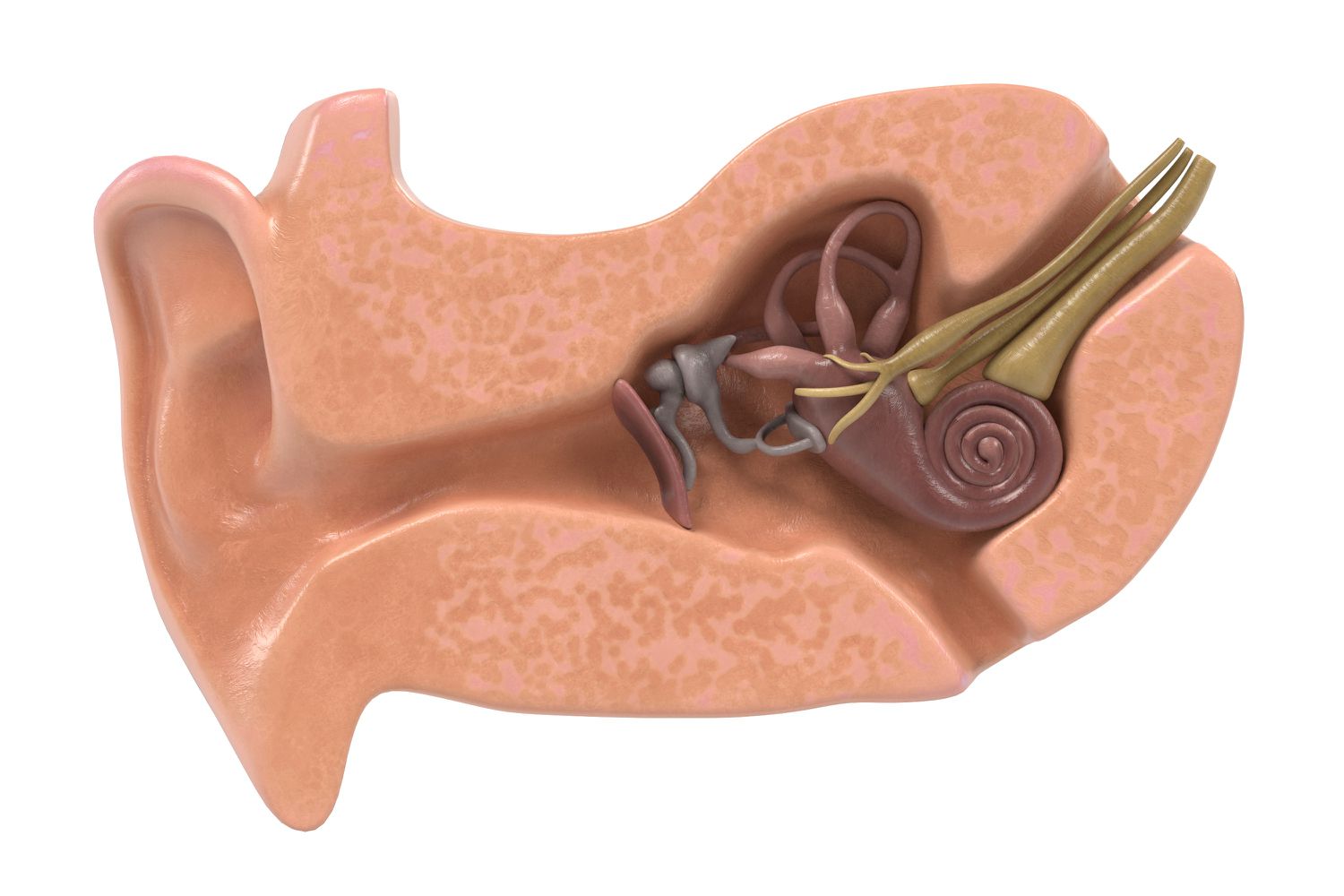
The ampulla of the semicircular canals is a fascinating part of the human anatomy that plays a crucial role in our sense of balance and spatial orientation. These unique structures, located in the inner ear, contain fluid-filled canals that are responsible for detecting rotational movements of the head. While you may be familiar with the concept of the inner ear, there are likely many surprising facts about the ampulla of the semicircular canals that you are unaware of. In this article, we will explore 17 intriguing and unexpected facts about these remarkable structures. From their evolutionary history to their connection to certain medical conditions, you will gain a deeper understanding of the ampulla of the semicircular canals and its importance to human physiology. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of these amazing sensory organs and uncover some astonishing facts along the way!
Key Takeaways:
- The ampulla of semicircular canals is like a superhero for our balance and spatial awareness, using hair cells to send signals to the brain and help us stay steady on our feet.
- If the ampulla gets damaged, our brain can do some amazing tricks to compensate and keep us balanced, showing just how incredible our bodies are at adapting and healing.
Fascinating Origin and Function
The ampulla of the semicircular canals is a crucial part of the ear’s vestibular system, responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation.
Incredible Three-Dimensional Sensing
The ampulla of the semicircular canals plays a significant role in detecting rotational movements in three dimensions, allowing us to adapt to changes in our body position and maintain stability.
Unbelievable Hair Cells and Sensory Information
Inside the ampulla, specialized hair cells are responsible for converting the physical movement of fluid into electrical signals, providing vital sensory information to the brain.
Mind-Blowing Vestibulo-ocular Reflex
The ampulla of the semicircular canals is closely connected to the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which allows our eyes to move in an opposite direction to our head movements, ensuring clear vision during motion.
Surprising Neural Pathways
The sensory information from the ampulla travels through the vestibular nerve to the brainstem and cerebellum, where it is processed and integrated with other sensory inputs for maintaining balance and coordinating movements.
Extraordinary Semicircular Canal Orientation
The three semicircular canals in each ear are oriented at right angles to each other, enabling the detection of movements in all planes of space.
Amazing Fluid-filled Chambers
The ampulla of the semicircular canals contains fluid-filled chambers known as endolymph, which aids in transmitting the movements of the head and body to the hair cells.
Astonishing Differentiated Sensitivity
Each semicircular canal within the ampulla has varying sensitivity to specific head movements, allowing for precise detection of rotations in different directions.
Startling Vestibular Disorders
Disruptions or malfunctions in the ampulla of the semicircular canals can lead to vestibular disorders such as vertigo, dizziness, and impaired balance.
Remarkable Role in Spatial Awareness
The ampulla aids in providing crucial spatial awareness information to the brain, allowing us to navigate through our surroundings with accuracy and confidence.
Fascinating Ampulla Development
The ampulla of the semicircular canals develops during embryonic stages and undergoes maturation, contributing to the integration of the vestibular system in the later stages of fetal development.
Incredible Vestibular Compensation
If one ampulla is damaged or incapacitated, the brain can undergo a process called vestibular compensation, where it adapts to the loss by relying on the intact ampullae to maintain balance.
Unbelievable Ampulla Anatomy
The ampulla consists of a dilated region at the base of each semicircular canal, housing the sensory cells and specialized structures responsible for detecting fluid movement.
Mind-Blowing Ampulla Sensitivity
The hair cells within the ampulla are incredibly sensitive and can detect even the slightest movements and changes in rotational acceleration.
Surprising Role in Eye Movements
The information provided by the ampulla to the brain helps in controlling and coordinating eye movements, allowing us to focus on objects while in motion.
Extraordinary Ampulla Repair
If the ampulla of the semicircular canals becomes damaged or injured, it has the potential to regenerate and repair itself, restoring its function over time.
Amazing Evolutionary Significance
The ampulla of the semicircular canals is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation that has enabled organisms to navigate their environments successfully.
Conclusion
The Ampulla of semicircular canals is a fascinating structure in the human inner ear that plays a crucial role in our sense of balance and spatial orientation. It consists of three interconnected canals filled with fluid, which detect rotational movements of the head. While it is a relatively small and hidden part of our anatomy, the ampulla of semicircular canals is a vital component of our everyday functioning. By understanding its structure and function, we can appreciate the complexity and ingenuity of the human body.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of the Ampulla of semicircular canals?
The Ampulla of semicircular canals is responsible for detecting rotational movements of the head and providing vital information for our sense of balance.
2. How many Ampullae of semicircular canals are there?
There are three ampullae of semicircular canals in each ear, corresponding to the three main planes of movement: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal.
3. How does the fluid in the Ampulla of semicircular canals contribute to balance?
The fluid in the ampulla of semicircular canals moves in response to head movements, stimulating specialized hair cells that send signals to the brain, which helps us maintain our balance and spatial orientation.
4. Can issues with the Ampulla of semicircular canals cause dizziness?
Yes, disruptions in the functioning of the ampulla of semicircular canals can lead to vertigo and dizziness, as it affects our body’s ability to accurately perceive movement.
5. How can we take care of our Ampulla of semicircular canals?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive exposure to loud noises, and protecting the ears from injuries can all contribute to the overall well-being of the ampulla of semicircular canals.
Intrigued by inner ear marvels? Explore more secrets of the vestibular system, from the fascinating maculae of utricle and saccule to mastering balance on beams. Uncover intriguing facts about achieving equilibrium in everyday life.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
