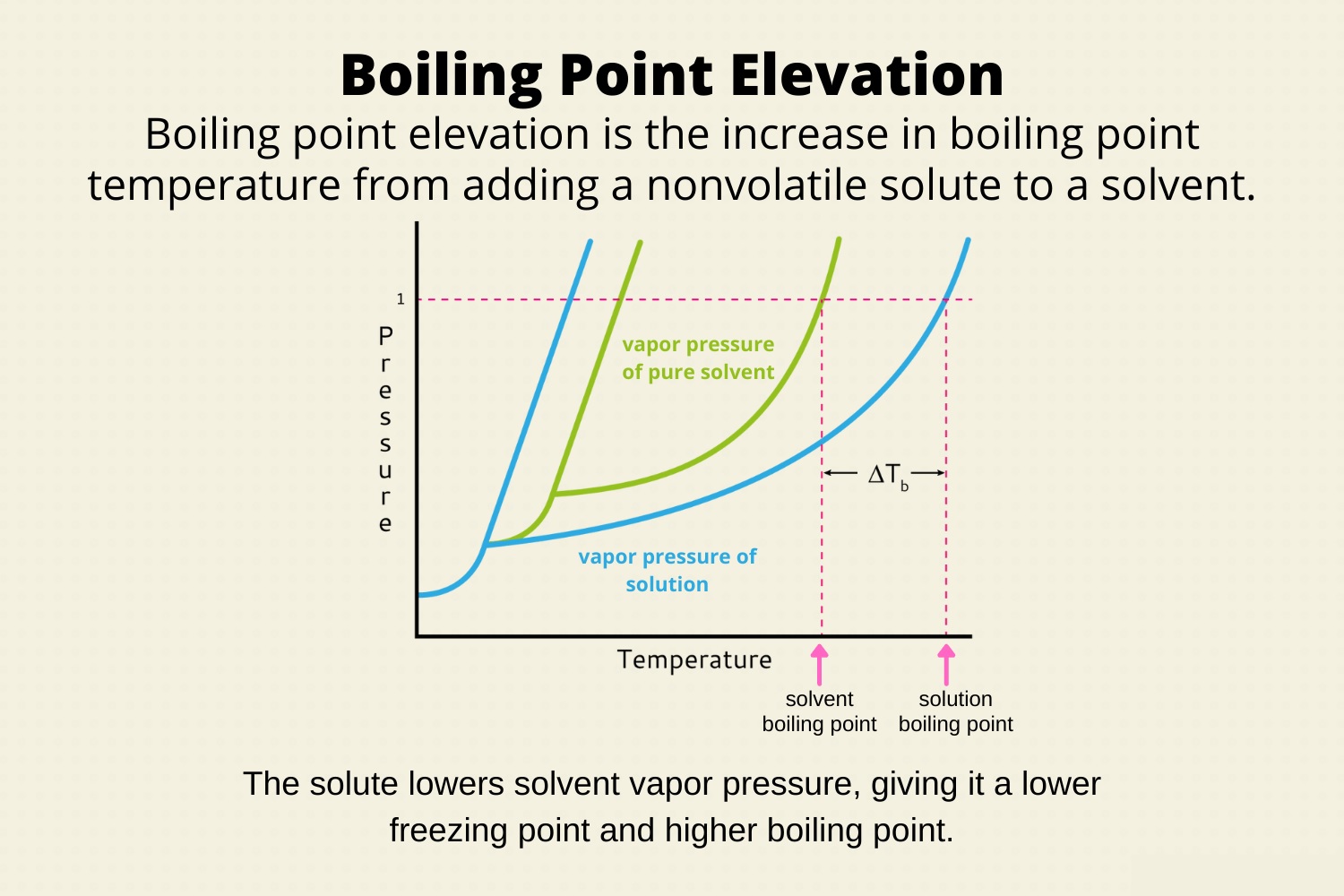
When it comes to the fascinating world of Chemistry, there are numerous topics and phenomena that captivate the curious minds of scientists and enthusiasts alike. One such captivating concept is boiling point elevation. Boiling point elevation refers to the increase in the boiling point of a solvent when a solute is dissolved in it, resulting in the formation of a solution. This phenomenon has significant implications and applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and industry.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of boiling point elevation and explore 20 fascinating facts that will shed light on this phenomenon. From its underlying principles to its practical implications, we will uncover the factors that contribute to boiling point elevation and the real-life applications it has in everyday scenarios. So, grab your lab coat and join us on this exciting journey into the world of boiling point elevation!
Key Takeaways:
- Boiling point elevation occurs when adding a substance to a liquid raises its boiling point, useful in cooking, antifreeze, and pharmaceuticals. It’s a cool way to change how liquids behave!
- The more solute added to a liquid, the higher the boiling point. This affects cooking, distillation, and even the study of unknown substances. It’s like a secret ingredient for liquids!
Boiling point elevation is a phenomenon where the boiling point of a liquid increases when another substance, such as a solute, is added to it.
When a solute is dissolved in a liquid, it disrupts the intermolecular forces between the solvent molecules, making it harder for them to escape into the vapor phase. This results in an increase in the boiling point of the solution compared to the pure solvent.
The boiling point elevation is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute.
The more solute particles present in the solution, the greater the extent of disruption in the intermolecular forces, leading to a higher boiling point elevation.
Boiling point elevation is a colligative property.
Colligative properties depend on the number of solute particles present in the solution, regardless of their nature. Boiling point elevation is one of the four colligative properties, along with freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
Adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent will always result in boiling point elevation.
Non-volatile solutes do not evaporate easily and therefore do not contribute to the vapor pressure of the solution. This causes an increase in the boiling point of the solution.
The boiling point elevation can be calculated using the equation: ?Tb = Kb * m * i.
?Tb represents the boiling point elevation, Kb is the molal boiling point elevation constant, m is the molality of the solute, and i is the van’t Hoff factor. The van’t Hoff factor accounts for the dissociation or association of particles in the solution.
Boiling point elevation is commonly observed in everyday life.
For example, adding salt to water when cooking pasta increases the boiling point of the water, allowing for better cooking of the pasta.
Boiling point elevation is used in antifreeze solutions.
Antifreeze solutions are made by adding solutes to water, which raises the boiling point of the mixture. This helps to prevent the engine coolant from boiling under high temperatures and protects the engine from damage.
Boiling point elevation is also utilized in the process of distillation.
Distillation is a technique used to separate components of a liquid mixture based on their boiling points. By adding a solute to the liquid, the boiling point of the mixture is elevated, making it easier to separate the components.
Boiling point elevation can be affected by external pressure.
At higher pressures, the boiling point of a solution is further elevated. This is particularly noticeable in high-altitude cooking, where the lower atmospheric pressure causes water to boil at a lower temperature.
The boiling point elevation is independent of the identity of the solute.
As long as the number of solute particles is the same, the boiling point elevation will be the same, regardless of the nature of the solute. This is why colligative properties are often used to determine the molecular weight of unknown substances.
Boiling point elevation is an important factor in the pharmaceutical industry.
It is utilized in the production of drugs and medicines to ensure their stability and efficacy. By adjusting the boiling points of the solvents used in manufacturing, specific reactions can be controlled to obtain desired products.
The boiling point elevation of a solution is always greater than the freezing point depression.
While both boiling point elevation and freezing point depression are colligative properties, the boiling point elevation is generally a larger change compared to the freezing point depression for a given solute concentration.
Boiling point elevation is influenced by the solvent-solute interactions.
The extent of boiling point elevation depends on the strength of the interactions between the solvent and solute particles. Stronger interactions can result in a greater increase in the boiling point.
Boiling point elevation can occur in both liquid-liquid and solid-liquid solutions.
Solutions can be formed between different combinations of solvents and solutes, leading to boiling point elevation in various systems.
The boiling point elevation constant, Kb, varies for different solvents.
Each solvent has its own characteristic boiling point elevation constant, which is determined experimentally. This constant reflects the unique properties and interactions of the solvent.
Boiling point elevation is used in the field of cryogenics.
By adding solutes to liquid nitrogen or helium, the boiling points of these cryogenic fluids can be increased, allowing for lower temperature operation in certain applications.
Boiling point elevation can cause changes in chemical reactions.
By increasing the boiling point of a solvent, the reaction rate may be altered, resulting in different products or reaction outcomes. This can be particularly significant in industrial processes.
Boiling point elevation is affected by atmospheric pressure.
At higher pressures, the boiling point of a solution is further elevated, while at lower pressures, the boiling point is decreased. This is why water boils at lower temperatures at higher altitudes.
Boiling point elevation is a dynamic process.
As solute particles are continuously added or removed from the solution, the boiling point elevation may change accordingly. This makes the phenomenon adaptable to different concentrations and conditions.
Boiling point elevation plays a crucial role in the study of colligative properties.
Understanding the principles and applications of boiling point elevation provides valuable insights into the behavior of solutions, chemical processes, and material science.
Conclusion
In conclusion, boiling point elevation is a fascinating phenomenon in chemistry that occurs when the boiling point of a solvent is raised due to the presence of solutes. This effect has practical applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food science, and chemical engineering.
By understanding the factors that contribute to boiling point elevation, scientists and engineers can better manipulate solvent properties to achieve desired outcomes. This knowledge is essential for developing new medications, optimizing food production processes, and designing more efficient industrial systems.
Overall, the study of boiling point elevation not only deepens our understanding of chemical properties and behavior but also provides valuable insights into how we can harness these phenomena for practical purposes.
FAQs
Q: What is boiling point elevation?
A: Boiling point elevation refers to the increase in the boiling point of a solvent when solutes are dissolved in it. This occurs due to the solute-solvent interactions, which disrupt the normal boiling process.
Q: What causes boiling point elevation?
A: Boiling point elevation is caused by the presence of solutes in a solvent. The solutes disrupt the intermolecular forces between solvent molecules, making it more difficult for them to escape into the vapor phase, thus increasing the boiling point.
Q: What are some real-life applications of boiling point elevation?
A: Boiling point elevation has various practical applications. It is utilized in the food industry to improve the cooking process and enhance the flavors of certain dishes. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to create concentrated drug solutions. Boiling point elevation is also important in chemical engineering for the design of distillation processes.
Q: How does boiling point elevation affect the boiling time?
A: Boiling point elevation increases the boiling time as it requires more energy to reach the elevated boiling point. This means that it takes longer for the solvent to reach the temperature at which it can vaporize and boil.
Q: Can boiling point elevation be reversed?
A: Yes, boiling point elevation can be reversed. By removing the solutes from the solvent, such as through distillation or evaporation, the boiling point of the solvent will return to its original value.
Boiling point elevation is just one of many captivating aspects of chemistry. Delving deeper into the world of solutions, molality offers a precise way to express concentration. Colligative properties, like boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure, depend on the number of solute particles rather than their identity. Raoult's Law, a fundamental principle in chemistry, describes the vapor pressure of solutions and their ideal behavior. Exploring these topics further will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the fascinating world of chemistry and its practical applications.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
