Aromaticity is a fascinating concept in chemistry that has captured the imaginations of scientists and students alike. It refers to the unique property of certain organic compounds that exhibit exceptional stability and distinctive chemical behavior.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of aromaticity and explore 20 intriguing facts that will enhance your understanding of this phenomenon. From its historical origins to its widespread applications in various industries, aromaticity continues to puzzle and amaze scientists around the globe.
So, grab your lab coat and safety goggles as we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of aromaticity and uncover its fascinating secrets.
Key Takeaways:
- Aromatic compounds have unique structures and properties, influencing everything from colors to drug development. They’re like the rockstars of the chemical world, with their own special way of bonding and captivating abilities.
- Aromaticity isn’t just about pleasant smells; it’s a fundamental concept in chemistry. From essential oils to environmental cleanup, aromatic compounds play a vital role in our everyday lives and the world around us.
Aromaticity is a chemical property that describes certain types of molecular structures.
Aromaticity refers to the stability and unique electronic structure of unsaturated organic compounds, known as aromatic compounds.
Aromatic compounds contain one or more aromatic rings.
An aromatic ring is a cyclic arrangement of carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds, where each carbon atom is also bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Aromaticity is characterized by a phenomenon called delocalized electron pi bonding.
In aromatic compounds, the pi electrons are spread out evenly over the entire ring, resulting in increased stability.
The term “aromatic” was initially used to describe compounds with a pleasant smell.
However, it was later discovered that aromaticity is not related to the odor of a compound.
Aromaticity plays a crucial role in organic chemistry and is involved in various reactions and processes.
It influences the reactivity, stability, and properties of aromatic compounds.
Benzene, with its six carbon atoms and alternating single and double bonds, is the most well-known aromatic compound.
It serves as a fundamental building block for many aromatic compounds.
Aromatic compounds can have different substituents attached to the aromatic ring.
The presence of these substituents can alter the properties and reactivity of the aromatic compound.
Aromaticity is not limited to carbon-based compounds.
Heterocyclic aromatic compounds contain atoms other than carbon in the aromatic ring, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur.
Aromatic compounds exhibit unique spectroscopic properties.
They often have characteristic absorption bands in UV-Vis spectroscopy and distinctive signals in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Aromaticity can be determined using various computational methods.
Chemists use computational tools to calculate properties and confirm the presence of aromaticity in a molecule.
Aromatic compounds are widely used in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.
Many drugs and pesticides contain aromatic structures that contribute to their biological activity.
Aromaticity is a common feature in natural products.
Many naturally occurring compounds, such as essential oils and pigments, possess aromatic frameworks.
Aromatic compounds have important applications in materials science.
They are used in the synthesis of polymers, dyes, and electronic materials due to their unique properties.
Aromaticity can influence the color of compounds.
Conjugated systems with aromatic rings often exhibit vivid colors due to their ability to absorb specific wavelengths of light.
The concept of aromaticity was first proposed by the chemist August Kekulé in the 19th century.
Kekulé’s structural formula for benzene, with alternating single and double bonds, laid the foundation for understanding aromatic compounds.
Aromatic compounds can undergo substitution reactions.
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a common reaction mechanism, where a substituent replaces a hydrogen atom on the aromatic ring.
Aromaticity influences the acidity and basicity of compounds.
Aromatic compounds can exhibit different acidity or basicity compared to non-aromatic molecules with similar functional groups.
Aromaticity is not solely restricted to organic compounds.
Transition metal complexes and other inorganic compounds can also exhibit aromatic behavior.
Aromatic compounds have been investigated for their potential use in environmental remediation.
Certain aromatic compounds can be used to remove pollutants from contaminated water and soil.
The study of aromaticity continues to be a fascinating research area, with new insights and applications being discovered.
Scientists are exploring the development of novel aromatic compounds and expanding our understanding of their properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aromaticity is a fascinating concept in organic chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of certain compounds. These 20 captivating facts about aromaticity highlight the significance of aromatic compounds and their unique properties. From understanding the stability of aromatic rings to exploring the aromaticity in heterocyclic compounds, there is much to uncover in this field.By delving into the world of aromaticity, chemists can unlock new insights into the reactivity, structure, and bonding of various compounds. The aromaticity concept has practical applications in drug design, materials science, and environmental sciences.Overall, aromaticity is an essential topic in chemistry that continues to intrigue researchers and students alike. Its impact in the field of organic chemistry cannot be overstated, and further exploration into the intricacies of aromatic compounds promises to yield exciting discoveries and advancements.
FAQs
Q: What is aromaticity?
A: Aromaticity refers to the peculiar stability and structure of certain organic compounds known as aromatic compounds. These compounds possess a resonance-stabilized ring of alternating single and double bonds, which contributes to their unique properties.
Q: How can aromaticity be determined?
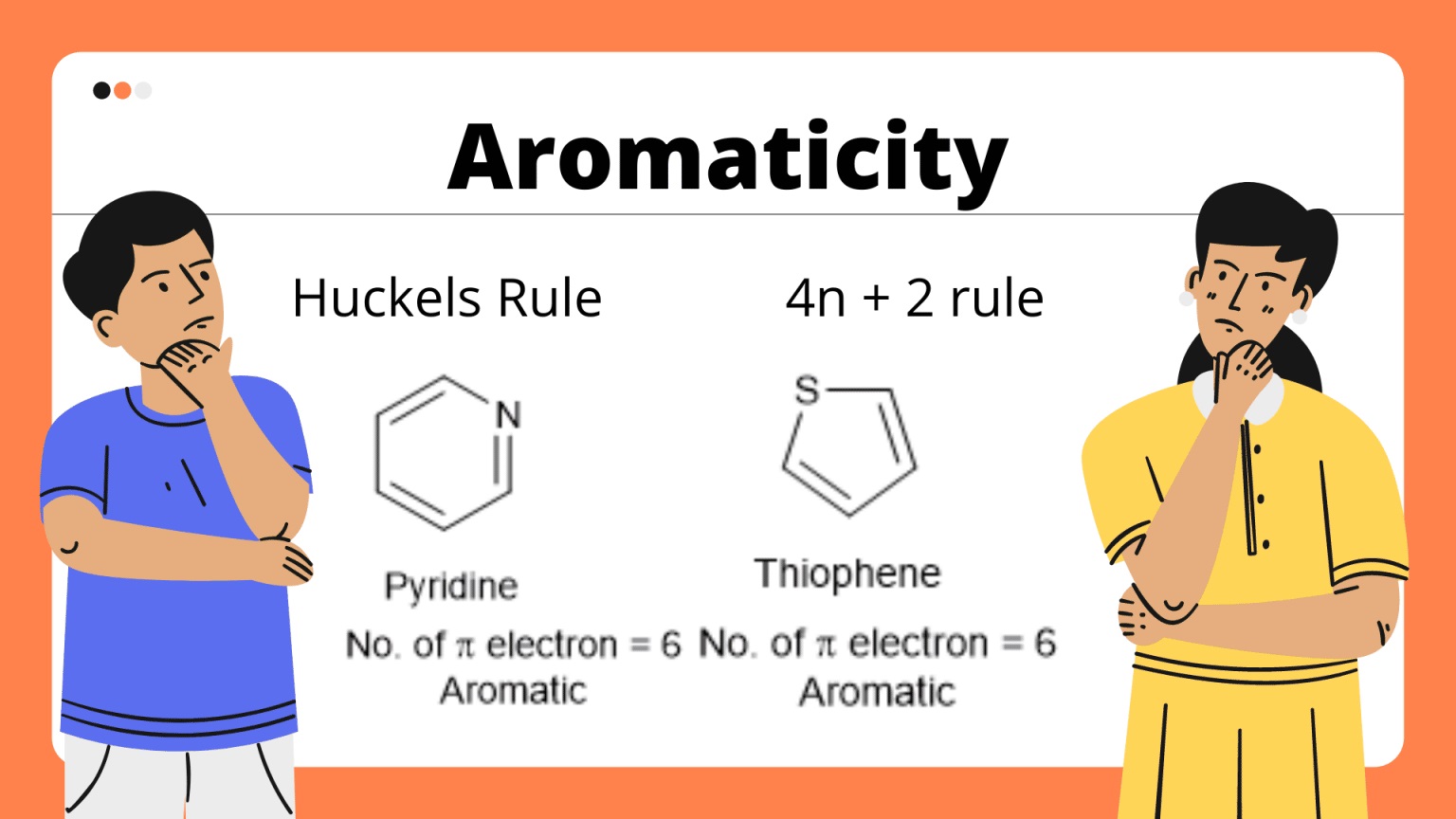
A: Aromaticity can be determined using various criteria, including Huckel’s rule, which states that a compound must have 4n + 2 ?-electrons in a cyclic, planar, and conjugated system to exhibit aromaticity.
Q: What are the main characteristics of aromatic compounds?
A: Aromatic compounds exhibit high stability, low reactivity, and distinctive electronic properties. They often possess pleasant odors and are commonly found in essential oils and fragrances.
Q: Can aromaticity be observed in inorganic compounds?
A: Yes, aromaticity can also be observed in certain inorganic compounds, such as metal clusters and boron compounds. These compounds exhibit aromatic behavior due to the presence of delocalized electrons.
Q: What are some practical applications of aromatic compounds?
A: Aromatic compounds have several practical applications, including pharmaceutical drug development, material synthesis, and the creation of dyes and pigments.
Aromaticity's captivating facts merely scratch the surface of this fascinating chemical phenomenon. Delve deeper into aromatic compounds' extraordinary properties, explore cassia bark's intriguing characteristics, or immerse yourself in the mindblowing world of Dubai's spice souk. Each topic offers a unique perspective on the diverse and compelling aspects of chemistry and culture. Whether you're a curious learner or a seasoned enthusiast, these articles promise to engage, inform, and inspire. Embark on a journey of discovery and uncover the remarkable secrets waiting to be revealed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
