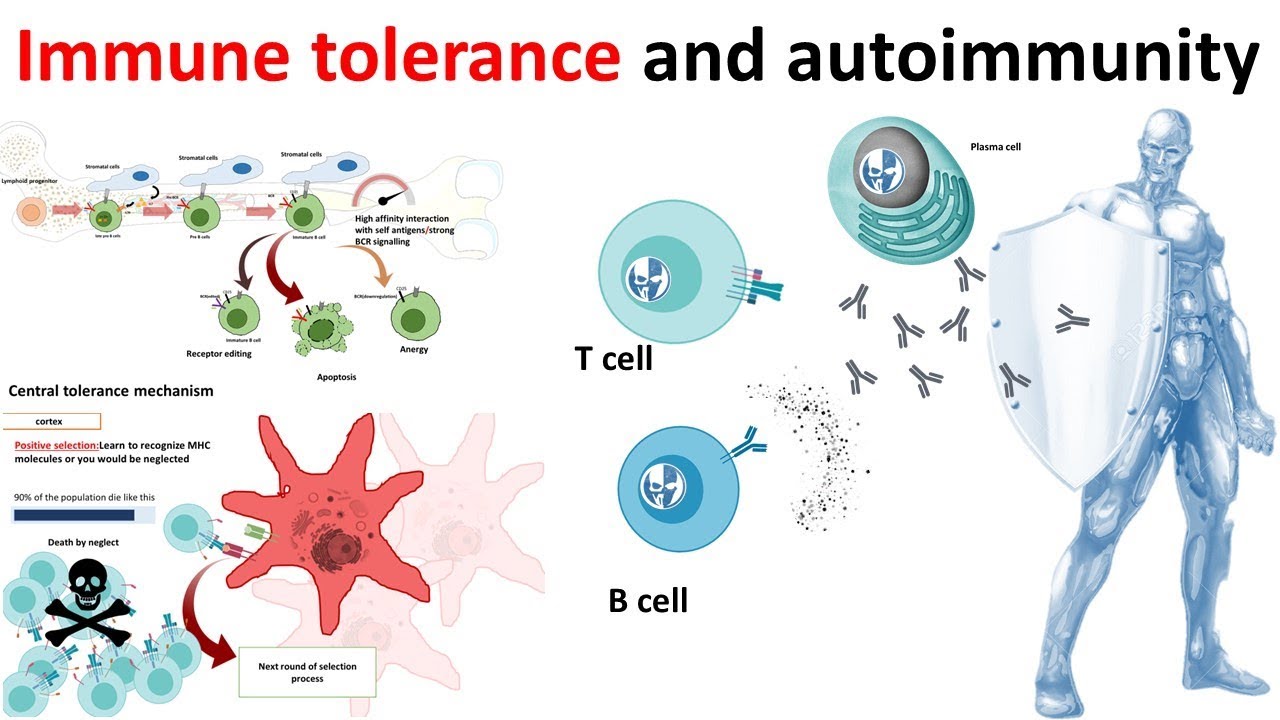
Immune tolerance is a fascinating and essential concept within the field of biology. Our immune system is a powerful defense mechanism that protects our bodies from harmful pathogens and foreign substances. However, in certain situations, the immune system needs to display tolerance towards certain entities, such as self-antigens or commensal microorganisms. This phenomenon, known as immune tolerance, ensures that our immune system does not attack our own cells and tissues, allowing for a healthy and well-functioning body.
In this article, we will delve into the realm of immune tolerance and explore 13 unbelievable facts that highlight the complexity and ingenuity of our immune system. From the mechanisms by which immune tolerance is established to the consequences of its breakdown, we will uncover intriguing insights that will deepen your understanding of this crucial aspect of our biological defense system.
Key Takeaways:
- Our immune system can tell the difference between friend and foe, helping to keep us healthy and prevent autoimmune diseases.
- Scientists are exploring ways to harness immune tolerance to improve treatments for diseases and organ transplants, offering hope for the future of medicine.
The immune system can distinguish between self and non-self.
One of the most remarkable aspects of immune tolerance is the ability of our immune cells to distinguish between the body’s own cells and foreign invaders. This discrimination is crucial for maintaining normal bodily functions and preventing autoimmune diseases.
Tolerance is established during early development.
Immune tolerance is primarily established during fetal development and early childhood. This process involves the education and training of immune cells to recognize self-antigens and not mount an immune response against them.
Peripheral tolerance mechanisms exist to maintain self-tolerance.
Even after early development, the body has mechanisms in place to maintain self-tolerance. These mechanisms include regulatory T cells and cells that promote immune suppression, preventing the immune system from attacking healthy tissues.
Immune tolerance helps prevent autoimmunity.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. Immune tolerance plays a crucial role in preventing the development of these diseases by ensuring that the immune system does not target self-antigens.
Tolerance can be disrupted, leading to autoimmune disorders.
In some cases, immune tolerance mechanisms can fail, leading to the development of autoimmune disorders. These conditions arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, causing chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Oral tolerance is a unique form of immune tolerance.
Oral tolerance is a phenomenon where the immune system becomes tolerant to substances encountered through the oral route, such as food antigens. This mechanism prevents an excessive immune response to harmless dietary components.
Maternal-fetal tolerance is crucial for a successful pregnancy.
The immune system’s ability to tolerate the fetus is critical for a successful pregnancy. The maternal immune system undergoes changes to ensure that it does not attack the developing fetus, allowing for a healthy pregnancy.
Tolerance can be induced in the laboratory.
Scientists have found ways to induce immune tolerance in the laboratory setting. This has the potential to revolutionize treatments for autoimmune diseases and organ transplantation by suppressing unwanted immune responses.
Immune tolerance can be beneficial in organ transplantation.
Organ transplantation often faces the challenge of immune rejection. Immune tolerance strategies can help promote the acceptance of transplanted organs, reducing the need for immunosuppressive drugs and improving patient outcomes.
Tolerance to allergens can be developed.
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances. However, it is possible to induce tolerance to allergens through immunotherapy, gradually exposing the immune system to increasing amounts of the allergen to build tolerance and reduce symptoms.
Tolerance is dynamic and can change over time.
Immune tolerance is not static and can be influenced by various factors. Environmental factors, infections, and genetic predispositions can all impact the balance of tolerance in the immune system.
Autoimmune diseases can have periods of remission and flare-ups.
Autoimmune diseases are often characterized by periods of remission where symptoms are minimal or absent, followed by flare-ups with increased disease activity. The fluctuations in disease severity can be influenced by the state of immune tolerance.
Research on immune tolerance is advancing therapeutic possibilities.
Advancements in understanding immune tolerance have opened up new avenues for the development of novel therapeutics. Scientists are exploring innovative approaches to modulate immune tolerance, aiming to improve treatment options for autoimmune diseases and other immune-related conditions.
These 13 unbelievable facts about immune tolerance highlight the intricacies and importance of this fundamental biological process. Understanding immune tolerance is crucial for improving our knowledge of immune-related diseases and developing innovative therapeutic strategies in the future.
Conclusion
Immune tolerance is a fascinating and complex phenomenon that has significant implications for our understanding of the immune system. These 13 unbelievable facts about immune tolerance shed light on the remarkable ways in which our bodies maintain balance and prevent autoimmune diseases.
From the ability of the immune system to distinguish self from non-self to the role of regulatory T cells in preventing harmful immune responses, immune tolerance plays a vital role in maintaining our health and well-being. The incredible mechanisms by which immune tolerance is achieved, such as clonal deletion and anergy, highlight the intricacies of our immune system.
Understanding immune tolerance can also pave the way for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases. By harnessing the fascinating properties of immune tolerance, researchers and scientists are exploring ways to modulate immune responses and restore balance in the immune system.
In summary, immune tolerance is a captivating area of study that continues to unravel the mysteries of our immune system. The more we learn about immune tolerance, the closer we get to developing innovative treatments and interventions that can improve the lives of millions of individuals affected by autoimmune disorders.
FAQs
1. What is immune tolerance?
Immune tolerance refers to the ability of the immune system to recognize and tolerate self-antigens while mounting an appropriate immune response against foreign antigens.
2. How is immune tolerance maintained?
Immune tolerance is maintained through various mechanisms, such as clonal deletion, anergy, immune privilege, and the action of regulatory T cells.
3. What are regulatory T cells?
Regulatory T cells, also known as Tregs, are a specialized subset of T cells that play a crucial role in maintaining immune tolerance by suppressing excessive immune responses and preventing autoimmune diseases.
4. What is clonal deletion?
Clonal deletion is a process in which immature self-reactive B and T cells are eliminated during development to prevent the production of harmful antibodies or immune responses against self-antigens.
5. Can immune tolerance be disrupted?
Yes, immune tolerance can be disrupted, leading to the development of autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the body’s own tissues and cells.
6. Are there genetic factors involved in immune tolerance?
Yes, genetic factors can contribute to immune tolerance. Certain genes and genetic variations have been associated with an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases.
7. Can immune tolerance be induced?
Yes, immune tolerance can be induced through various therapeutic approaches, such as antigen-specific immunotherapy and the administration of regulatory T cells.
8. How does immune tolerance impact organ transplantation?
Immune tolerance plays a critical role in organ transplantation. Achieving immune tolerance can minimize the risk of rejection and improve the long-term success of the transplant.
9. Are there any natural substances that can enhance immune tolerance?
While further research is needed, certain natural substances, such as curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids, have shown potential in modulating immune responses and promoting immune tolerance.
10. Can immune tolerance be targeted for the treatment of autoimmune diseases?
Efforts are underway to develop therapies that specifically target immune tolerance pathways to treat autoimmune diseases. These approaches aim to restore balance and prevent the destructive immune responses associated with these conditions.
11. Can stress affect immune tolerance?
Chronic stress has been shown to impact immune function and potentially disrupt immune tolerance. Managing stress levels is important for maintaining overall immune health.
12. Is immune tolerance only relevant to humans?
No, immune tolerance is a fundamental aspect of the immune system in various organisms, including other mammals, birds, reptiles, and even invertebrates.
13. What are the future perspectives in immune tolerance research?
The future of immune tolerance research holds promise for the development of novel therapies, personalized medicine approaches, and a deeper understanding of the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in immune-related disorders.
Immune tolerance is a fascinating aspect of our immune system, but it's just the tip of the iceberg. Dive deeper into the world of autoimmunity and discover 13 astonishing facts that will leave you in awe. If you're curious about how doctors manage overactive immune responses, explore the intriguing realm of immunosuppressants and uncover six essential facts you must know. Embark on a journey through the complex and captivating world of our immune system, where every turn reveals new wonders and surprises.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


