Bone marrow, a soft, spongy tissue found inside the bones, is often referred to as the “hidden treasure” of the human body. While most people are familiar with its role in producing blood cells, bone marrow has many other extraordinary functions that often go unnoticed.
In this article, we will explore 14 fascinating facts about bone marrow that will not only expand your knowledge but also spark a sense of awe for the incredible complexities of the human anatomy. From its essential role in the immune system to its potential in treating diseases, bone marrow is truly a remarkable substance that deserves our attention. So, buckle up and prepare to dive into the mesmerizing world of bone marrow!
Key Takeaways:
- Bone marrow is like a superhero factory inside our bones, making blood cells and even immune cells to keep us healthy and strong.
- Donating bone marrow can save lives, and ongoing research is unlocking its potential for new treatments and cures.
Bone Marrow is Essential for Blood Cell Production
Bone marrow is a vital component of our body’s hematopoietic system, responsible for the production of blood cells. It serves as the primary site for hematopoiesis, where stem cells differentiate and mature into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
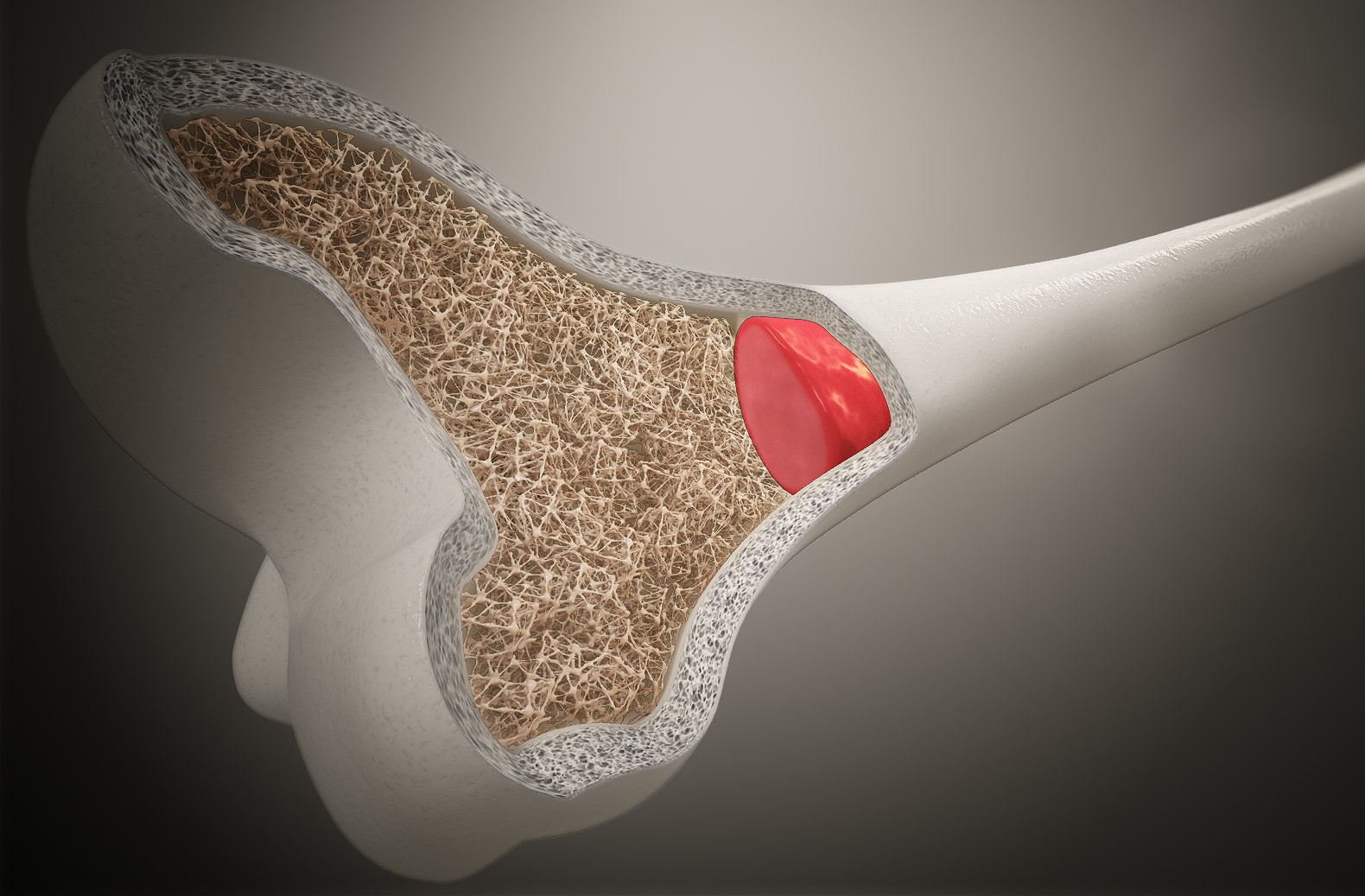
Bone Marrow Comes in Two Types
There are two types of bone marrow: red marrow and yellow marrow. Red marrow is responsible for creating new blood cells, while yellow marrow is composed mainly of fat cells. In adults, red marrow is found in the vertebrae, pelvic bones, sternum, and ribs, while yellow marrow is present in the long bones such as the femur and humerus.
Bone Marrow Transplantation is a Life-Saving Procedure
Bone marrow transplantation, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, is a medical procedure used to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy stem cells. It is a crucial treatment option for individuals with leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood-related disorders.
Bone Marrow Contains Mesenchymal Stem Cells
In addition to hematopoietic stem cells, bone marrow also houses a population of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. These cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. This makes bone marrow an essential source for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Bone Marrow Donors Save Lives
Donating bone marrow can be a life-saving act for patients with blood disorders. Through a process called peripheral blood stem cell donation or bone marrow aspiration, healthy individuals can provide stem cells to those in need. Joining a bone marrow registry can significantly increase the chances of finding a matching donor.
Leukemia Normally Originates in Bone Marrow
Leukemia, a cancer of the blood cells, often begins in the bone marrow. The abnormal production of white blood cells crowds out healthy cells, impairing the body’s ability to fight infections. Bone marrow biopsies are commonly performed to detect leukemia and determine the course of treatment.
Bone Marrow Has Immune Functions
Besides its role in blood cell production, bone marrow also plays a critical role in immune functions. It houses immune cells, such as lymphocytes, which are crucial for the body’s defense against infections and diseases.
Some Bone Marrow Disorders are Genetic
Certain bone marrow disorders, such as aplastic anemia and Fanconi anemia, have a genetic basis. These conditions affect the bone marrow’s ability to produce an adequate number of functional blood cells, leading to various health complications.
Bone Marrow Can Be Harvested for Research
Bone marrow can be collected for scientific research purposes. Scientists study bone marrow to gain insights into blood disorders, develop new treatments, and explore the potential of stem cells in regenerative medicine.
Bone Marrow Contains Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Hematopoietic stem cells are responsible for generating all blood cell types. These cells are found in high concentrations in bone marrow and have the ability to differentiate and replenish the blood cell supply throughout a person’s lifetime.
Bone Marrow Disorders Require Medical Intervention
Conditions such as myelodysplastic syndromes and multiple myeloma are examples of bone marrow disorders that require medical intervention. Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or bone marrow transplantation.
Bone Marrow Biopsies are Diagnostic Procedures
Bone marrow biopsies are commonly performed diagnostic procedures used to assess the health and functioning of the bone marrow. A small sample is obtained from the bone marrow, typically from the hip bone, and analyzed under a microscope to evaluate cell counts, morphology, and any abnormalities.
Bone Marrow Can be Obtained from Multiple Sources
In addition to bone marrow aspiration, bone marrow can also be extracted from the umbilical cord blood of newborns and from peripheral blood stem cells. These alternative sources provide valuable options for bone marrow transplantation.
Research is Ongoing to Unlock the Potential of Bone Marrow
Scientists continue to explore the potential applications of bone marrow in regenerative medicine, immune therapies, and innovative treatments for various diseases. Ongoing research aims to harness the extraordinary capabilities of bone marrow for the benefit of medical science and patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bone marrow is an extraordinary part of the human body that plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. It is responsible for producing blood cells, which are essential for carrying oxygen, fighting infections, and maintaining a strong immune system. Additionally, bone marrow contains valuable stem cells that have the potential to treat a variety of diseases and conditions.Understanding the importance of bone marrow and its functions can help us appreciate the complexity of our bodies and inspire us to take steps to maintain our bone marrow health. From eating a nutritious diet to engaging in regular exercise, there are various ways we can support and nourish our bone marrow.Next time you marvel at the intricate workings of the human body, remember the remarkable capabilities of bone marrow and its role in keeping us alive and thriving.
FAQs
1. What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue found inside our bones. It is responsible for producing blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
2. How does bone marrow produce blood cells?
Bone marrow contains specialized cells called hematopoietic stem cells. These cells have the unique ability to divide and differentiate into different types of blood cells. Through a process called hematopoiesis, these stem cells give rise to red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
3. What is the role of bone marrow in the immune system?
Bone marrow plays a vital role in the immune system by producing white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting infections and diseases. These immune cells help protect the body against harmful pathogens and maintain overall health.
4. Can bone marrow be used for medical treatments?
Yes, bone marrow contains valuable stem cells that can be used for various medical treatments. Stem cell transplantation is a common procedure that involves replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells to treat conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and certain genetic disorders.
5. How can I support bone marrow health?
A healthy lifestyle can support bone marrow health. Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients, regularly exercising, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking can help maintain the overall health and function of bone marrow.
6. Can bone marrow diseases be prevented?
While some bone marrow diseases may be genetic or unavoidable, adopting a healthy lifestyle and following medical guidelines can reduce the risk of developing certain bone marrow disorders. Regular check-ups and early detection can also help in effective management and treatment.
Bone marrow plays a vital role in our bodies, but there's still much to learn about this fascinating tissue. If you're curious about related topics, consider reading more about leukemia-facts/">leukemia, a cancer that often starts in the bone marrow. You might also find interesting facts about the femur, the longest bone in the human body, which contains a significant amount of marrow. Exploring these subjects can help you gain a deeper understanding of how our bodies work and the importance of ongoing medical research.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
