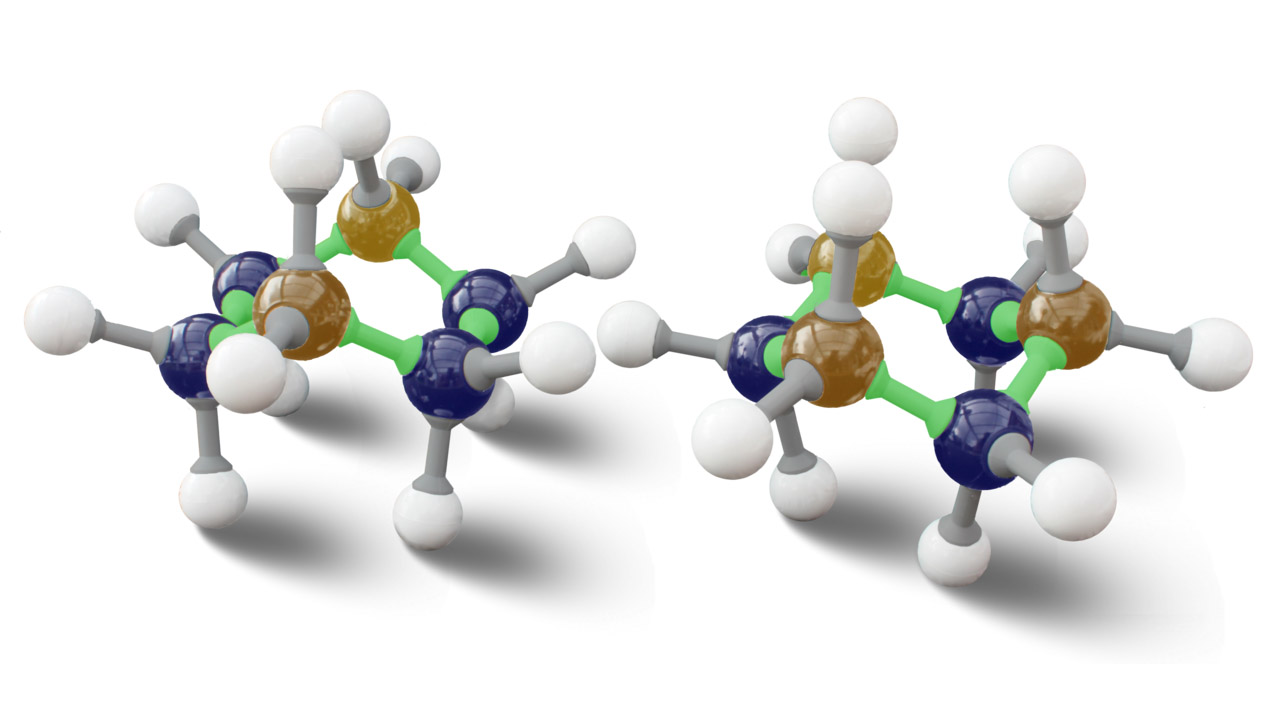
Isomerism is a fascinating concept in the field of chemistry that unlocks a world of enigmatic possibilities. It refers to the phenomenon where two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangement. This results in distinct physical and chemical properties, making isomerism a captivating topic for both chemists and enthusiasts alike.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of isomerism and explore 20 astonishing facts about this phenomenon. From the mind-boggling number of possible isomers to the various types of isomerism and their practical applications, you’ll discover the remarkable diversity and significance that isomerism brings to the study of chemistry.
Key Takeaways:
- Isomerism, the study of molecules with the same formula but different structures, impacts everything from drug development to fragrance creation. It’s like a secret code that unlocks the mysteries of chemistry!
- Understanding isomerism helps scientists create safer drugs, innovative materials, and even unique fragrances. It’s like discovering a hidden world within the world of chemistry!
Isomerism was first discovered in the early 19th century.
Back in 1827, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas was the first to notice that certain organic compounds had the same molecular formula but distinct properties. This groundbreaking observation laid the foundation for the exploration of isomerism.
Isomerism exists in various forms.
Isomerism is not limited to a single type. There are different types of isomers, including structural isomers, stereoisomers, and conformational isomers, each with its own unique characteristics and arrangements.
Isomerism plays a crucial role in drug development.
The phenomenon of isomerism is of great significance in the pharmaceutical industry. Isomerism affects the properties and efficacy of drugs, as different isomers may interact differently with the human body.
Isomerism can lead to different physical and chemical properties.
Even though isomers have the same molecular formula, their structural differences result in distinct physical and chemical properties. This variation is often attributed to differences in bonding, shape, and functional groups.
Isomerism can be found in both organic and inorganic compounds.
Isomerism is not limited to organic compounds. Inorganic compounds, such as coordination complexes and transition metal compounds, can also exhibit various forms of isomerism.
Isomerism has implications in the field of food science.
Isomerism affects the taste, aroma, and nutritional value of food. For example, the different isomers of glucose have distinct sweetness levels, with one form being significantly sweeter than the other.
Isomerism can result in different toxicities.
Different isomers of compounds can have varying toxicity levels. This aspect is crucial in understanding the safety and potential side effects of certain chemicals.
Isomerism can impact the stability of molecules.
The arrangement of atoms in isomers affects the stability of molecules. Some isomers may be more stable than others, leading to differences in reactivity and chemical behavior.
Isomerism has applications in the field of materials science.
Isomerism plays a significant role in designing and developing new materials with desired properties. Understanding the different forms of isomerism helps researchers create innovative materials for various applications.
Isomerism can influence the bioavailability of drugs.
Isomerism can impact the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs in the body. Different isomers may have varying affinities for receptors and enzymes, affecting their efficacy and therapeutic potential.
Isomerism allows for the creation of mirror-image molecules.
Chirality is a form of isomerism that gives rise to mirror-image molecules, known as enantiomers. Enantiomers have identical physical properties but can exhibit different interactions with other chiral molecules.
Some isomers have distinct smells.
In the world of fragrance and perfumery, isomers play a vital role. Different isomers can produce unique scents, allowing perfumers to create diverse and captivating fragrances.
Isomerism challenges scientists to develop analytical techniques.
Identifying and distinguishing between isomers can be a complex task. Scientists continuously strive to develop advanced analytical techniques that can accurately characterize and differentiate various forms of isomerism.
Isomerism can lead to unexpected and surprising reactions.
The presence of isomerism can significantly influence chemical reactions, sometimes resulting in unexpected products. This aspect of isomerism keeps chemists intrigued and drives the exploration of new synthetic methodologies.
Isomerism can affect the physical properties of polymers.
Polymers, such as plastics and fibers, can exhibit different physical properties depending on the arrangement of monomer units. Isomers can impact factors such as strength, flexibility, and thermal stability.
Isomerism can be used to create selective catalysts.
Isomeric differences in catalysts can be exploited to achieve selectivity in chemical reactions. By designing catalysts with specific structural arrangements, chemists can control the outcome of reactions and enhance efficiency.
Isomerism has implications in environmental chemistry.
Understanding isomerism is crucial in studying the fate and behavior of pollutants in the environment. Isomeric forms of chemicals can exhibit different persistence, toxicity, and transport properties in natural systems.
Isomerism can occur in cyclic compounds as well.
While isomerism is commonly associated with straight-chain compounds, cyclic compounds can also possess different isomeric forms. The arrangement of atoms in the ring structure can give rise to distinct isomers.
Isomerism is a subject of ongoing research and discovery.
Scientists continue to explore new forms of isomerism and delve deeper into its implications across various branches of chemistry and beyond. The enigmatic world of isomerism offers endless opportunities for exploration.
Isomerism revolutionizes drug delivery systems.
Isomers play a crucial role in designing drug delivery systems that provide targeted and controlled release of medications. Different isomers can have varying stability, solubility, and compatibility, enabling the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
These 20 enigmatic facts about isomerism showcase the complexity and significance of this captivating field. From its impact on drug development to its role in materials science, isomerism continues to unravel mysteries, driving scientific innovation and exploration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of isomerism is a fascinating and complex one. From its origins in the early days of organic chemistry to the modern advances in understanding molecular structures, isomerism continues to captivate scientists and researchers alike. The 20 enigmatic facts about isomerism mentioned in this article only scratch the surface of this vast and intricate field.Exploring the various types of isomerism, such as structural, stereo, and tautomeric isomerism, allows us to appreciate the diversity and intricacy of nature’s building blocks – molecules. Isomerism plays a crucial role in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and many other areas of chemistry, making it an essential part of scientific research and discovery.As we delve deeper into the world of isomerism, we are bound to unravel even more mysteries and unlock new horizons in the quest for knowledge. So, next time you come across an isomer, remember the hidden complexities and the intricate dance of atoms that give rise to its unique properties. Isomerism truly is a testament to the wondrous intricacies of chemistry.
FAQs
Q: What is isomerism?
A: Isomerism refers to the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in their arrangement or orientation of atoms.
Q: What are the different types of isomerism?
A: There are several types of isomerism, including structural isomerism, stereo isomerism, and tautomeric isomerism.
Q: How does isomerism affect the properties of compounds?
A: Isomerism can lead to significant differences in the physical and chemical properties of compounds, such as boiling points, melting points, and reactivity.
Q: What are some examples of isomerism in everyday life?
A: Examples of isomerism include glucose and fructose, which are structural isomers, and cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene, which are stereo isomers.
Q: How is isomerism important in the field of pharmaceuticals?
A: Isomerism plays a crucial role in drug design and development, as different isomers can have varying pharmacological activities and side effects.
Q: Are all compounds capable of exhibiting isomerism?
A: No, not all compounds can exhibit isomerism. Isomerism is dependent on the molecular structure and arrangement of atoms within a compound.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


