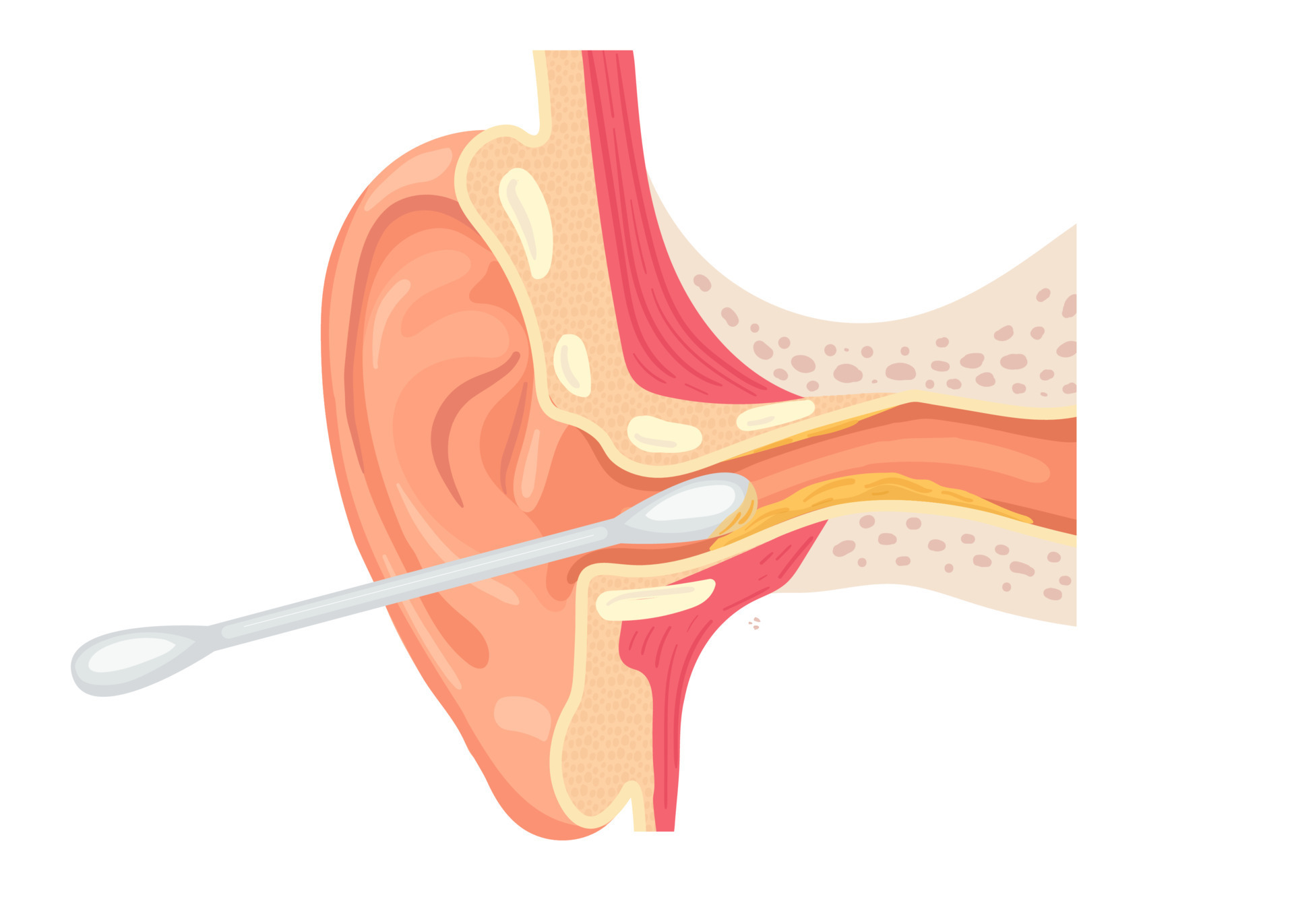
The ear canal, also known as the external auditory meatus, is a fascinating part of the human anatomy that plays a vital role in our ability to hear and perceive the world around us. While it may seem like a simple tunnel that leads sound waves to the eardrum, the ear canal is much more than that. It is a complex structure that has its own set of astonishing facts and features.
In this article, we will delve into 15 astonishing facts about the ear canal. From its unique anatomy to its role in protecting the delicate structures of the inner ear, you will discover just how remarkable this small passage truly is. So, let’s dive in and explore the intricate world of the ear canal!
Key Takeaways:
- The ear canal is a crucial part of the ear that helps us hear by funneling sound waves to the eardrum. It also has natural defenses and self-cleaning mechanisms to protect itself.
- It’s important to take care of our ear canals and avoid inserting objects like cotton swabs. Excessive noise exposure can also harm the ear canal, leading to hearing loss.
The ear canal is a tube-like structure.
The ear canal, also known as the external auditory meatus, is a cylindrical passage that connects the outer ear to the middle ear.
It plays a crucial role in the process of hearing.
The ear canal acts as a pathway for sound waves to enter the ear and reach the eardrum, where they are converted into electrical signals for the brain to interpret as sound.
The ear canal is lined with ceruminous glands.
These glands produce cerumen, commonly known as earwax, which helps protect the ear canal by trapping dust, debris, and harmful microorganisms.
The length of the ear canal varies among individuals.
The length of the ear canal can range from 2.5 to 3.5 centimeters, and it may differ between the left and right ears.
The ear canal has a curved shape.
This curved shape helps to amplify and funnel sound waves towards the eardrum, enhancing the efficiency of sound transmission.
The ear canal is susceptible to infections.
Otitis externa, also known as swimmer’s ear, is a common infection that affects the ear canal, causing pain, itching, and inflammation.
The ear canal is self-cleaning.
The movement of the jaw during activities such as chewing helps to push old earwax towards the outer part of the ear, where it can be easily removed.
Cotton swabs should not be inserted into the ear canal.
Using cotton swabs or any other objects to clean the ear canal can push the earwax deeper, potentially causing blockages or damage to the delicate structures of the ear.
The ear canal has natural defenses against foreign objects.
The presence of hair follicles and the inward slope of the ear canal help prevent foreign objects from easily entering and causing harm.
The size of the ear canal can change with age.
As a person grows older, the ear canal may become narrower, potentially affecting the individual’s ability to hear certain frequencies.
The ear canal can act as a resonator.
By adjusting the shape of the mouth and throat, the ear canal can amplify specific frequencies, allowing humans to produce different vocal sounds.
The ear canal can be affected by excessive noise exposure.
Loud noises over extended periods can damage the sensitive structures of the ear canal, leading to hearing loss or tinnitus.
The ear canal is part of the external ear.
The external ear, composed of the pinna and the ear canal, helps to collect and direct sound waves towards the middle ear.
The average diameter of the ear canal is around 7-8 millimeters.
This diameter can vary among individuals, and it may affect the fitting of hearing aids or earphones.
The ear canal has a rich blood supply.
The blood vessels in the ear canal help in regulating the temperature and maintaining the overall health of the ear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ear canal, also known as the external auditory meatus, is a fascinating part of the human anatomy. It plays a vital role in our ability to hear and perceive sound. From protecting the delicate structures of the inner ear to amplifying and conducting sound waves, the ear canal is truly remarkable.Understanding the anatomy and functions of the ear canal can help us appreciate the complexity of our auditory system. It’s essential to take care of our ears and seek professional help if we experience any hearing-related issues.So, the next time you clean your ears or put on a pair of headphones, remember the astonishing facts about the ear canal and the incredible work it does to help us experience the world of sound.
FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of the ear canal?
A: The ear canal serves as a protective passageway for sound waves to travel from the outer ear to the middle and inner ear. It also helps in keeping the delicate structures of the middle and inner ear safe from damage.
Q: How long is the average ear canal?
A: The length of the ear canal varies among individuals, but on average, it measures around 2.5 centimeters in adults.
Q: Can the ear canal become blocked?
A: Yes, the ear canal can become blocked due to various reasons such as excessive earwax buildup, foreign objects, or swelling caused by an infection. It is recommended to seek medical attention if you experience a blockage that affects your hearing or causes discomfort.
Q: Is it safe to clean the ear canal with cotton swabs?
A: No, it is not safe to clean the ear canal with cotton swabs as they can push the earwax deeper into the canal or even cause injury to the delicate structures. It is best to consult a healthcare professional for safe and effective earwax removal.
Q: Can the ear canal get infected?
A: Yes, the ear canal can get infected, resulting in a condition known as otitis externa or swimmer’s ear. This infection is usually caused by bacteria or fungi and can lead to pain, swelling, and discharge from the ear. Prompt medical treatment is necessary to prevent complications.
Exploring ear canal facts is just the beginning of your auditory adventure. Delve deeper into the intricacies of the external acoustic meatus, a vital component of your hearing system. Ensure peaceful slumber with our top picks for earplugs designed specifically for sleeping. Ready to express your unique style? Our comprehensive guide to ear piercings covers everything from traditional lobes to daring cartilage options. Embark on a journey of discovery as you uncover more fascinating aspects of your ears and how to care for them.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
