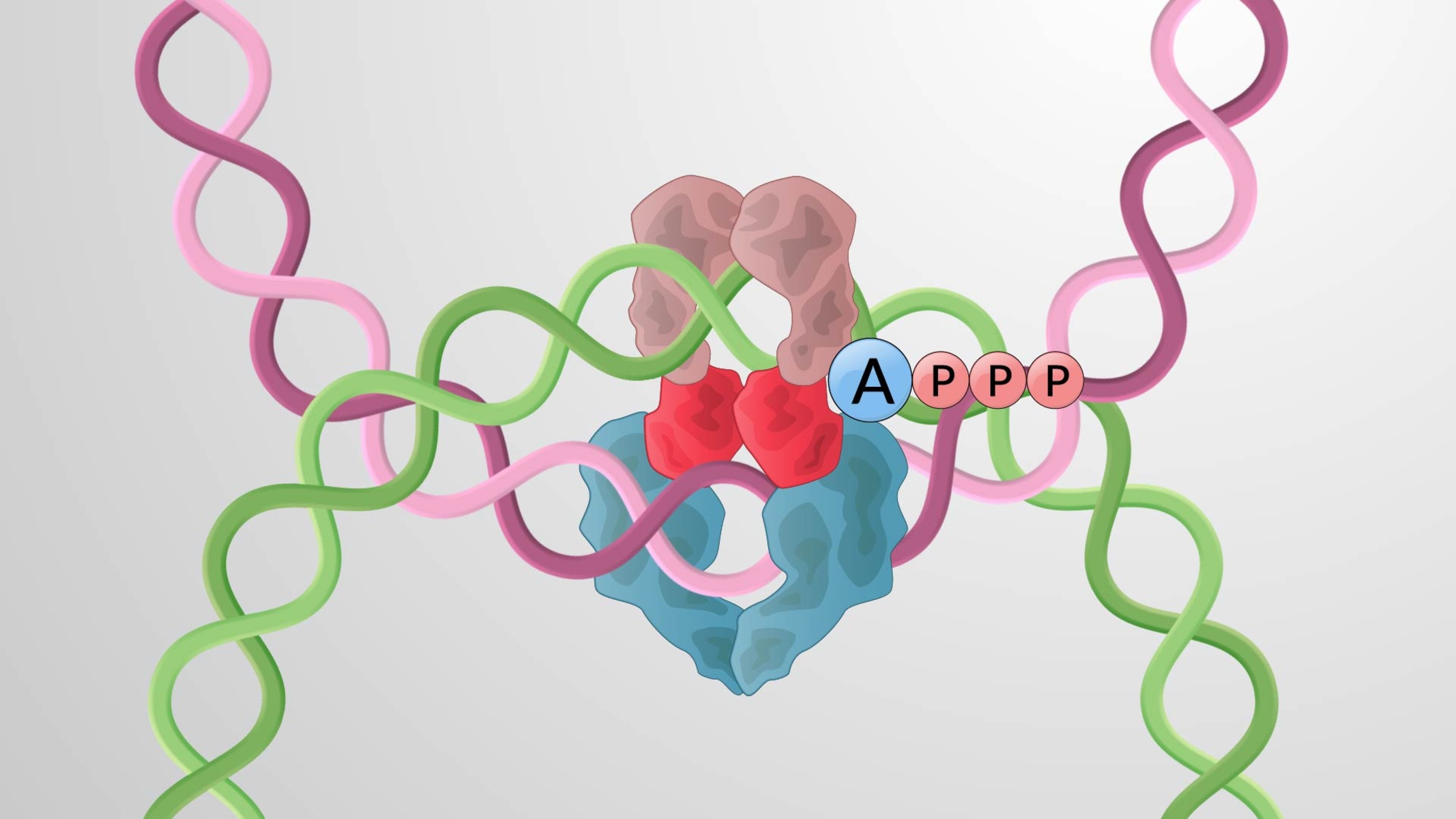
DNA topoisomerases are fascinating enzymes that play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and stability of our genetic material. These remarkable proteins are essential for various cellular processes, including DNA replication, transcription, and repair. Understanding the functions and mechanisms of DNA topoisomerases is not only vital in the field of molecular biology but also for developing targeted therapies for diseases such as cancer.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of DNA topoisomerases and explore 16 intriguing facts about these enzymes. From their discovery to their role in untangling DNA, these facts will shed light on the significance of DNA topoisomerases in cellular function and provide a deeper appreciation for the wonders of molecular biology.
Key Takeaways:
- DNA topoisomerases are essential for DNA replication, preventing tangling, and aiding in gene expression. They are also targeted by antibiotics and anticancer drugs, making them crucial for biological processes and potential therapies.
- DNA topoisomerases play a vital role in maintaining genome stability, influencing gene expression, and aiding in viral replication. Their functions have implications in aging, disease, and potential therapeutic interventions.
DNA topoisomerases are vital for DNA replication.
During DNA replication, the intertwined double helix needs to be unwound and separated to allow for the accurate copying of genetic information. DNA topoisomerases relieve the tension by cutting the DNA strands, allowing the DNA to unwind and then resealing the cut ends.
There are two types of DNA topoisomerases: type I and type II.
Type I topoisomerases create transient breaks in one DNA strand, while type II topoisomerases create double-stranded breaks. These two types have distinct mechanisms and functions, but both are essential for DNA metabolism.
DNA topoisomerases prevent DNA tangling and knotting.
As DNA molecules are highly dynamic and constantly in motion, they can become tangled or knotted. DNA topoisomerases help to remove these entanglements by cutting and rejoining the DNA strands, ensuring the smooth flow of genetic information.
Topoisomerases are classified into different families.
DNA topoisomerases are categorized into four families: type IA, type IB, type IIA, and type IIB. Each family has unique characteristics and functions, contributing to the overall diversity and complexity of topoisomerase enzymes.
Eukaryotes have multiple DNA topoisomerases.
Eukaryotic cells possess several DNA topoisomerases, each with specific roles in different cellular processes. These include topoisomerase I, II, III, and IV, each contributing to the regulation of DNA structure and function.
Topoisomerases have key roles in gene expression.
By controlling the supercoiling and structural changes in DNA, topoisomerases influence the accessibility of genes for transcription and the binding of regulatory proteins. This regulation is crucial for accurately modulating gene expression.
Some antibiotics target DNA topoisomerases.
Certain antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones, specifically inhibit bacterial DNA topoisomerases as a means to disrupt bacterial replication and kill the infecting bacteria. This highlights the significance of these enzymes as potential therapeutic targets.
DNA topoisomerases can repair DNA damage.
When DNA is damaged, topoisomerases can facilitate the repair process by loosening the DNA structure around the damaged site, allowing repair proteins to access and rectify the damage.
Topoisomerases are involved in chromosome condensation.
During cell division, DNA molecules condense into condensed structures known as chromosomes. DNA topoisomerases play a critical role in this process by aiding in the organization and compaction of DNA strands.
DNA topoisomerases are essential for viral replication.
Many viruses, including the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV), require the activity of DNA topoisomerases for their replication. Targeting these viral topoisomerases may offer potential strategies for antiviral therapy.
DNA topoisomerases are highly conserved across species.
The fundamental mechanisms and functions of DNA topoisomerases are so crucial that they have been conserved throughout evolution. This conservation implies the vital roles these enzymes play in maintaining genome stability.
Changes in topoisomerase activity are linked to human diseases.
Altered topoisomerase function has been associated with various human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the role of topoisomerases in disease can pave the way for targeted therapies.
Topoisomerases can create DNA knots intentionally.
Although topoisomerases are primarily responsible for detangling DNA, they can also intentionally generate DNA knots as part of specific cellular processes, including DNA recombination and chromosome segregation.
DNA topoisomerases are implicated in aging processes.
Accumulation of DNA damage over time is one of the contributing factors to aging. As DNA topoisomerases play a role in DNA repair, alterations in their activity or function can impact cellular aging processes.
Topoisomerases can act as molecular switches.
By modulating DNA supercoiling, topoisomerases can act as molecular switches that regulate the activity of certain genes or signaling pathways, providing dynamic control over cellular processes.
DNA topoisomerases are the targets of anticancer drugs.
Several anticancer drugs, such as topoisomerase inhibitors, target the activity of DNA topoisomerases in cancer cells, disrupting their ability to replicate and leading to cell death. These drugs have been instrumental in cancer treatment.
Now that we’ve explored these 16 captivating facts about DNA topoisomerases, it’s evident that these enzymes play a critical role in DNA regulation and have far-reaching implications in various biological processes. The intricate mechanisms and functions of DNA topoisomerases continue to be a subject of intense research, offering new insights into the complexity of DNA biology and potential therapeutic interventions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNA topoisomerases are fascinating enzymes that play a crucial role in maintaining the structure and integrity of DNA molecules. From their involvement in DNA replication and transcription to their ability to regulate DNA supercoiling, these enzymes are essential for various cellular processes. The discovery of different types of topoisomerases and their distinct mechanisms of action has provided valuable insights into the complexity of DNA metabolism.Throughout this article, we have explored sixteen captivating facts about DNA topoisomerases. We learned about their classification into two main types, their role in untangling DNA strands, and their contribution to DNA repair and recombination. Additionally, we discussed the importance of topoisomerases in controlling DNA supercoiling and their potential as targets for developing anti-cancer drugs.As our understanding of DNA topoisomerases continues to grow, so does our appreciation for these remarkable enzymes. Their ability to manipulate DNA structure with precision and efficiency is truly awe-inspiring. Further research in this field will undoubtedly uncover more intriguing facts and expand our knowledge of these essential molecular machines.
FAQs
1. What is the function of DNA topoisomerases?
DNA topoisomerases are enzymes that play a crucial role in regulating the structure and topology of DNA molecules. They are involved in processes such as DNA replication, transcription, and repair.
2. How do DNA topoisomerases work?
These enzymes work by transiently breaking one or both strands of DNA, allowing the DNA to unwind or unwind to relieve torsional stress. They then reseal the DNA strands, ensuring the proper winding and unwinding of DNA.
3. How many types of DNA topoisomerases are there?
There are two main types of DNA topoisomerases: type I and type II. Type I topoisomerases make transient single-stranded breaks in DNA, while type II topoisomerases make double-stranded breaks.
4. What are the clinical implications of DNA topoisomerases?
Due to their essential role in DNA processes, DNA topoisomerases are targets for certain anticancer drugs. Inhibiting these enzymes can disrupt DNA replication and cell division, leading to the death of cancer cells.
5. Are DNA topoisomerases found only in humans?
No, DNA topoisomerases are present in a wide range of organisms, including bacteria, plants, and animals. They are highly conserved across evolution, indicating their vital role in DNA metabolism.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
