When it comes to understanding the world of chemistry, one cannot overlook the importance of anode. Anode, a term widely used in electrochemistry, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and processes. Whether it’s batteries, electroplating, or electrolysis, anode is a key component that helps in the flow of electrons and drives the chemical reactions forward.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the fascinating world of anode and uncover 13 interesting facts about this essential part of chemistry. From its definition and function to its types and applications, we will dissect the anode to understand its significance in the realm of science and technology. So, let’s dive in and discover the intriguing facts that make anode a fundamental element in the world of chemistry.
Key Takeaways:
- Anodes are important in various processes, like batteries and electrolysis, where they help generate electricity and facilitate chemical reactions by attracting charged particles.
- Sacrificial anodes are like superheroes for metal structures, protecting them from corrosion by sacrificing themselves to divert the corrosion process.
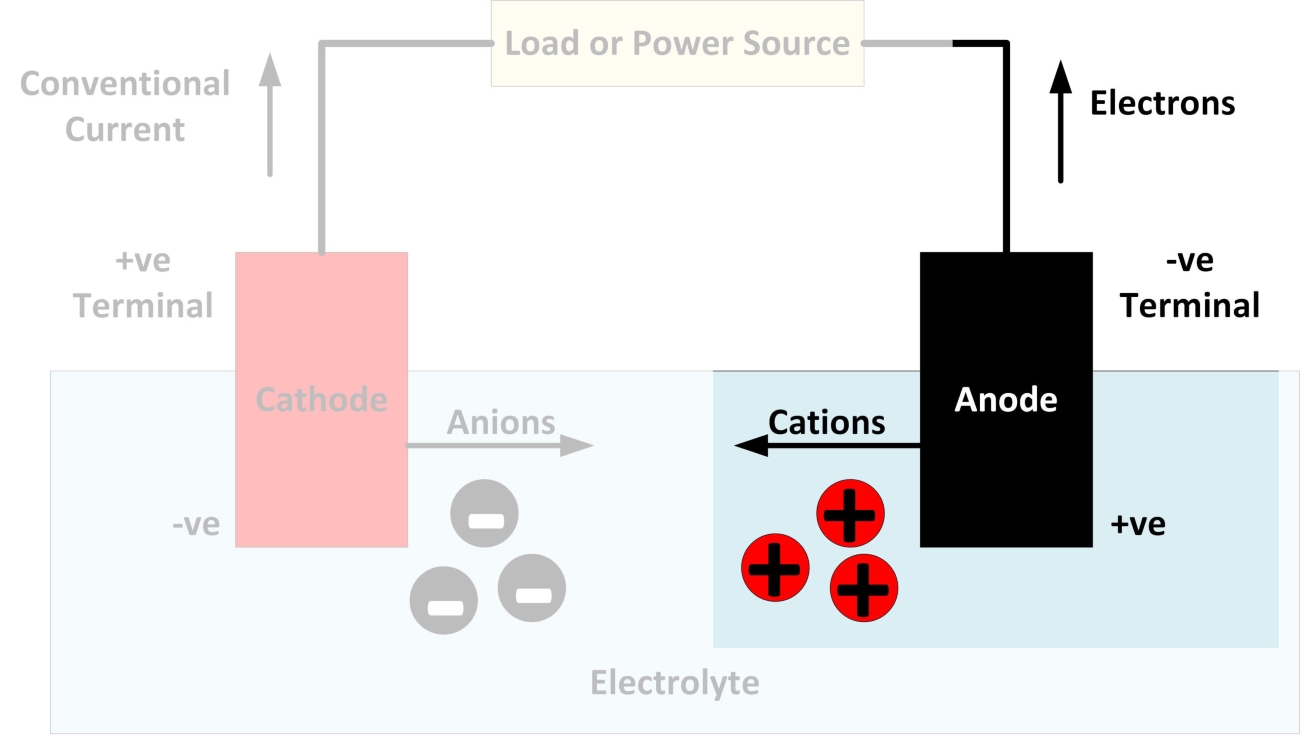
What is an Anode?
An anode is an electrode through which conventional current flows into a polarized electrical device.
The Role of Anode in Electrochemical Processes
The anode plays a crucial role in electrochemical processes by attracting negatively charged particles (anions) and facilitating various chemical reactions.
Anode Materials
Anode materials can vary depending on the application. Common anode materials include graphite, lithium, zinc, and aluminum.
Anode in Batteries
In batteries, the anode is the electrode where oxidation occurs, releasing electrons that flow through an external circuit.
Anode in Electrolysis
In electrolysis, the anode is the positive electrode where oxidation occurs, leading to the discharge of ions.
Sacrificial Anodes
Sacrificial anodes are used to protect metal structures from corrosion by serving as a more easily corroded material, diverting the corrosion process.
Anode in Cathodic Protection
Anode systems are commonly used in cathodic protection to prevent corrosion of metal structures submerged in water or buried underground.
Anode in X-ray Tubes
In X-ray tubes, the anode is a rotating disc made of tungsten that generates X-rays when bombarded by high-speed electrons.
The Polarity of the Anode
The anode is typically designated as the positive electrode in a device, although the naming convention can vary depending on the context.
Anode in Electronic Components
Anodes are commonly found in electronic components such as diodes, vacuum tubes, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Anode in Fuel Cells
In fuel cells, the anode facilitates the oxidation of fuel, generating a flow of electrons that can be harnessed as electrical energy.
Anode in Galvanic Cells
In galvanic cells, the anode is the electrode where oxidation occurs, producing a flow of electrons through an external circuit.
Anode in Electroplating
In the process of electroplating, the anode is the source of metal ions that are deposited onto the object being plated.
Conclusion
Anode is a fascinating element in the field of chemistry, with a wide range of applications and interesting facts associated with it. From its role in electrochemical reactions to its significance in various industries, anode plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. Whether you’re interested in understanding its function in batteries or curious about its impact on corrosion prevention, exploring the world of anode can lead to a deeper appreciation for the wonders of chemistry.
FAQs
1. What is an anode?
An anode is the positively charged electrode in an electrochemical cell or device. It serves as a site for oxidation, where electrons are released, supporting various chemical reactions.
2. Is an anode the same as a cathode?
No, an anode and cathode are two different electrodes in an electrochemical cell. While the anode is the positively charged electrode, the cathode is the negatively charged electrode.
3. How does anode oxidation prevent corrosion?
Anode oxidation, also known as sacrificial anode protection, is a technique used to prevent corrosion. By connecting a more reactive metal, such as zinc or aluminum, to a metal structure, the anode corrodes instead of the protected metal, sacrificing itself to protect the structure from corrosion.
4. What are some common applications of anode?
Anode is used in various applications, including batteries, electroplating, electrolysis, and water treatment. It is also utilized in industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, and metallurgy.
5. Can anode be recycled?
Yes, anode materials can be recycled. The recycling process involves extracting valuable metals from spent anodes, reducing the environmental impact and conserving resources.
6. Are there different types of anodes?
Yes, there are different types of anodes, including sacrificial anodes, impressed current anodes, and MMO (mixed metal oxide) anodes. Each type has unique properties and applications depending on the desired outcome.
Anodes play a crucial role in various electrochemical processes, offering protection against corrosion. Sacrificial anodes, made from materials like zinc or magnesium, provide an effective way to safeguard metal structures. For outdoor enthusiasts, having the right gear is essential; mess kits make camping meals a breeze. Keychain knives, with their compact size and versatile functionality, are must-have tools for everyday carry.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
