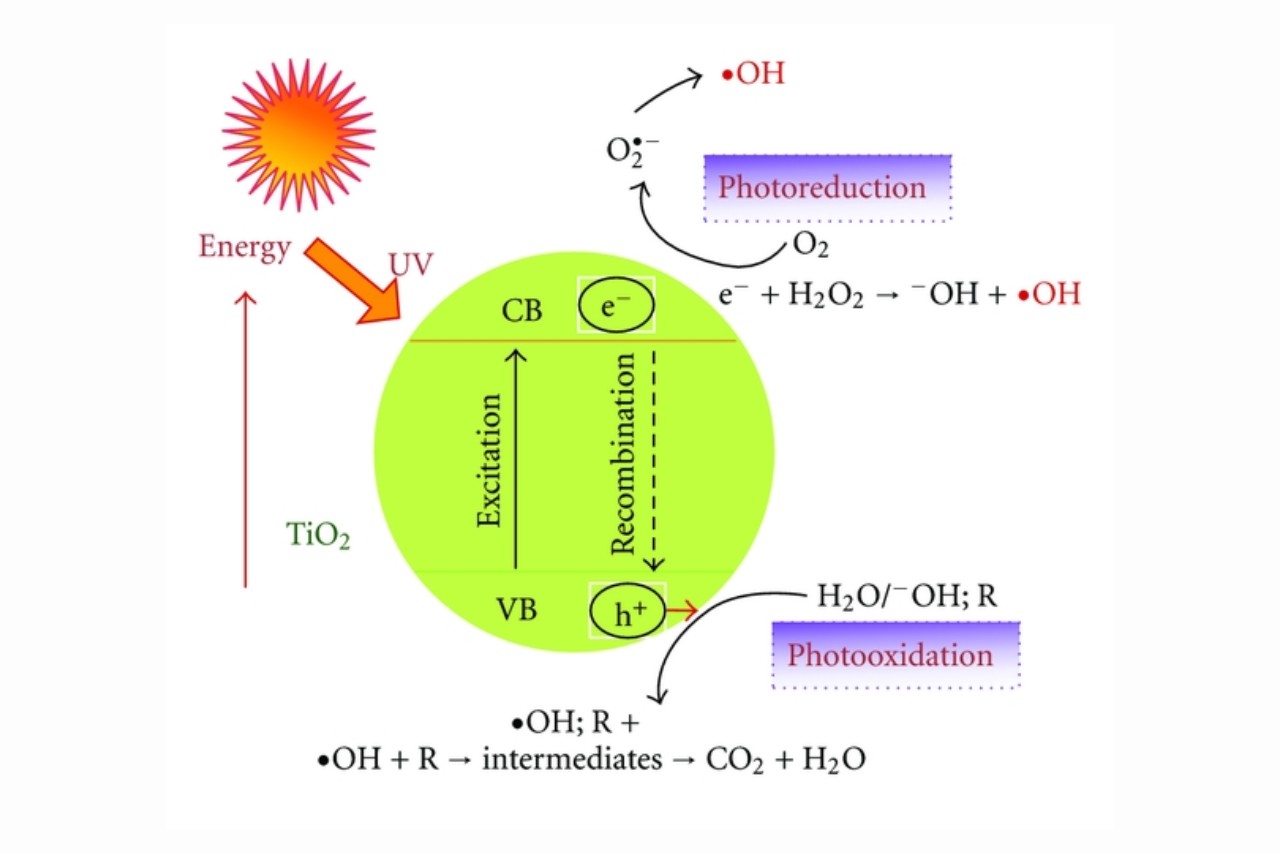
Photocatalysis is a fascinating field of study that merges the principles of chemistry and light. It involves the use of catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions through the absorption of light energy. This process has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in various industries, including environmental remediation, energy production, and even medicine.
In this article, we will delve into the world of photocatalysis and explore 14 extraordinary facts about this remarkable phenomenon. From its history and discovery to its mechanism and practical applications, we will uncover the mysteries behind photocatalysis and highlight its significance in shaping our present and future.
Key Takeaways:
- Photocatalysis uses light to clean water, produce energy, and make medicine, offering cool solutions for a cleaner and healthier world.
- Scientists are always finding new ways to make photocatalysis even better, so get ready for more amazing discoveries in the future!
Photocatalysis is a process that harnesses light energy to drive chemical reactions.
Photocatalysis utilizes a photocatalyst, typically a semiconductor material, to absorb photons and initiate chemical transformations.
Photocatalysis is used in various industries, including environmental remediation.
Photocatalysts can break down pollutants such as organic compounds and help purify air and water.
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is one of the most commonly used photocatalysts.
It exhibits excellent photocatalytic properties and is widely employed in applications like self-cleaning surfaces and solar cells.
Photocatalysis can be used to generate renewable energy.
By harnessing the power of sunlight, photocatalytic systems can produce hydrogen, a clean and sustainable fuel source.
Photocatalysis plays a role in the development of artificial photosynthesis.
Researchers are exploring photocatalytic systems to mimic the natural process of photosynthesis and convert sunlight into chemical energy.
Photocatalysis offers a promising solution for carbon dioxide reduction.
By using photocatalysts, carbon dioxide can be converted into valuable chemicals, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The efficiency of photocatalysis can be enhanced through the modification of photocatalyst surfaces.
Surface modifications, such as doping or creating nanostructures, can improve light absorption and increase reaction rates.
Photocatalysis has the potential to revolutionize wastewater treatment.
By harnessing photocatalytic properties, contaminants in wastewater can be efficiently degraded, leading to cleaner and safer water sources.
Photocatalysis is being explored for the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
Using photocatalytic reactions, chemists can access unique pathways to produce intricate molecular structures that are difficult to obtain by conventional means.
Photocatalysis can be used for the production of sustainable building materials.
By incorporating photocatalytic additives, construction materials like cement can exhibit self-cleaning properties, reducing maintenance requirements.
Photocatalysis has found applications in the field of medicine.
Photocatalytic processes can be utilized for disinfection and sterilization, offering a chemical-free alternative to traditional methods.
Photocatalysis has been studied for the degradation of harmful organic pollutants, such as pesticides.
Photocatalytic reactions can break down these environmental contaminants into non-toxic byproducts.
Researchers are exploring the use of photocatalysis in the field of energy storage.
By utilizing photocatalysts, it is possible to convert and store sunlight energy in the form of chemical bonds, offering potential solutions for renewable energy storage.
The development of novel photocatalytic materials is an ongoing area of research.
Scientists are continuously exploring new materials and improving photocatalytic processes to enhance efficiency and expand the range of applications.
In conclusion, these 14 extraordinary facts about photocatalysis highlight the vast potential of this field in various industries, including environmental remediation, energy production, and organic synthesis. Photocatalysis offers innovative solutions for a sustainable future and continues to be an exciting area of scientific research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photocatalysis is a remarkable process that has revolutionized various fields, from environmental remediation to energy production. Understanding the extraordinary facts about photocatalysis highlights its potential to address pressing global challenges and improve our quality of life.By harnessing the power of light and catalysts, photocatalysis offers a sustainable and efficient way to degrade pollutants, generate clean energy, and synthesize valuable chemicals. The ability to harness sunlight as an abundant and renewable energy source makes photocatalysis a promising solution for meeting our growing energy demands.Moreover, the versatility of photocatalytic materials allows for the development of innovative applications, such as self-cleaning surfaces, antibacterial coatings, and even artificial photosynthesis. The constant advancements in photocatalysis research are paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.As we continue to explore and optimize photocatalytic systems, it is crucial to address challenges such as catalyst stability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. By overcoming these hurdles, we can unlock the full potential of photocatalysis and realize its widespread implementation across multiple industries.In summary, photocatalysis has proven to be a powerful and versatile technology with a wide range of practical applications. Its ability to harness the energy of light and catalytic reactions opens up endless opportunities for addressing environmental, energy, and societal challenges.
FAQs
1. What is photocatalysis?
Photocatalysis is a process that utilizes light energy and catalysts to drive chemical reactions. It involves the interaction between photons, a photocatalyst, and a target compound to initiate a reaction.
2. What are some applications of photocatalysis?
Photocatalysis has diverse applications, including air and water purification, self-cleaning surfaces, solar energy conversion, hydrogen production, and organic synthesis.
3. How does photocatalysis help in environmental remediation?
Photocatalysis can effectively degrade pollutants and contaminants, such as volatile organic compounds, heavy metals, and bacteria, through photochemical reactions, leading to their transformation into harmless substances.
4. Is photocatalysis a sustainable technology?
Yes, photocatalysis is considered a sustainable technology due to its ability to utilize renewable energy sources (such as sunlight) and its potential for reducing environmental impacts by degrading pollutants and generating clean energy.
5. Are there any drawbacks to photocatalysis?
Challenges in photocatalysis include catalyst stability, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Ongoing research aims to address these issues and improve the overall efficiency of photocatalytic systems.
6. Can photocatalysis be used in the pharmaceutical industry?
Yes, photocatalysis can be utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for organic synthesis, drug discovery, and the design of photoresponsive drug delivery systems.
7. How does photocatalysis contribute to renewable energy production?
Photocatalysis plays a significant role in renewable energy production by harnessing solar energy to drive reactions such as water splitting to produce hydrogen fuel or generating electricity through photovoltaic cells.
8. Is photocatalysis a well-established field of research?
Yes, photocatalysis has gained significant attention over the years, and it continues to be a vibrant research area with ongoing advancements in catalyst design, reaction mechanisms, and practical applications.
Photocatalysis is just one fascinating aspect of chemistry and its applications. Dive into the world of solar energy and discover its incredible potential for a sustainable future. Explore the intricacies of semiconductor materials and how they revolutionize modern technology. Lastly, uncover the mysteries of microbial biofilms and their role in shaping our environment. Each topic offers a captivating journey through the marvels of science and innovation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


