Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) play a crucial role in the body’s immune response, yet they often remain a mysterious component for many. These remarkable cells function as the key mediators between the innate and adaptive immune systems, allowing the body to effectively recognize and combat pathogens and foreign substances.
In this article, we will explore 18 surprising facts about antigen-presenting cells that will shed light on their fascinating characteristics and functions. From their diverse types and locations in the body to their specialized mechanisms of antigen presentation and activation of immune responses, APCs are truly remarkable players in the complex orchestra of the immune system.
So, get ready to dive into the world of antigen-presenting cells and uncover some fascinating insights about these often-overlooked immune cells.
Key Takeaways:
- Antigen-Presenting Cells are like superheroes of the immune system, capturing and presenting antigens to activate T cells, essential for fighting off infections and diseases.
- These versatile cells have unique functions, from preventing autoimmunity to being potential allies in cancer treatment. They continue to surprise scientists and hold promise for future therapies.
Antigen-Presenting Cells are essential components of the immune system
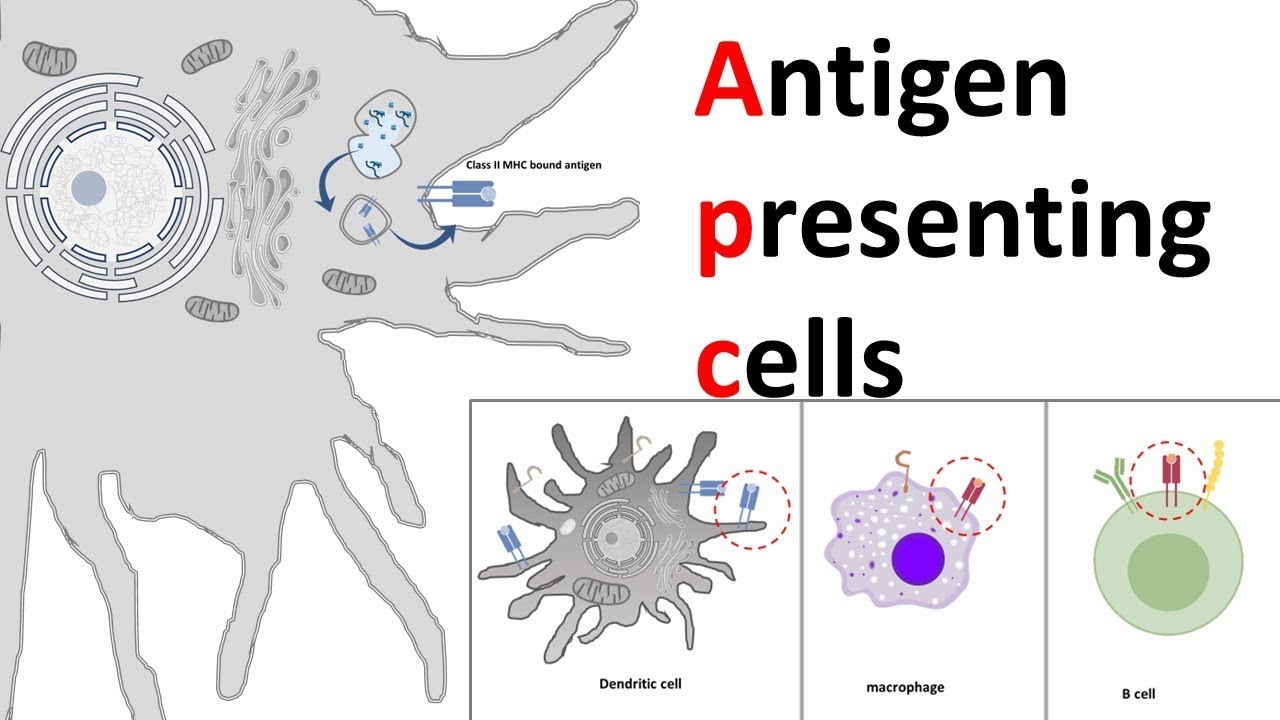
Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs) play a crucial role in the immune response by capturing, processing, and presenting antigens to T cells.
There are three major types of Antigen-Presenting Cells
The three main types of APCs are dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. Each type has its own unique properties and functions within the immune system.
Dendritic cells are the most potent APCs
Dendritic cells are highly specialized in capturing antigens and initiating immune responses. They are considered the most efficient APCs in activating T cells.
Antigen-Presenting Cells can be found throughout the body
APCs are distributed in various tissues and organs, including the skin, lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosal surfaces. This allows them to efficiently encounter antigens and trigger immune responses.
Macrophages are versatile Antigen-Presenting Cells
Macrophages not only present antigens but also play a critical role in phagocytosis, cytokine production, and tissue homeostasis. They are key players in both innate and adaptive immune responses.
B cells have a unique role as Antigen-Presenting Cells
B cells not only produce antibodies but also have the ability to present antigens to T cells. This dual functionality allows B cells to effectively participate in both the humoral and cellular immune responses.
Antigen-Presenting Cells have specialized receptors for antigen uptake
APCs express various receptors for recognizing and binding antigens, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), scavenger receptors, and Fc receptors. These receptors facilitate antigen uptake and subsequent presentation to T cells.
Antigen-Presenting Cells play a crucial role in immune tolerance
APCs are involved in maintaining immune tolerance to self-antigens and preventing autoimmunity. They help educate T cells to distinguish between self and foreign antigens, preventing inappropriate immune responses.
Antigen-Presenting Cells can activate naive T cells
APCs present antigens to naive T cells, leading to their activation and differentiation into effector T cells. This process is essential for mounting an effective immune response against pathogens.
Antigen-Presenting Cells have specialized structures for antigen presentation
Dendritic cells possess long extensions called dendrites, which increase their surface area for capturing antigens. This unique structural feature enhances their ability to present antigens to T cells.
Antigen-Presenting Cells can migrate to lymphoid organs
After capturing antigens, APCs can migrate to lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and the spleen, where they present antigens to T cells and initiate immune responses.
Antigen-Presenting Cells interact with helper and cytotoxic T cells
APCs present antigens to both helper T cells (CD4+) and cytotoxic T cells (CD8+). This interaction is crucial for orchestrating an efficient immune response against pathogens.
Antigen-Presenting Cells can activate memory T cells
APCs also play a role in activating memory T cells upon re-exposure to previously encountered antigens. This leads to a faster and more effective immune response during secondary infections.
Antigen-Presenting Cells can be hijacked by pathogens
Some pathogens have evolved mechanisms to exploit APCs or interfere with their antigen presentation function. This evasion strategy allows pathogens to evade immune recognition and establish infections.
Antigen-Presenting Cells are involved in cancer immunotherapy
Researchers are exploring ways to harness the power of APCs in cancer immunotherapy. By modulating antigen presentation and immune responses, APC-based therapies show promise in the fight against cancer.
Antigen-Presenting Cells can induce immune tolerance
In certain contexts, APCs also have the ability to induce immune tolerance, suppressing immune responses and preventing excessive inflammation or autoimmunity.
Antigen-Presenting Cells are influenced by the microenvironment
The microenvironment, including cytokines and chemokines, can impact the function and behavior of APCs. This dynamic interaction plays a role in shaping the immune response.
Antigen-Presenting Cells are a subject of ongoing research
Scientists continue to explore the fascinating world of APCs, uncovering new insights into their roles, functions, and potential therapeutic applications. The study of APCs remains a vibrant and active field in immunology research.
Overall, the 18 Surprising Facts About Antigen-Presenting Cells highlight the significance of these cells in immune responses, their diverse functions, and their potential in therapeutic interventions. Understanding the crucial role of APCs contributes to our knowledge of the immune system and aids in the development of novel strategies for combating diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, antigen-presenting cells (APCs) play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells. These specialized cells are responsible for initiating and regulating immune reactions, ensuring that the body can eliminate harmful pathogens and maintain overall health. Throughout this article, we have explored 18 surprising facts about antigen-presenting cells. We learned about the different types of APCs, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, as well as their unique characteristics and functions. We discovered how APCs capture, process, and present antigens to T cells, initiating an immune response. Furthermore, we delved into the various receptors and molecules involved in APC function, including major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs), Toll-like receptors (TLRs), and co-stimulatory molecules. We also discussed the importance of APCs in immune regulation and their involvement in various diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders. Understanding the intricate workings of antigen-presenting cells is crucial for unraveling the complexities of the immune system and developing targeted therapies. With further research, we can uncover more exciting discoveries and advancements in this field, leading to improved treatments and a better understanding of immunological processes.
FAQs
1. What are antigen-presenting cells (APCs)?
Antigen-presenting cells are specialized cells of the immune system responsible for capturing, processing, and presenting antigens to T cells, thus initiating an immune response.
2. What are the different types of APCs?
The main types of APCs are dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. Each type has specific functions and locations within the body.
3. How do APCs capture antigens?
APCs capture antigens through various mechanisms, such as phagocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis.
4. How do APCs present antigens to T cells?
APCs present antigens to T cells by displaying them on their cell surface using major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
5. What is the role of co-stimulatory molecules in APC function?
Co-stimulatory molecules expressed on APCs provide essential signals to T cells, ensuring the activation and proliferation of T cells during an immune response.
6. Can APCs play a role in cancer and autoimmune disorders?
Yes, dysregulation of APC function can contribute to the development of cancer or autoimmune disorders. Understanding APCs’ role in these conditions can help develop targeted therapies.
7. Are all APCs located in the lymph nodes?
No, while lymph nodes are a common location, APCs can be found in various tissues throughout the body, including the skin, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract.
8. How do APCs contribute to immunological memory?
APCs play a crucial role in generating immunological memory by presenting antigens to naïve T cells, leading to the formation of memory T cells that provide long-term protection against future infections.
9. Can APCs present self-antigens?
Yes, APCs can present self-antigens, which is essential for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune responses.
10. Are all cells capable of antigen presentation?
No, only specialized APCs have the ability to efficiently capture, process, and present antigens to T cells. Other cells, such as red blood cells or muscle cells, do not possess this capability.
Antigen-presenting cells are vital for immune function, but their roles extend beyond what's covered here. Delve into the groundbreaking work of Dr. Ralph Steinman, whose research on dendritic cells revolutionized our understanding of the immune system. B cells also play a unique part as antigen-presenting cells, contributing to the immune response in fascinating ways. Explore more captivating facts about the immune system and its intricate workings, as we continue to unravel its mysteries through ongoing research and discovery.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
