Electrolytic cells are fascinating devices that play a crucial role in various chemical processes. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or just curious about how things work at the molecular level, learning about electrolytic cells can be truly mind-blowing. These cells are employed in a wide range of applications, from electroplating to the production of chemicals and even in the field of medicine.
In this article, we will explore 16 fascinating facts about electrolytic cells that will leave you amazed and wanting to delve deeper into the world of chemistry. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready for an electrifying journey as we unravel the mysteries behind electrolytic cells and their remarkable properties.
Key Takeaways:
- Electrolytic cells use electricity to drive chemical reactions, from producing metals to generating clean fuel, making them essential for innovation and sustainability.
- These remarkable cells play a crucial role in various industries and scientific research, from electroplating to medical treatments, showcasing their versatility and significance in our modern world.
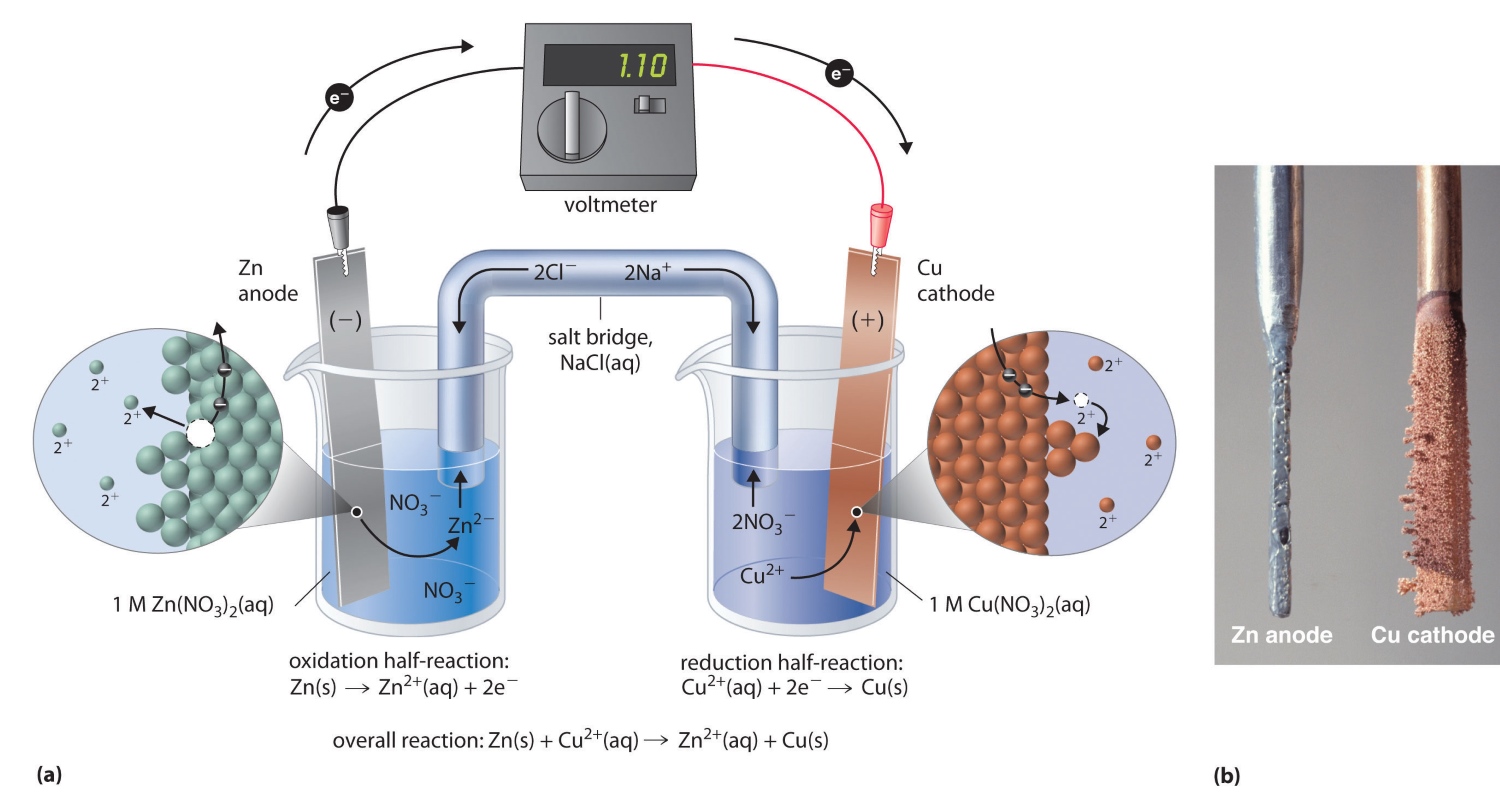
An Electrolytic Cell Utilizes External Electrical Energy
An electrolytic cell is a device that uses electrical energy from an external source to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. It differs from a galvanic cell, also known as a voltaic cell, which generates electrical energy from a spontaneous chemical reaction.
Electrolytic Cells are Used in Electroplating
One of the most common applications of electrolytic cells is electroplating. This process involves depositing a layer of metal onto a surface, enhancing its appearance or providing additional protection against corrosion.
Electrolytic Cells Can Split Water into Hydrogen and Oxygen
An electrolytic cell can be used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen gases through a process called electrolysis. This has important implications for the development of clean and sustainable energy sources.
They Are Key Components in the Production of Aluminum
The production of aluminum involves the use of large-scale electrolytic cells. Aluminum oxide is dissolved in a molten cryolite solution, and an electric current is passed through the cell to extract pure aluminum metal.
Electrolytic Cells Play a Role in the Electrorefining of Metals
The electrorefining process is used to purify impure metals through electrolysis. Electrolytic cells are employed to remove impurities and obtain high-purity metals for various industrial applications.
They Facilitate Electrosynthesis
Electrosynthesis is the process of utilizing electricity to drive chemical reactions that would not occur spontaneously. Electrolytic cells are crucial in this field, enabling the synthesis of various compounds and materials.
Electrolytic Cells Facilitate the Detection of Metals
In analytical chemistry, electrolytic cells are used for the detection and quantification of metals. By applying an electric current, the metal ions in a sample can be selectively deposited onto an electrode for analysis.
They are Essential in the Production of Chlorine and Sodium Hydroxide
The chlor-alkali industry relies heavily on electrolytic cells for the production of chlorine gas, sodium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas. These compounds have a wide range of applications in manufacturing various products.
Electrolytic Cells Can Recharge Batteries
In rechargeable batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, electrolytic cells are used to reverse the chemical reactions that occur during discharge. This allows the battery to be recharged and used again.
They Play a Role in Environmental Remediation
Electrolytic cells are utilized in environmental remediation processes to remove pollutants from soil and water. By applying an electric current, contaminants are either attracted to an electrode or transformed into less harmful substances.
Electrolytic Cells Can be Used for Desalination
In desalination, electrolytic cells are employed to remove salt and other impurities from seawater, making it suitable for consumption or agricultural purposes. This technology has the potential to address global water scarcity issues.
They Enable the Production of Hydrogen Fuel
Electrolytic cells are crucial in generating hydrogen gas, a clean and renewable source of fuel. Through the process of water electrolysis, hydrogen fuel can be produced, offering an alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Electrolytic Cells Help in the Study of Redox Reactions
Redox reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between molecules, are fundamental to chemistry. Electrolytic cells provide a means to study and understand these reactions in a controlled and measurable environment.
They Have Medical Applications
Electrolytic cells find applications in medicine, such as in electrotherapy and transdermal drug delivery systems. These technologies utilize controlled electrical currents to treat certain medical conditions or deliver medications through the skin.
Electrolytic Cells are Used in Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors typically use an electrolyte-filled electrolytic cell to store and release electrical energy. These capacitors have high capacitance values and are commonly used in electronic devices.
They Are Used in Electrowinning
Electrowinning is a process that involves the extraction of metal ions from an electrolyte solution by applying an electric current. Electrolytic cells are pivotal in this technique, commonly used in the mining industry to recover metals from ores.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrolytic cells are fascinating devices that have revolutionized the world of chemistry. They allow for the production of essential metals, the extraction of useful substances, and so much more. Understanding how electrolytic cells work and their various applications is crucial for anyone interested in the field of chemistry. From electroplating to the production of hydrogen and oxygen gases, these cells have countless practical uses.We have explored 16 mind-blowing facts about electrolytic cells, ranging from their historical significance to their role in industries. Whether you are a chemistry enthusiast or just curious about the world around you, these facts provide a glimpse into the wonders of electrolytic cells.So, delve into the world of electrolytic cells, and uncover the amazing science behind these incredible devices. The more you learn, the more you will appreciate the transformative power of chemistry in our daily lives.
FAQs
Q: What is an electrolytic cell?
An electrolytic cell is a device that uses an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction, resulting in the decomposition of compounds or the production of new substances.Q: How does an electrolytic cell work?
An electrolytic cell consists of two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in an electrolyte solution. When an electric current is passed through the cell, cations move toward the cathode, while anions migrate towards the anode. This movement of ions causes chemical reactions to occur at the electrodes.Q: What are some applications of electrolytic cells?
Electrolytic cells have numerous applications. They are used in electroplating processes, the production of chlorine and sodium hydroxide, the extraction of metals from ores, and the electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen and oxygen gases.Q: What is electroplating?
Electroplating is a process in which a metal object is coated with a thin layer of another metal using an electrolytic cell. This technique is widely used to improve the appearance, corrosion resistance, and durability of objects.Q: Are there any risks associated with electrolytic cells?
While electrolytic cells are generally safe, some risks may arise from the chemicals used or from mishandling electricity. It is important to follow proper safety precautions and work in a well-ventilated area when using electrolytic cells.
Electrolytic cells offer a captivating glimpse into the world of electrochemistry. From their role in producing essential materials like aluminum and chlorine to their potential for environmental remediation and medical applications, these fascinating devices showcase the power of redox reactions. Exploring the intricacies of electrolytic cells unveils a realm of possibilities, from splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen to recharging batteries and enabling the production of hydrogen fuel. For those curious about the inner workings of these remarkable cells, delving deeper into the concept of cell potential promises even more mind-blowing revelations.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


