When it comes to chemical reactions, reducing agents play a crucial role in facilitating electron transfer and driving the process forward. These compounds have the capability to donate electrons to other molecules, resulting in the reduction of the latter. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or just curious about the world of science, learning about reducing agents is sure to captivate your interest.
In this article, we will explore 20 fascinating facts about reducing agents that will deepen your understanding of their significance and applications. From their importance in industrial processes to their role in biochemical reactions, reducing agents are essential components in a wide range of scientific fields. So, let’s dive into the world of reducing agents and uncover the intriguing secrets behind their incredible properties.
Key Takeaways:
- Reducing agents are like electron donors in chemical reactions, helping to transform substances and play a crucial role in industries like metallurgy and pharmaceuticals.
- They are also found in everyday life, from food preservation to photography, and even in our bodies as antioxidants, protecting our cells from damage.
Definition of a Reducing Agent
A reducing agent, also known as a reductant, is a substance that donates electrons during a chemical reaction. This electron transfer leads to the reduction of another reactant.
Key Role in Redox Reactions
Reducing agents are an essential component of redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions. They enable the reduction of the oxidizing agent by losing electrons.
Electron Donors
Reducing agents act as electron donors by providing electrons to other chemical species in a reaction, resulting in their reduction.
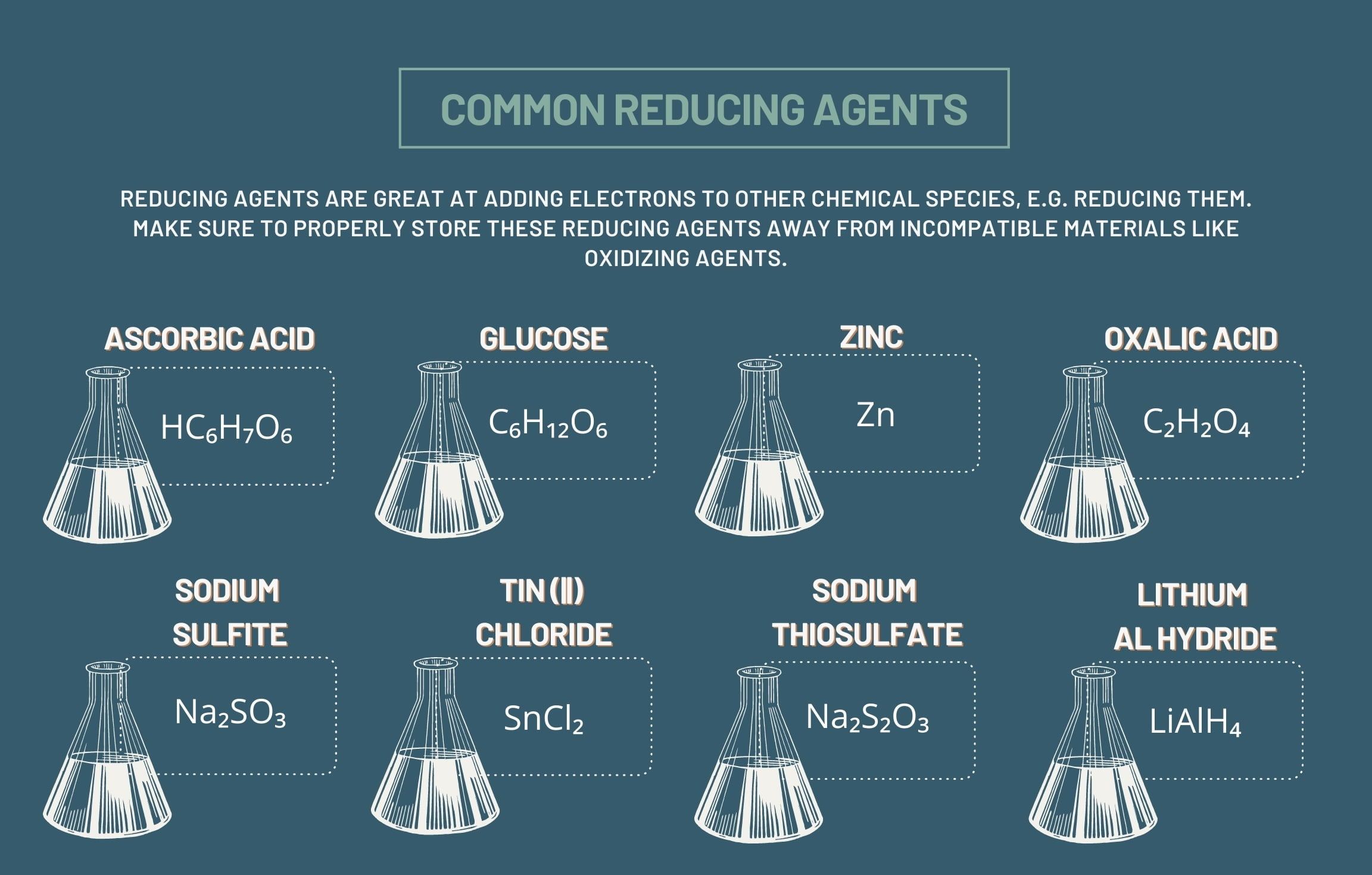
Common Reducing Agents
Some common reducing agents include hydrides (such as Lithium aluminum hydride), metal ions (like Fe2+), alkali metals (such as sodium and potassium), and organic compounds like alcohols and aldehydes.
Types of Reducing Agents
There are two main types of reducing agents: strong reducing agents, which readily donate electrons, and weak reducing agents, which donate electrons less easily.
Industrial Applications
Reducing agents find applications in various industries like metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, organic synthesis, and photography.
Role in Metallurgy
In the field of metallurgy, reducing agents are used to extract metals from their ores. The metal ions present in ores are reduced to their elemental forms.
Importance in Organic Synthesis
Reducing agents are extensively used in organic synthesis to convert functional groups and facilitate the formation of desired products.
Biological Function
Reducing agents play a vital role in biological systems. They are involved in numerous cellular processes, including metabolism and energy production.
Balancing Redox Equations
Reducing agents are essential for balancing redox equations. They help ensure that the number of electrons lost during oxidation matches the number gained during reduction.
Oxidation State Changes
During redox reactions, reducing agents undergo oxidation themselves, experiencing a change in oxidation state by losing electrons.
Role in Photography
Developing solutions used in photography often contain reducing agents. These agents help reduce exposed silver halide crystals into metallic silver, forming the captured image.
Reducing Agents in Medicinal Chemistry
Reducing agents have valuable applications in medicinal chemistry, as they are used to convert functional groups and create specific pharmacologically active compounds.
Environmental Significance
Reduction reactions facilitated by reducing agents play a vital role in environmental processes, including the breakdown of pollutants and detoxification of harmful compounds.
Reducing Agents in Fuel Cells
Hydrogen gas is often used as a reducing agent in fuel cells, where it undergoes oxidation to generate electrical energy.
Reducing Agents as Flame Retardants
In certain applications, reducing agents can also serve as flame retardants by inhibiting the combustion process.
Reducing Agents and Antioxidants
Many antioxidants in our diet, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, act as reducing agents, helping to neutralize free radicals and protect our cells from oxidative damage.
Reducing Agents in Food Preservation
Reducing agents are frequently used in food preservation to prevent spoilage and maintain the freshness of certain products.
Compatibility with Oxidizing Agents
Reducing agents and oxidizing agents are often used together in chemical reactions to facilitate electron transfer and achieve the desired transformations.
Safety Considerations
When handling reducing agents, it is crucial to follow proper safety protocols, as some agents can be highly reactive or even explosive under certain conditions.
These 20 fascinating facts about reducing agents shed light on their significant role in various aspects of chemistry, industry, and our daily lives. Understanding their properties and applications can help us appreciate the intricate world of chemical reactions and electron transfer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reducing agents play a vital role in various chemical reactions. They are essential in the world of chemistry, being used for a wide range of applications. Understanding the properties and characteristics of reducing agents is crucial in conducting experiments and synthesizing compounds.From its ability to donate electrons to its role in redox reactions, reducing agents have proven to be fascinating substances. They can act as powerful antioxidants, allowing them to protect against harmful oxidative damage. Moreover, reducing agents are instrumental in the production of certain metals and in various industrial processes.As we delve deeper into the world of chemistry, the study of reducing agents offers exciting possibilities for exploration and advancement. Their unique properties and versatility make them an intriguing subject for researchers and scientists alike. By harnessing the power of reducing agents, we can continue to unlock new discoveries and advancements in the field of chemistry.
FAQs
1. What is a reducing agent?
A reducing agent is a substance that has the ability to donate electrons to another chemical species. It is involved in redox reactions where it facilitates the reduction of the oxidizing agent by transferring electrons.
2. How do reducing agents work?
Reducing agents work by donating electrons to other substances in a chemical reaction. They have a tendency to lose electrons, which allows them to reduce the oxidation state of other compounds.
3. What are some common examples of reducing agents?
Common examples of reducing agents include hydrogen gas (H2), sodium borohydride (NaBH4), and sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). These substances are frequently used in various chemical processes and industrial applications.
4. Can reducing agents be harmful?
While reducing agents can be highly reactive and potentially hazardous, proper handling and precautions can minimize the risks. It is important to follow safety guidelines and use protective equipment when working with reducing agents.
5. What are the applications of reducing agents?
Reducing agents are widely used in the production of metals, such as in the extraction of iron from its ore. They are also employed in various industrial processes, including the synthesis of organic compounds and the purification of water.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
