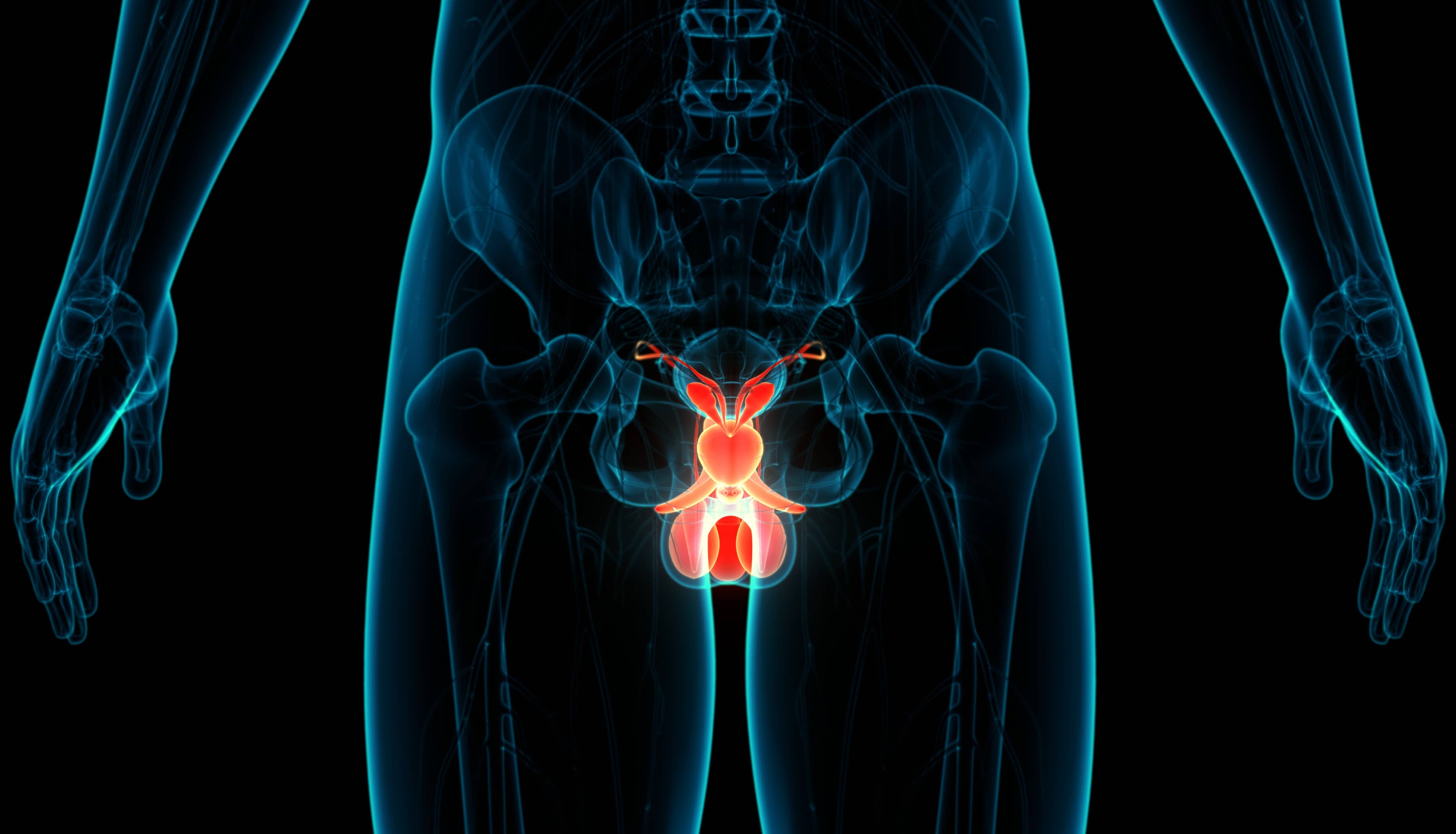
The testicles, also known as testes, are a vital part of the male reproductive system. These small, egg-shaped organs are responsible for producing sperm and testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. Despite their significance, testicles are often overlooked in discussions about men's health. In this article, we will explore 19 fascinating facts about testicles that shed light on their crucial role in the male body. From their development and function to common health concerns, understanding these facts can provide valuable insights into men's reproductive health and overall well-being. So, let's delve into the intriguing world of testicles and uncover some surprising truths about these often underappreciated organs.
Key Takeaways:
- Testicles are responsible for sperm production and the male sex hormone, testosterone, which is crucial for male reproductive development and characteristics.
- The scrotum’s unique design helps maintain the testes at the right temperature for healthy sperm production, and regular self-exams are important for detecting any abnormalities.
Testicles are responsible for producing the male sex hormone, testosterone.
These two small, egg-shaped organs, also known as testes, play a crucial role in the male reproductive system. They are responsible for producing sperm and the male sex hormone, testosterone, which is vital for the development of male reproductive tissues and characteristics.
Testicles are located outside the body for a specific reason.
Unlike most internal organs, the testicles are situated outside the body in the scrotum. This positioning helps maintain the testes at a slightly lower temperature than the rest of the body, which is essential for healthy sperm production. The scrotum adjusts to keep the testes at an optimal temperature, contracting in cold conditions to retain heat and relaxing in warmer environments to prevent overheating.
Each testicle is approximately the size of a large olive.
Despite their significant role in the male reproductive system, the average size of each testicle is only about 4-5 centimeters in length and 2-3 centimeters in width, similar to a large-sized olive. However, it’s important to note that there can be natural variations in size among individuals.
The left testicle typically hangs lower than the right.
It’s common for one testicle to hang lower than the other, and in most males, the left testicle is positioned slightly lower than the right. This asymmetry is completely normal and doesn’t affect testicular function.
Testicles are protected by a tough, sensitive covering called the scrotum.
The scrotum acts as a protective layer for the testes, shielding them from potential injuries while also providing sensitivity to temperature changes. This unique structure helps safeguard the delicate testicles from external harm.
The testicles are connected to the rest of the body through the spermatic cord.
The spermatic cord contains blood vessels, nerves, the vas deferens, and other components that link the testicles to the body. It plays a crucial role in facilitating the transport of sperm and blood to and from the testes.
Testicles develop inside the abdomen before birth.
During the fetal stage, the testicles form within the abdomen and gradually descend into the scrotum before birth. In some cases, one or both testicles may not descend properly, requiring medical attention to prevent potential complications.
Testicles can vary in weight.
While the average combined weight of both testicles is around 20-25 grams, individual testicles can differ in weight. However, significant deviations in weight may indicate underlying health issues and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Testicles have a network of coiled tubes where sperm is produced.
Inside the testicles, there are numerous coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules, which are responsible for producing and transporting sperm. This intricate network is fundamental to the process of sperm development.
Testicles can be affected by various medical conditions.
Several conditions, such as testicular cancer, epididymitis, varicocele, and testicular torsion, can impact the health and function of the testicles. It’s essential to be aware of these potential issues and seek prompt medical attention if any abnormalities or discomfort are noticed.
Testicles undergo changes during puberty.
Puberty triggers significant changes in the testicles, leading to the production of sperm and the release of testosterone. These transformations are a natural part of male development and are essential for reproductive maturity.
Testicles are sensitive to impact and injury.
Due to their delicate nature, testicles are vulnerable to injury from direct impacts or trauma. Wearing protective gear during sports and physical activities can help reduce the risk of testicular injuries.
Testicles play a role in sexual function.
Aside from sperm production, the testicles also contribute to sexual function by producing testosterone, which influences libido, erectile function, and secondary sexual characteristics in males.
Testicles can experience discomfort due to overheating.
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as hot baths or saunas, can temporarily affect sperm production by raising the temperature of the testicles. However, this is usually a temporary issue, and the testicles typically return to normal function once they cool down.
Testicles have a self-regulating mechanism for temperature control.
The testicles have a built-in mechanism to regulate their temperature, allowing them to adjust to environmental changes. This self-regulating function helps maintain an optimal environment for sperm production and overall testicular health.
Testicles can be examined for signs of abnormalities.
Regular testicular self-exams are recommended to check for any lumps, swelling, or changes in the testicles, as these could be early indicators of potential health issues. Early detection and prompt medical attention are crucial for addressing any concerns related to testicular health.
Testicles have a rich blood supply.
The testicles receive a significant blood supply, which is essential for providing oxygen and nutrients to support sperm production and overall testicular function. This intricate network of blood vessels plays a vital role in maintaining testicular health.
Testicles can be affected by hormonal imbalances.
Imbalances in hormone levels, particularly testosterone, can impact testicular function and reproductive health. It’s important to address any hormonal irregularities through medical evaluation and appropriate treatment, if necessary.
Testicles are a key component of the male reproductive system.
Overall, the testicles are a critical part of the male reproductive system, contributing to fertility, sexual function, and hormone production. Understanding the importance of testicular health and being aware of potential issues can help promote overall well-being and reproductive wellness.
Conclusion
Testicles are a crucial and fascinating part of the male reproductive system. They play a vital role in hormone production and sperm development, and their health is essential for overall well-being. Understanding the functions and facts about testicles can lead to better awareness and care for this often overlooked part of the body. From their unique anatomy to their role in fertility, testicles are truly remarkable organs that deserve attention and proper maintenance. By learning more about testicles, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure their reproductive health and overall quality of life.
FAQs
Q: What is the average size of adult testicles?
A: The average size of adult testicles is approximately 2 inches in length and 1 inch in width.
Q: Can testicles be affected by certain medical conditions?
A: Yes, testicles can be affected by various medical conditions such as testicular cancer, epididymitis, and testicular torsion.
Q: Do testicles have any other functions besides sperm production?
A: Yes, testicles are also responsible for producing testosterone, the primary male sex hormone.
Q: Can injuries to the testicles impact fertility?
A: Yes, injuries to the testicles can potentially impact fertility, depending on the severity of the injury.
Q: What are some common signs of testicular problems that should not be ignored?
A: Common signs of testicular problems include pain, swelling, lumps, and changes in size or texture of the testicles.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
