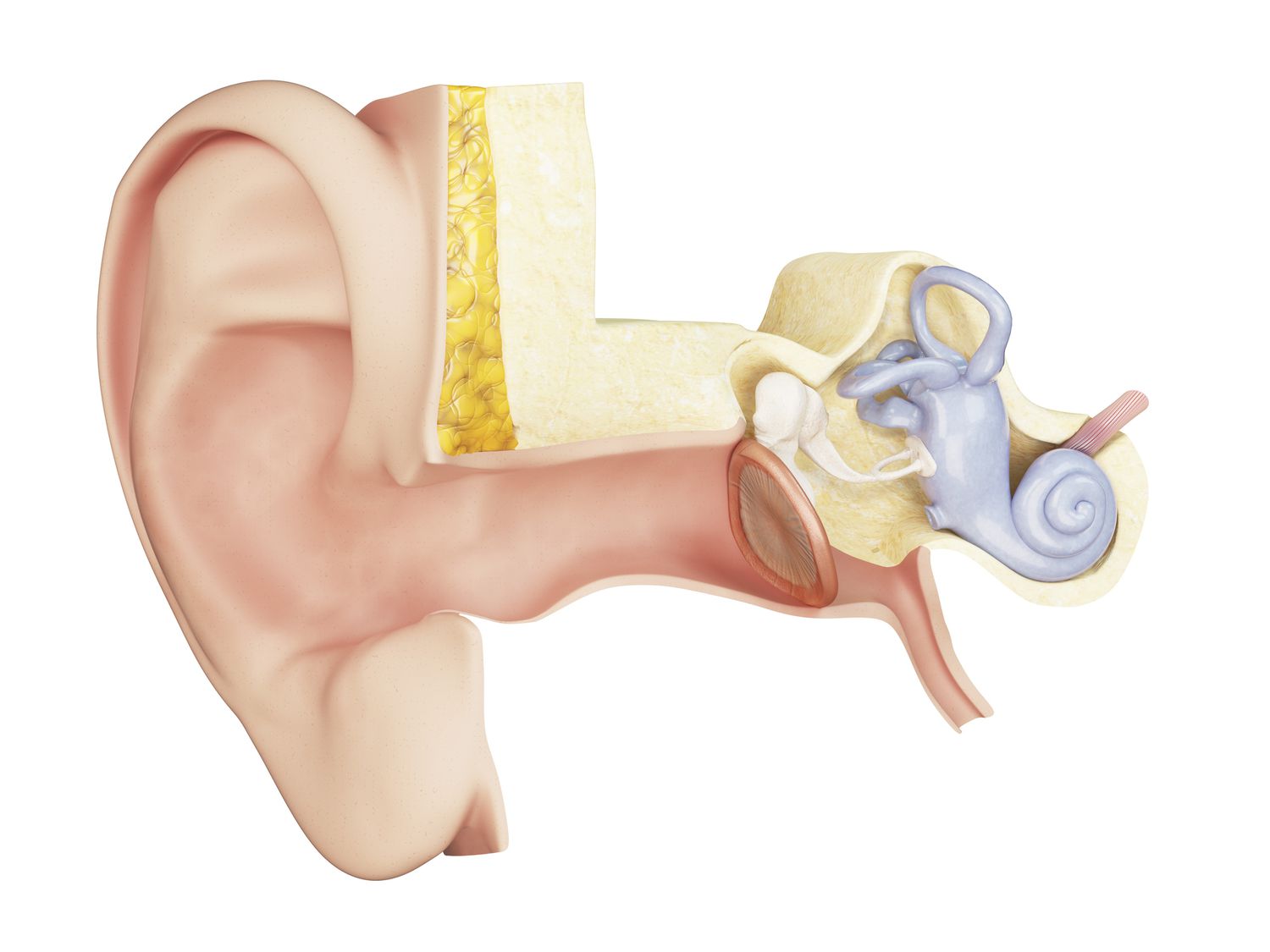
The tympanic membrane, commonly known as the eardrum, is a delicate and essential part of the human ear. While most people are familiar with the basic function of the eardrum – transmitting sound vibrations to the inner ear – there are a myriad of fascinating facts that are often overlooked. In this article, we will explore 10 surprising facts about the tympanic membrane that will not only deepen your understanding of this crucial anatomical structure but also give you a newfound appreciation for the complexity of the human ear. From its unique structure to its crucial role in hearing, get ready to be amazed by the remarkable capabilities of the eardrum.
Key Takeaways:
- The eardrum is thinner than paper and can vibrate over 20,000 times per second, helping us hear and protecting our middle ear from harm. It’s like a superhero shield for our hearing!
- Our eardrum can heal itself if damaged, but we should still protect it from loud noises and pressure changes. It’s a delicate part of our body that needs our care and attention.
The Tympanic Membrane Is Vital for Hearing
The Tympanic membrane, also known as the eardrum, is a crucial component of the human auditory system. It plays a significant role in transmitting sound waves from the outer ear to the middle ear, where the delicate mechanisms of hearing are located.
Tympanic Membrane Is Thinner Than a Piece of Paper
Despite its importance, the eardrum is incredibly thin. In fact, it is thinner than a standard piece of paper, measuring approximately 0.1 millimeters in thickness. This thin and delicate structure is essential for its sound transmission capabilities.
The Eardrum Can Vibrate More Than 20,000 Times Per Second
The remarkable flexibility of the tympanic membrane allows it to vibrate in response to sound waves. These vibrations can occur at a rapid rate, with the eardrum capable of vibrating more than 20,000 times per second in response to high-frequency sounds.
Your Tympanic Membrane Can Regenerate
In the case of a perforated or damaged eardrum, the body has the remarkable ability to heal and regenerate this vital structure. However, it is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect any damage to your eardrum.
The Tympanic Membrane Protects the Middle Ear
The eardrum acts as a protective barrier, preventing foreign objects, such as dust, insects, or water, from entering the middle ear. It also helps to maintain the delicate balance of air pressure within the ear.
Eardrum Vibrations Can Amplify Sound
When sound waves strike the eardrum, its vibrations are transmitted to the small bones in the middle ear, known as the ossicles. These vibrations amplify the sound, allowing for efficient transmission and interpretation by the inner ear.
The Tympanic Membrane Can Be Damaged by Loud Noises
Exposure to loud noises can have detrimental effects on the eardrum. Prolonged or sudden exposure to excessive noise levels can cause temporary or permanent damage to the delicate structure, leading to hearing loss or tinnitus.
Changes in Air Pressure Can Affect the Eardrum
One common experience related to the tympanic membrane is the feeling of pressure changes during activities such as flying in an airplane or diving underwater. The eardrum adjusts to equalize the pressure between the outer and middle ear, allowing for comfortable hearing.
The Tympanic Membrane Contains Nerve Endings
The eardrum is not only a physical structure but also contains a network of sensory nerve endings. These nerve endings pick up the vibrations from sound waves and transmit electrical signals to the brain for interpretation and perception of sound.
The Tympanic Membrane Can Reflect Your Health
Changes in the appearance or function of the eardrum can sometimes indicate underlying health conditions. A skilled healthcare professional can examine the eardrum and identify potential issues, providing valuable insights into your overall well-being.
Conclusion
The tympanic membrane, or eardrum, is a remarkable structure that plays a crucial role in our ability to hear. It is a thin, sensitive membrane located in the middle ear, separating it from the external ear canal. The eardrum vibrates in response to sound waves, transmitting these vibrations to the middle and inner ear, where they are transformed into electrical signals that our brain can interpret as sound.
While the eardrum may seem simple, there are several surprising facts about it. From its incredible sensitivity to its unique anatomy, the eardrum is an essential component of our auditory system. Understanding these facts can deepen our appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that enable us to perceive sound.
Whether it’s protecting our ears from loud noises or ensuring proper hearing function, the tympanic membrane is a critical structure that deserves our attention and care.
FAQs
1. What is the tympanic membrane?
The tympanic membrane, commonly known as the eardrum, is a thin, sensitive membrane located in the middle ear.
2. What is the function of the tympanic membrane?
The main function of the tympanic membrane is to vibrate in response to sound waves, transmitting them to the middle and inner ear.
3. How sensitive is the tympanic membrane?
The tympanic membrane is incredibly sensitive and can detect sound vibrations as low as 20 to 20,000 hertz.
4. Can the tympanic membrane be damaged?
Yes, the eardrum can be damaged due to factors such as loud noises, infections, or trauma. It is important to protect our ears and seek medical attention if any problems occur.
5. Does the tympanic membrane heal itself?
Yes, in many cases, the tympanic membrane can heal itself if it sustains minor injuries. However, severe damage may require medical intervention.
From the tympanic membrane's fascinating facts, dive deeper into audiology's captivating world, uncovering surprising truths about sound processing. Prioritizing ear health through proper care preserves hearing for years to come. Embark on a quest to understand hearing's intricacies, gaining newfound appreciation for our ears' incredible workings.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
