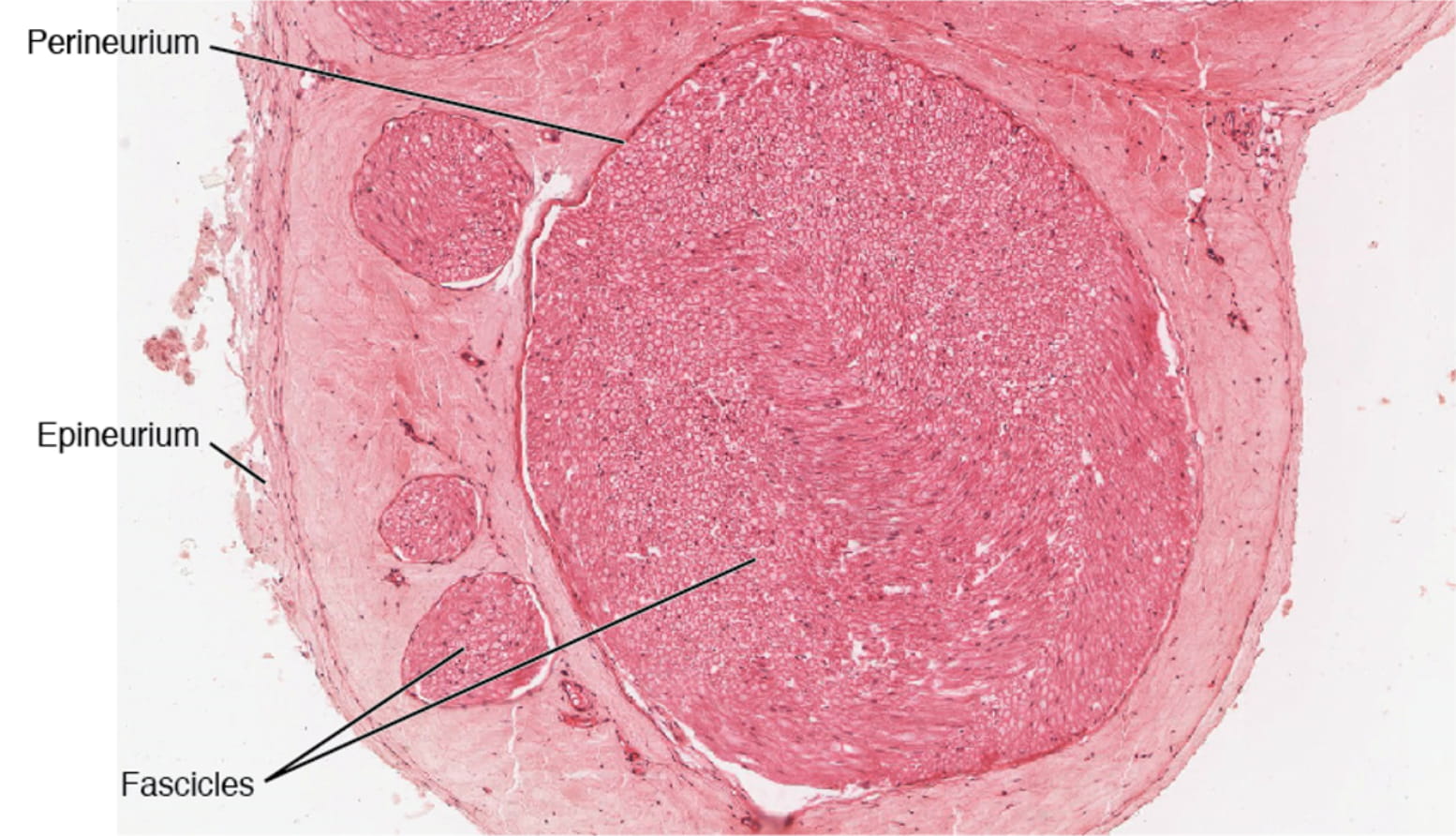
The human body is a complex and intricate system, and one of its wonders lies in the intricate network of nerves that allow us to sense and respond to the world around us. And within this complex network, there is a lesser-known yet fascinating structure called the perineurium. The perineurium is a protective sheath that surrounds and supports nerve fibers, ensuring their proper function. While it may not be as widely discussed as other anatomical structures, the perineurium plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and integrity of our nerves. In this article, we will uncover 8 intriguing facts about the perineurium that will enlighten you about its significance and contribution to our overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The perineurium is like a bodyguard for nerve fibers, protecting them from harm and regulating what goes in and out to keep them healthy and functioning properly.
- It’s like a nourishing support system for nerves, supplying them with essential nutrients and oxygen while also guiding them during regeneration and protecting them from injury.
Structure and Function
The perineurium is a specialized connective tissue that surrounds individual nerve fascicles, providing structural support and protection to the delicate nerve fibers. It acts as a barrier, regulating the movement of substances into and out of the nerve bundle.
Unique Composition
The perineurium consists of multiple layers of collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and elastic fibers. These layers make it stronger and more resistant to mechanical stress compared to other connective tissues in the body.
Blood-Nerve Barrier
The perineurium plays a crucial role in maintaining the blood-nerve barrier, which prevents the unregulated exchange of molecules between the blood vessels and the nerve tissue. This barrier protects the nerves from potentially harmful substances and maintains the precise microenvironment required for proper nerve function.
Selective Permeability
The perineurium is selectively permeable, allowing only specific molecules to enter or exit the nerve fascicles. This helps to maintain the optimal internal environment for nerve conduction and protects against toxins or pathogens that could disrupt nerve function.
Nourishing the Nerves
The perineurium contains blood vessels that supply essential nutrients and oxygen to the nerve fibers within the fascicle. These blood vessels also aid in the removal of waste products produced by the nerves, ensuring their optimal function.
Protection from Mechanical Stress
By providing structural support and a protective barrier, the perineurium helps to safeguard the nerve fibers against mechanical stress and injury. It acts as a cushion, absorbing external forces and minimizing damage to the delicate nerves.
Role in Nerve Regeneration
During nerve regeneration, the perineurium plays a vital role in guiding and directing the regrowing nerve fibers. It provides a scaffolding for the regenerating axons, helping them to navigate and reconnect with their target tissues.
Pathological Changes
Pathological changes in the perineurium, such as thickening or fibrosis, can occur in various neuropathies and nerve disorders. These changes can disrupt the normal flow of nutrients and oxygen to the nerve fibers and impair their function.
These are just 8 fascinating facts about perineurium, showcasing its importance and intricate role in the nervous system. From its unique composition to its protective functions, the perineurium is a remarkable structure worth exploring in greater detail.
If you want to learn more about perineurium and its significance, delve deeper into the complexities of this tissue and its association with nerve health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the perineurium is a fascinating and vital component of the human anatomy. It plays a crucial role in protecting and maintaining the integrity of peripheral nerves. Its specialized structure provides a barrier that prevents the leakage of important substances and controls the exchange of nutrients and waste products between nerve fibers and surrounding tissues.The perineurium also contributes to the unique electrical properties of peripheral nerves, facilitating the conduction of nerve impulses. Its tight arrangement of cells acts as an insulating layer, allowing for efficient and rapid transmission of signals throughout the body.Understanding the structure and function of the perineurium enhances our knowledge of how the nervous system works and its remarkable ability to coordinate complex processes within the body. By delving into the intricacies of the perineurium, we gain valuable insights into the fundamental mechanisms that underlie human physiology.
FAQs
1. What is the perineurium?
The perineurium is a protective connective tissue layer that surrounds individual nerve fascicles, providing structural support and aiding in the maintenance of peripheral nerves.
2. What is the role of the perineurium?
The perineurium acts as a barrier, preventing the leakage of important substances and controlling the exchange of nutrients and waste products between nerve fibers and surrounding tissues.
3. How does the perineurium contribute to nerve conduction?
The perineurium’s tight arrangement of cells acts as an insulating layer, allowing for efficient and rapid transmission of nerve impulses along peripheral nerves.
4. Is the perineurium found throughout the body?
Yes, the perineurium is found in peripheral nerves, which are distributed throughout the body, connecting the central nervous system to various organs and tissues.
5. Can the perineurium be damaged?
Yes, the perineurium can be damaged due to trauma or certain medical conditions. Damage to the perineurium can lead to impaired nerve function and potentially result in neurological symptoms.
6. Can the perineurium regenerate?
In certain cases, the perineurium has the ability to regenerate along with damaged nerves. However, the extent of regeneration depends on various factors, including the severity of the injury and individual healing capacities.
7. Are there any disorders associated with the perineurium?
There are several disorders that can affect the perineurium, such as nerve entrapment syndromes and peripheral neuropathies. These conditions can result in pain, sensory disturbances, and impaired motor function.
8. How can I keep my perineurium healthy?
Maintaining overall good health is crucial for the well-being of your perineurium. This includes engaging in regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding behaviors that may cause nerve damage, such as excessive alcohol consumption or smoking.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
