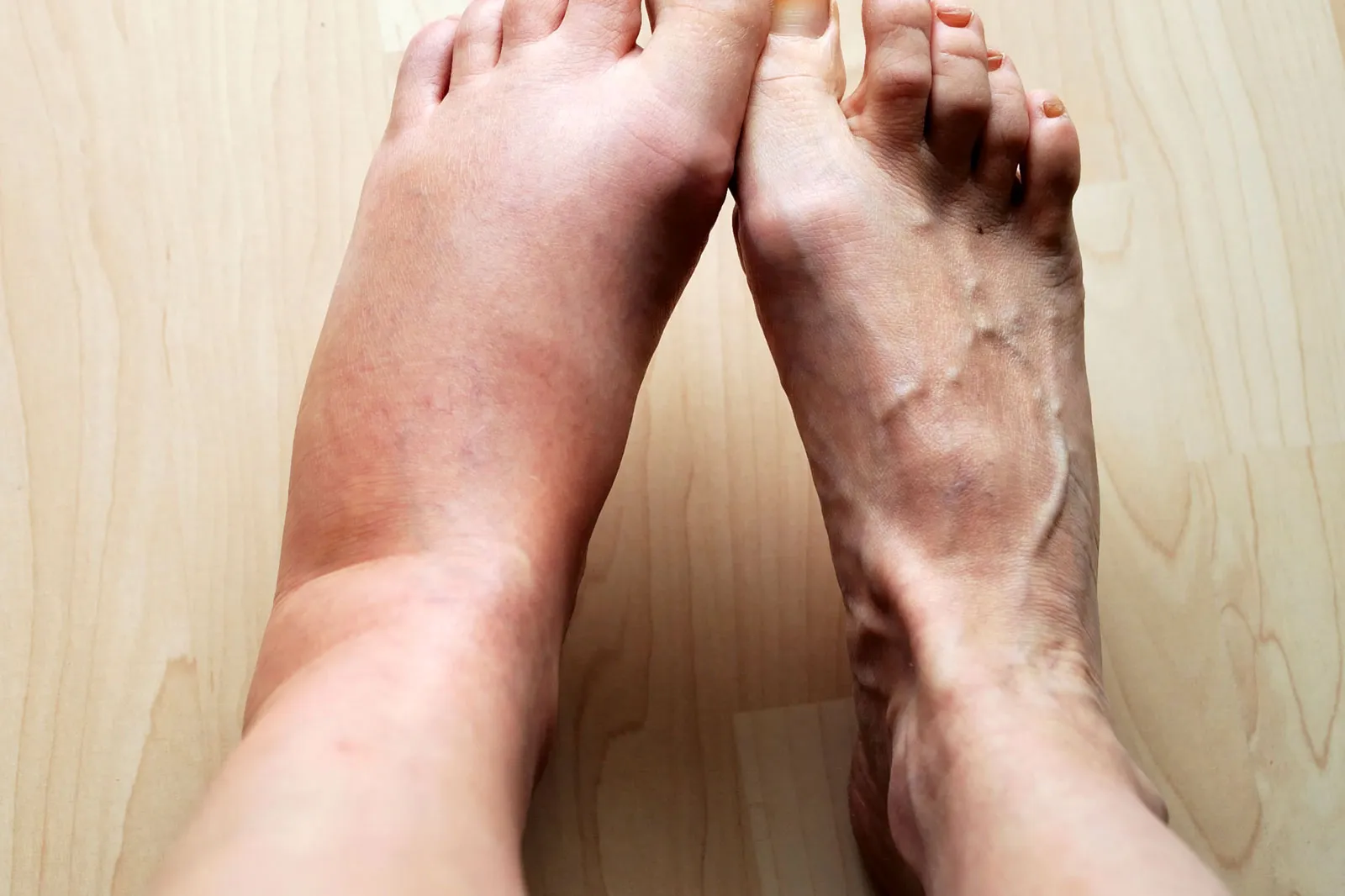
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to fight against infections, injuries, and diseases. While inflammation is typically associated with swelling, redness, and pain, it plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall well-being. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding inflammation due to its connection to various health conditions, such as arthritis, heart disease, and cancer.
In this article, we will explore 18 surprising facts about inflammation that shed light on its complex nature and its impact on our health. From uncovering the different types of inflammation to discussing the role of diet and lifestyle in managing inflammation, we will dive into intriguing scientific findings and practical tips to help you better understand and address this essential bodily process.
Key Takeaways:
- Inflammation is the body’s natural defense against harmful invaders, but chronic inflammation can lead to diseases. Eating anti-inflammatory foods, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
- Chronic inflammation is linked to aging, mental health disorders, heart disease, and cancer. Making lifestyle changes, such as exercising, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep, can help reduce inflammation and support overall well-being.
The body’s natural defense mechanism
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism against harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, toxins, or irritants. It is a complex biological response that involves increased blood flow, white blood cell activity, and the release of various chemical mediators.
Two types of inflammation
There are two types of inflammation: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation is a short-term response triggered by tissue injury or infection, while chronic inflammation lasts for prolonged periods and can lead to tissue damage and various diseases, including arthritis, asthma, and cardiovascular disorders.
Inflammation can be beneficial
Inflammation is not always a bad thing. It plays a crucial role in the healing process by eliminating pathogens and initiating tissue repair. However, when inflammation becomes chronic or excessive, it can have detrimental effects on the body.
Heat, redness, swelling, and pain
The four classic signs of inflammation are heat, redness, swelling, and pain. These symptoms are caused by increased blood flow, dilated blood vessels, accumulation of fluid, and the release of chemical inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and histamines.
Inflammation and the immune system
Inflammation is closely intertwined with the immune system. When the body recognizes a threat, immune cells release inflammatory proteins and chemicals to fight off the invaders. This immune response is essential for defending the body against infections and diseases.
The role of cytokines
Cytokines play a crucial role in inflammation by serving as chemical messengers between cells. They regulate immune responses, coordinate inflammation, and promote the recruitment of immune cells to the site of injury or infection.
Inflammation and aging
Chronic inflammation has been linked to the aging process. As we age, our immune system may become less efficient at regulating inflammation, leading to a higher risk of chronic diseases.
Dietary factors and inflammation
Certain dietary factors can either promote or reduce inflammation in the body. Foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can trigger inflammation, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and Omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation.
Stress and inflammation
Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation. Psychological stress activates the body’s stress response, leading to the release of stress hormones that can increase inflammation levels in the body.
Exercise and inflammation
Moderate exercise has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body. Regular physical activity can help reduce chronic inflammation and lower the risk of inflammatory diseases.
Inflammatory skin conditions
Inflammation is a common underlying factor in many skin conditions, such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. These conditions involve an abnormal immune response and inflammation in the skin.
Inflammation and mental health
Research suggests a link between inflammation and mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety. Chronic inflammation in the body can have an impact on brain function and neurotransmitter activity, potentially contributing to the development of mental health issues.
Inflammatory bowel diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are characterized by chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. These conditions can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal symptoms.
Inflammation and heart health
Chronic inflammation has been identified as a risk factor for heart disease. Inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), can indicate the presence of systemic inflammation and predict the likelihood of cardiovascular events.
The role of antioxidants
Antioxidants help combat inflammation by neutralizing free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to inflammation. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, dark leafy greens, and nuts, can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Sleep and inflammation
Poor sleep quality and inadequate sleep duration can increase inflammation levels in the body. Lack of sleep disrupts immune function and increases the production of inflammatory proteins.
Inflammation and cancer
Chronic inflammation has been associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer. Inflammatory cells and molecules can promote tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis.
Lifestyle changes can reduce inflammation
Making certain lifestyle changes can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. These include maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, managing stress, getting regular exercise, and following a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
As you can see, inflammation is a complex and fascinating process that plays a significant role in both our health and disease. Understanding the various aspects of inflammation can help us make informed choices to support our well-being.
Conclusion
Inflammation is a complex biological process that plays a crucial role in the body’s defense against harmful stimuli, such as infections and injuries. While inflammation is a necessary and beneficial response, chronic inflammation can have harmful effects on our health. By understanding the surprising facts about inflammation, we can take steps to manage and prevent chronic inflammation, leading to improved well-being and overall health.
FAQs
Q: What causes inflammation?
A: Inflammation can be caused by various factors, including infections, injuries, autoimmune disorders, and environmental triggers.
Q: How can I reduce inflammation naturally?
A: You can reduce inflammation naturally by incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Regular exercise, stress management, and getting enough sleep also play a crucial role in reducing inflammation.
Q: Can inflammation be helpful to the body?
A: Yes, acute inflammation is a necessary bodily response to protect and heal tissues. It helps to remove damaged cells, promote healing, and fight off infections.
Q: What are the symptoms of chronic inflammation?
A: Symptoms of chronic inflammation can vary and may include fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, skin problems, and frequent infections.
Q: Are there any foods that can worsen inflammation?
A: Yes, certain foods like processed meats, sugary snacks, refined grains, and excessive alcohol can promote inflammation in the body. It is best to limit their consumption.
Q: Can lifestyle choices affect inflammation levels?
A: Absolutely! Lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive alcohol intake, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet can contribute to chronic inflammation. Making positive lifestyle changes can help reduce inflammation levels.
Inflammation plays a crucial role in our health, but there's still much to learn. Explore intriguing facts about inflammatory diseases and how they affect the body. Sesame seeds may seem small, but they pack a nutritional punch with surprising benefits. Ginger juice is another powerhouse, offering numerous advantages for overall well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
