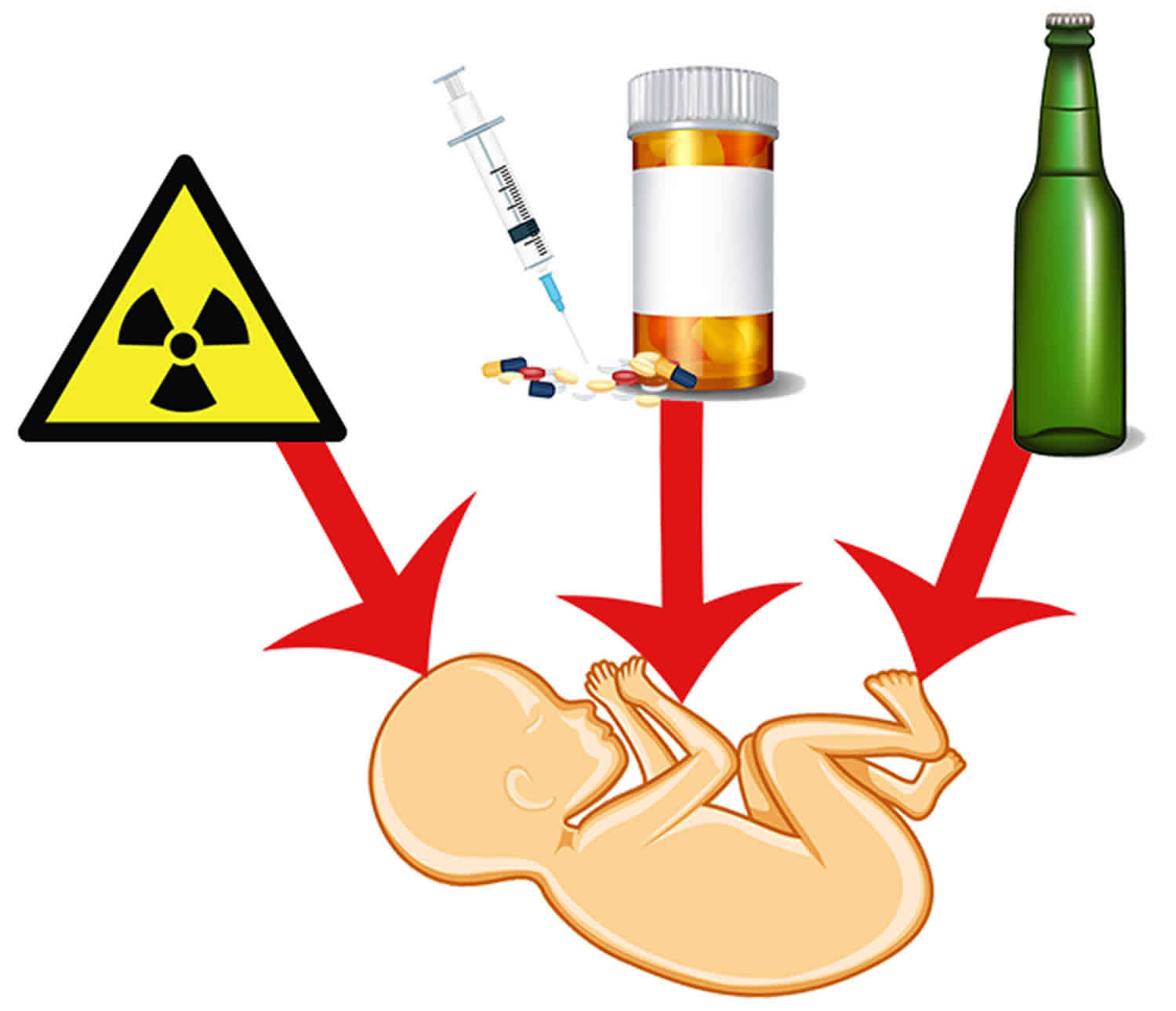
Teratogens are substances that can cause abnormal development in embryos or fetuses, leading to the formation of physical or cognitive birth defects. These harmful agents can be found in various forms, such as chemicals, medications, radiation, infections, or even maternal behaviors. Understanding the impact of teratogens is crucial in safeguarding the health and well-being of expectant mothers and their unborn babies.
In this article, we will explore nine astounding facts about teratogens. From their types and sources to the potential effects they can have on embryonic development, we will delve into the fascinating world of teratology. So, if you’re curious to learn more about the dangers of teratogens and how they can influence prenatal development, strap in and get ready for an enlightening journey!
Key Takeaways:
- Teratogens are substances that can harm a developing baby, causing birth defects. They can be found in everyday items, so it’s important for expectant mothers to avoid them and seek prenatal care.
- Exposure to teratogens at different stages of pregnancy can lead to a wide range of birth defects. Prevention is key, so expectant mothers should maintain a healthy lifestyle and avoid harmful substances.
Teratogens are substances that can cause birth defects.
Teratogens refer to any environmental agent that can interfere with the development of an embryo or fetus, leading to abnormalities or malformations. These substances can include chemicals, drugs, infections, and even certain maternal behaviors. The impact of teratogens can vary depending on the timing, duration, and dosage of exposure.
Teratogens can affect the developing baby during different stages of pregnancy.
The effects of teratogens can vary depending on when exposure occurs. Certain teratogens may have a greater impact during specific stages of development. For example, exposure to alcohol during the first trimester can lead to facial abnormalities and organ damage, while exposure to certain infections during the third trimester can result in developmental delays.
Common teratogens include alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications.
Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can cause fetal alcohol syndrome, which can result in physical, behavioral, and cognitive impairments. Smoking tobacco increases the risk of low birth weight and respiratory problems in newborns. Additionally, certain medications, such as certain acne medications or anticonvulsants, can pose risks to developing babies.
Teratogens can cause a wide range of birth defects.
Birth defects caused by teratogens can affect various body systems, including the heart, brain, limbs, and sensory organs. These defects can lead to lifelong disabilities or conditions that require ongoing medical care and support.
Some teratogens have known thresholds of exposure.
Certain teratogens have specific thresholds of exposure, meaning that the extent of the damage caused depends on the amount or duration of exposure. For example, high levels of radiation exposure can result in severe birth defects, while low levels may have a minimal or no effect.
Teratogens can have different effects on individuals.
The impact of teratogens can vary from person to person. Factors such as genetic susceptibility, maternal health, and overall prenatal care can influence how an individual responds to teratogenic exposure.
Teratogens can be found in various everyday substances.
Teratogens can be present in everyday substances, including certain cleaning products, pesticides, and even some cosmetics. It is important for expectant mothers to be aware of potential teratogens and take necessary precautions to minimize exposure.
Teratogens can sometimes go unnoticed until birth.
Some birth defects caused by teratogens may not be immediately apparent and can only be detected after the baby is born. Regular prenatal check-ups and medical screenings can help identify and manage any potential issues.
Prevention is key when it comes to teratogens.
Avoiding exposure to known teratogens is crucial in preventing birth defects. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding harmful substances, following proper medication guidelines, and seeking prenatal care from healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, teratogens are substances that can have a significant impact on fetal development, leading to a wide range of birth defects and other health issues. It is crucial for expectant mothers to be aware of the potential risks associated with teratogens and take appropriate precautions to minimize exposure.By understanding the nature of teratogens and their effects, individuals can make informed choices to safeguard their health and the health of their unborn child. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals, avoid harmful substances, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and follow precautionary measures during pregnancy.Remember, knowledge is power. By staying informed and taking necessary steps to avoid teratogens, we can greatly reduce the likelihood of any adverse effects on the developing fetus. It is our responsibility to prioritize the well-being of our future generation and promote healthy pregnancies for all.
FAQs
1. What are some common teratogens?
Common teratogens include alcohol, tobacco, certain medications (such as isotretinoin), illicit drugs, and certain infections like rubella.
2. How do teratogens affect fetal development?
Teratogens can disrupt normal fetal development by interfering with various biological processes, such as cell division, tissue formation, and organ growth.
3. Can teratogens cause birth defects?
Yes, teratogens can cause birth defects, which are structural or functional abnormalities present at birth, resulting from exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy.
4. Are all teratogens equally harmful?
No, the level of harm can vary depending on factors such as the type of teratogen, dosage, timing of exposure during pregnancy, and individual susceptibility.
5. How can I protect my unborn child from teratogens?
To protect your unborn child from teratogens, it is essential to avoid known teratogens, such as alcohol and tobacco, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and follow your healthcare provider’s guidance during pregnancy.
6. Can teratogenic effects always be prevented?
While it is not possible to prevent 100% of teratogenic effects, taking proactive measures to avoid exposure to known teratogens can significantly reduce the risk of adverse outcomes.
7. Can teratogens affect the baby’s development after birth?
Depending on the nature and extent of exposure, teratogens can potentially affect the baby’s development and health not only during pregnancy but also after birth.
8. Are genetic conditions considered teratogens?
No, genetic conditions are not considered teratogens. Teratogens refer specifically to external substances or agents that cause developmental abnormalities.
9. Where can I get more information about teratogens?
You can consult your healthcare provider, read reputable medical sources, or visit organizations dedicated to providing information on pregnancy and prenatal health for more information on teratogens.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
