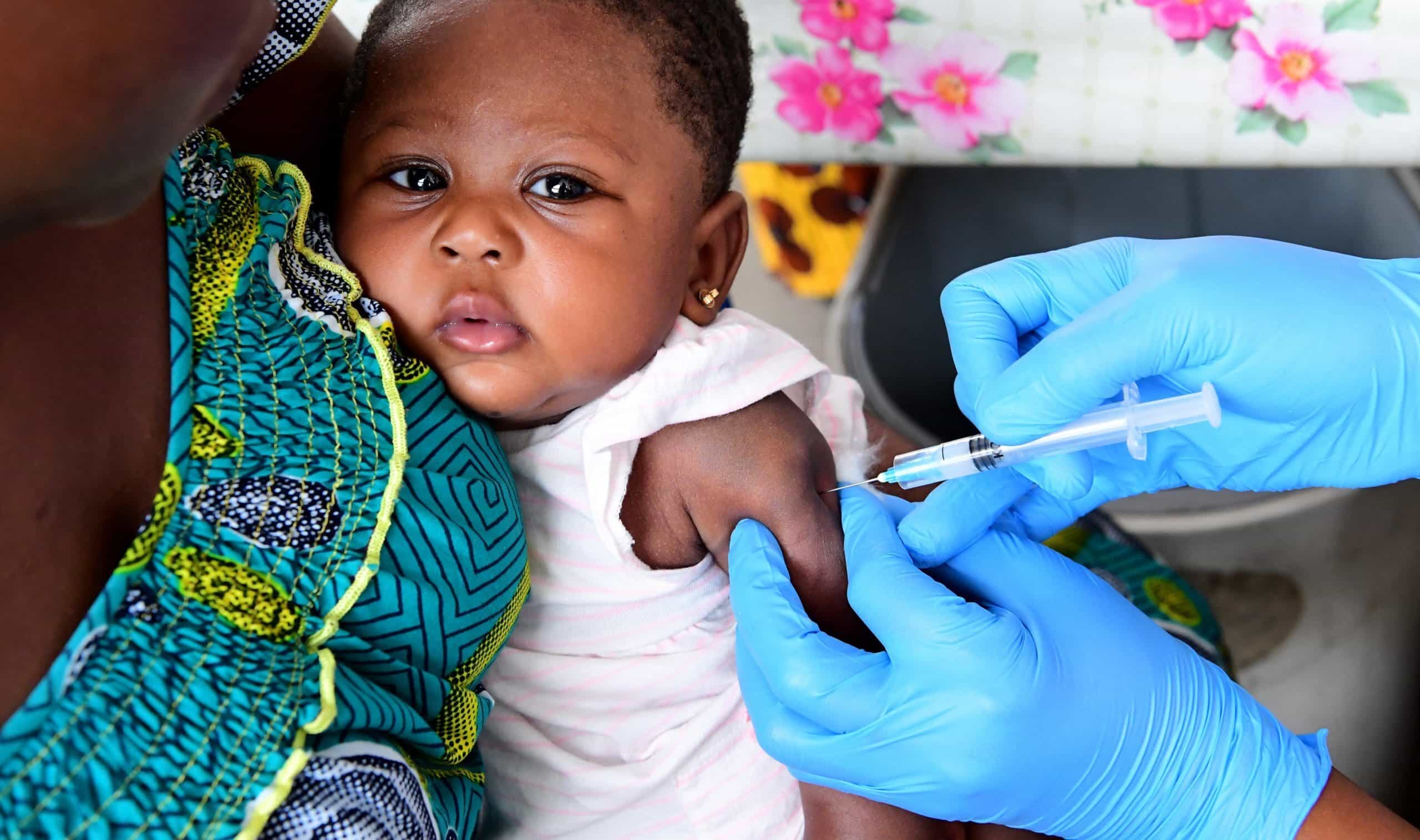
Immunization, also known as vaccination, is a critical aspect of public health that helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases. By stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight off specific pathogens, vaccines have saved countless lives and played a crucial role in eradicating deadly diseases. While most people are familiar with the concept of immunization, there are several surprising facts that are often overlooked. From the history of vaccines to their impact on global health, this article will explore 19 intriguing and lesser-known facts about immunization. Whether you’re a staunch advocate or simply curious about the subject, prepare to be enlightened and amazed by the remarkable world of immunization.
Key Takeaways:
- Vaccines save millions of lives and are rigorously tested for safety. They also protect against more than just infectious diseases, like cancer, and are a cost-effective health intervention.
- Immunization is a lifelong commitment, from infancy to old age. It helps prevent the spread of diseases, reduces hospitalization rates, and is not just for children.
Vaccines save millions of lives every year.
Immunization is a critical tool in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and has been proven to save millions of lives globally.
Immunization can prevent up to 3 million deaths annually.
By protecting individuals from deadly diseases such as measles, polio, and influenza, vaccines play a crucial role in reducing mortality rates worldwide.
Vaccines are rigorously tested for safety and efficacy.
Before being approved for public use, vaccines undergo extensive testing and evaluation to ensure their safety and effectiveness in preventing targeted diseases.
Immunization is one of the most cost-effective health interventions.
Investing in immunization programs not only saves lives but also offers significant economic benefits by reducing healthcare costs and improving productivity.
Vaccines can protect against more than just infectious diseases.
Immunization can also provide protection against certain types of cancer, such as cervical and liver cancer, through vaccines like the HPV and hepatitis B vaccines.
Vaccines work by stimulating the body’s immune response.
When we receive a vaccine, it prompts our immune system to recognize and remember specific pathogens, equipping our bodies with the tools to fight off future infections.
Immunization helps maintain herd immunity.
By vaccinating a significant portion of the population, we can create herd immunity, which limits the spread of diseases and protects vulnerable individuals who cannot be vaccinated.
Vaccines have virtually eradicated diseases.
Thanks to widespread immunization efforts, diseases like smallpox have been eradicated, and others, such as polio and measles, are on the verge of elimination in many parts of the world.
Immunization can be life-saving for newborns and infants.
Infants are particularly vulnerable to infectious diseases, but with timely immunization, we can protect them from serious illnesses and potentially fatal complications.
Vaccines undergo rigorous surveillance even after approval.
Once vaccines are approved, systems are in place to monitor their safety and effectiveness continuously, ensuring ongoing protection for those who receive them.
Immunization programs require collaboration and coordination.
Successful immunization initiatives involve partnerships between healthcare providers, governments, communities, and international organizations to ensure access to vaccines and proper delivery.
Vaccines can help prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
By reducing the incidence of certain infectious diseases, immunization can help decrease the overuse of antibiotics, which contributes to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Immunization campaigns can reach remote and marginalized populations.
Efforts are made to ensure that even the most vulnerable populations, including those living in remote areas or facing social and economic challenges, have access to life-saving vaccines.
Vaccines have a long history of success.
Immunization dates back centuries, and the continued use of vaccines has led to significant reductions in the prevalence and impact of numerous infectious diseases.
Immunization can reduce hospitalization rates.
Vaccines help prevent severe illness and complications, leading to a decrease in hospital admissions and the burden on healthcare systems.
Vaccines are not just for children.
While childhood immunization is crucial, vaccines are also available for adults to protect against illnesses such as influenza, pneumonia, and shingles.
Immunization programs are tailored to specific regions and populations.
Efforts are made to understand the local disease burden and tailor vaccination programs to meet the specific needs of different regions and populations.
Vaccines have an excellent safety record.
The overwhelming majority of vaccine administrations result in minor and temporary side effects, with serious adverse events being extremely rare.
Immunization is a lifelong commitment.
From infancy to old age, maintaining immunization throughout our lives ensures that we continue to receive protection against diseases and contribute to the overall health of our communities.
Immunization is a critical aspect of public health, and by knowing these surprising facts about immunization, we can appreciate the importance of vaccines in preventing disease and promoting well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, immunization is a crucial aspect of public health that has had a significant impact on reducing the burden of infectious diseases. Through vaccination, individuals develop immunity to specific diseases, providing protection not only for themselves but also for the community as a whole. Immunization has been proven to be safe and effective, and it continues to save millions of lives worldwide.It is important to stay informed about immunization and address any concerns or misconceptions that may arise. By understanding the facts and benefits of immunization, we can make informed decisions to protect ourselves and our loved ones. Vaccines have played a vital role in preventing the spread of diseases and have been instrumental in eradicating or significantly reducing the incidence of many deadly illnesses.By ensuring that both children and adults are up to date with the recommended immunizations, we can contribute to a healthier and safer society. Let us embrace the power of immunization and work together towards a world with fewer preventable diseases.
FAQs
1. Are vaccines safe?
Yes, vaccines are rigorously tested for safety before being approved for use. The benefits of vaccines far outweigh the risks. Serious side effects are extremely rare.
2. Can vaccines cause autism?
No. Extensive research has shown no link between vaccines and autism. Multiple studies have debunked this myth.
3. Do vaccines provide lifelong immunity?
Some vaccines provide long-lasting protection, while others may require booster shots. It is important to follow the recommended vaccination schedule to maintain immunity.
4. Can vaccines make you sick?
Vaccines stimulate the immune system to produce an immune response, which may result in mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site. This is a normal response and a sign that the vaccine is working.
5. Why are vaccines necessary if the diseases they prevent are rare?
Vaccines prevent diseases from re-emerging by maintaining community immunity. Even if a disease is rare, outbreaks can still occur if enough people are left unvaccinated.
6. Can adults benefit from vaccines?
Absolutely. Vaccines are not just for children. Adults can benefit from various vaccinations, including influenza, pneumococcal, and hepatitis vaccines, among others.
7. Can vaccines be given to pregnant women?
Yes, certain vaccines are safe and even recommended for pregnant women to protect both the mother and the developing baby. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine which vaccines are appropriate.
8. Can individuals with allergies receive vaccines?
In most cases, individuals with allergies can receive vaccines. Vaccine providers are trained to manage allergies and provide necessary precautions.
9. Can vaccines cause serious side effects?
Serious side effects are extremely rare. Vaccines are closely monitored for safety, and any potential side effects are thoroughly investigated.
10. Can vaccines prevent all diseases?
Vaccines are highly effective in preventing many infectious diseases. However, they may not provide 100% protection in all cases. It is still important to practice good hygiene and follow other preventive measures.
Immunization is a powerful tool in the fight against disease, but there's still much to learn. Curious about how your body develops active immunity or the intricacies of cellular immunity? Want to explore the enigmatic world of immune memory? Keep reading to unravel more surprising facts and deepen your understanding of the incredible immune system.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


