The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a remarkable biological process with a significant impact on both development and disease. Named after the spiky mammal due to the appearance of early experiments on fruit fly embryos, this pathway plays a crucial role in regulating cell growth, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
First discovered in the 1980s, the Hedgehog signaling pathway has since become the focus of intense research in the field of biology. It is involved in various developmental processes, including embryogenesis, organogenesis, and stem cell regulation.
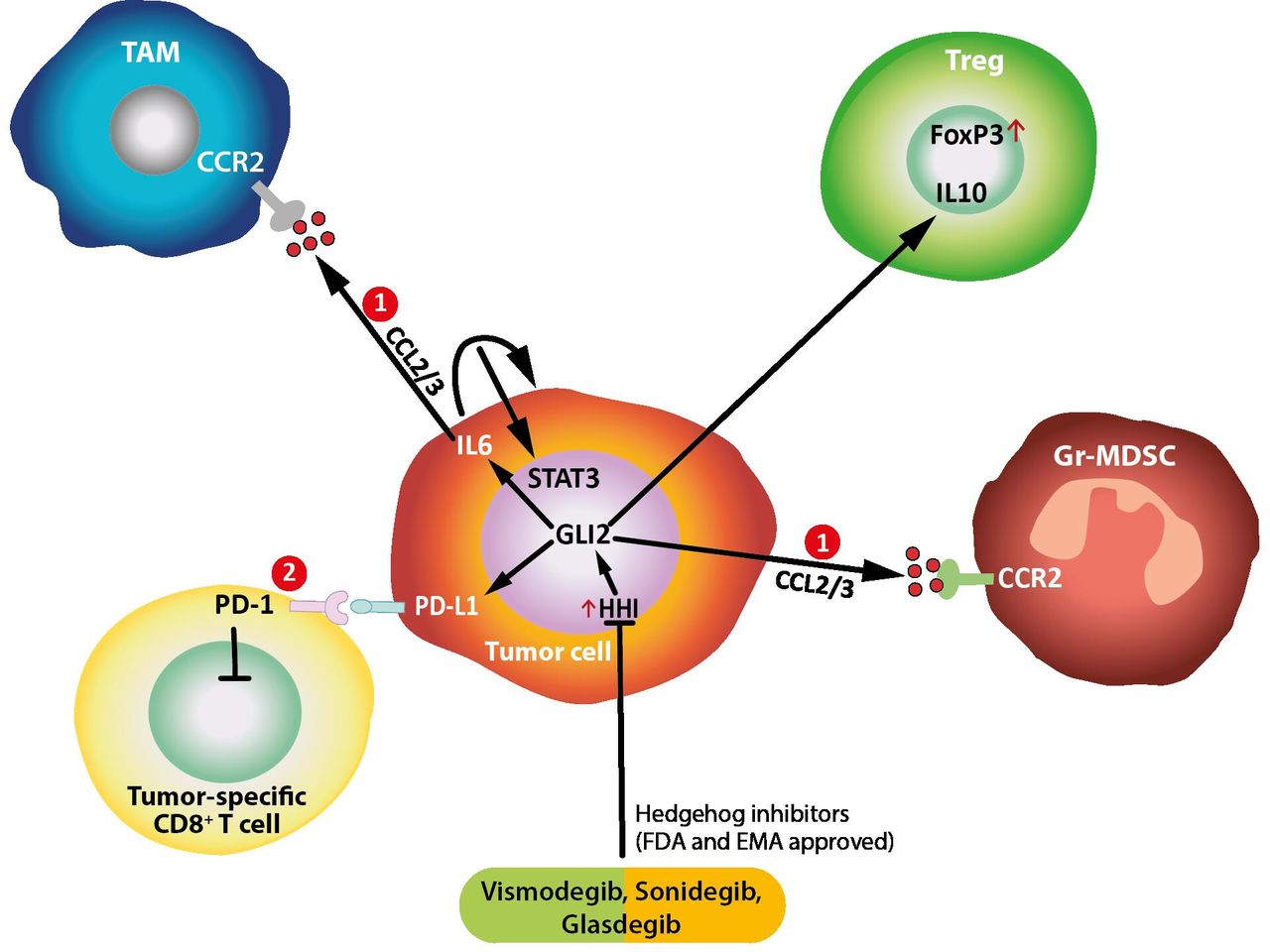
In addition to its developmental functions, the Hedgehog pathway has also been implicated in several diseases, including cancer. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to abnormal cellular behaviors, contributing to tumor growth and progression.
In this article, we will explore 12 extraordinary facts about the Hedgehog signaling pathway, highlighting its intricate mechanisms and its relevance in both normal physiology and pathological conditions.
Key Takeaways:
- The Hedgehog signaling pathway is crucial for embryonic development, cell proliferation, and tissue regeneration. It also plays a role in neural development and stem cell maintenance, with potential therapeutic applications in cancer treatment.
- Cilia, small hair-like structures on cells, are essential for Hedgehog signaling. This pathway is conserved across species and is linked to birth defects and therapeutic targeting in cancer treatment.
The discovery of the Hedgehog signaling pathway
The Hedgehog signaling pathway was first discovered in the early 1980s by developmental biologists studying the embryonic development of fruit flies. They observed that mutations in a specific gene called Hedgehog caused defects in the patterning of the fly’s body segments, resembling a spiky hedgehog. This groundbreaking discovery led to further research on this pathway in various organisms, including humans.
Key role in embryonic development
The Hedgehog signaling pathway plays a crucial role in embryonic development by guiding the formation of various tissues and organs. It helps determine the body axis, limb development, and the differentiation of cells into specific lineages. This pathway is essential for the proper growth and development of organisms from insects to mammals, including humans.
Regulation of cell proliferation
One of the central functions of the Hedgehog signaling pathway is to regulate cell proliferation. It ensures that cells divide and proliferate at the appropriate times and in the proper manner. Disruptions in this pathway can lead to abnormal cell growth and contribute to the development of various diseases, including cancer.
Signal transduction through receptors
The Hedgehog signaling pathway involves signal transduction through two receptors: Patched (Ptc) and Smoothened (Smo). When no Hedgehog ligands are present, Ptc inhibits Smo, preventing downstream signaling. However, when Hedgehog ligands bind to Ptc, it relieves the inhibition on Smo, allowing the cascade of intracellular signaling events to occur.
Activation of Gli transcription factors
Upon activation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway, the Smo receptor triggers a series of intracellular events that ultimately lead to the activation of Gli transcription factors. These factors then translocate to the nucleus and regulate the expression of target genes involved in various cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Hedgehog signaling in tissue regeneration
Recent research has shown that the Hedgehog signaling pathway also plays a crucial role in tissue regeneration. It helps drive the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues, such as in the liver and skin. Understanding the mechanisms behind this process could potentially lead to the development of therapeutic strategies for promoting tissue regeneration in various conditions.
Hedgehog signaling in neural development
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is essential for neural development in organisms. It guides the formation and patterning of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. Defects in this pathway can lead to severe developmental disorders such as holoprosencephaly, where the forebrain fails to divide properly.
Role in stem cell maintenance
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is involved in the maintenance and regulation of stem cells in various tissues. It helps to preserve the stem cell population and control their differentiation into specialized cell types. This pathway is vital for tissue homeostasis and repair, as well as for the potential application of stem cells in regenerative medicine.
Implications in birth defects
Disruptions in the Hedgehog signaling pathway have been associated with a range of birth defects, including craniofacial abnormalities, limb malformations, and heart defects. Understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms involved in this pathway can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of these conditions and potential strategies for prevention or treatment.
Therapeutic targeting of Hedgehog signaling
The Hedgehog signaling pathway has emerged as a promising target for therapeutic intervention, particularly in the field of cancer treatment. Several drugs that specifically inhibit its activity have been developed and approved for the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma, a form of skin cancer. Ongoing research is exploring the potential of targeting this pathway in other types of cancers as well.
Cilia’s role in Hedgehog signaling
Cilia, small hair-like structures protruding from the surface of cells, play a crucial role in Hedgehog signaling. They serve as important hubs for the pathway’s components, facilitating signaling and ensuring its proper regulation. Defects in cilia structure or function can disrupt Hedgehog signaling and lead to developmental abnormalities and diseases.
Conservation across species
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is highly conserved across different species, from fruit flies to humans. This conservation underscores its fundamental importance in development and highlights its evolutionary significance. Studying this pathway in model organisms has provided valuable insights into its mechanisms and biological functions, with implications extending to human health and disease.
Conclusion
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a fascinating and complex mechanism that plays a crucial role in embryonic development and tissue regeneration. It has also been implicated in various diseases, including cancer. Understanding the intricacies of this pathway not only sheds light on fundamental biological processes but also holds great potential for therapeutic interventions.
Through the exploration of 12 extraordinary facts about the Hedgehog signaling pathway, we have delved into its regulatory mechanisms, signaling components, and the impact it has on cellular function. From its discovery in fruit flies to its conserved nature across species, this pathway continues to captivate researchers with its intricate network of interactions.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the Hedgehog signaling pathway, the knowledge gained can lead to novel therapeutic approaches and shed light on the underlying mechanisms of various diseases. Excitingly, this pathway holds promise for future advancements in regenerative medicine and targeted cancer therapies.
FAQs
1. What is the Hedgehog signaling pathway?
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a crucial cellular communication pathway that regulates various developmental processes and tissue homeostasis.
2. How does the Hedgehog signaling pathway work?
The Hedgehog pathway is activated when a ligand, known as Hedgehog, binds to its receptor, leading to a cascade of intracellular events that ultimately regulate gene expression and cell fate determination.
3. What are the components of the Hedgehog signaling pathway?
The main components of the Hedgehog pathway include the ligand (Hedgehog), receptors (Patched and Smoothened), and downstream effectors (Gli family of transcription factors).
4. What role does the Hedgehog signaling pathway play in development?
The Hedgehog pathway is crucial for embryonic development, including the formation of limbs, brain, and organs. It also plays a role in tissue regeneration and maintenance in adult organisms.
5. How is the Hedgehog signaling pathway associated with cancer?
Dysregulation of the Hedgehog pathway is linked to several types of cancer. Mutations or abnormal activation of pathway components can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation.
6. Are there any drugs targeting the Hedgehog signaling pathway?
Yes, there are drugs that specifically target components of the Hedgehog pathway. These drugs have shown promise in the treatment of certain cancers where the pathway is dysregulated.
7. Is the Hedgehog signaling pathway conserved across species?
Yes, the Hedgehog pathway is highly conserved across a wide range of species, from fruit flies to humans. This conservation highlights its fundamental importance in biological processes.
Unraveling the secrets of the Hedgehog signaling pathway is just the beginning of our fascinating journey through the world of cellular communication and development. Dive deeper into the captivating realm of signal transduction, where molecular messages shape the very fabric of life. Explore the intricacies of developmental biology and witness the awe-inspiring process of gastrulation, a crucial stage that sets the stage for the formation of a complex organism from a single cell.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


