Organogenesis is a fascinating biological process that holds the key to the development and formation of organs in living organisms. From the intricate development of vital organs such as the heart and lungs, to the growth of sensory organs like the eyes and ears, organogenesis plays a crucial role in shaping and defining the anatomy and function of different organisms.
In this article, we will explore 17 astonishing facts about organogenesis that highlight the complexity and beauty of this remarkable biological phenomenon. From the early stages of embryonic development to the intricate signaling pathways involved in organ formation, these facts will showcase the incredible intricacies of organogenesis and shed light on the incredible world of developmental biology.
Key Takeaways:
- Organogenesis is the amazing process of forming organs in living beings, involving complex cell interactions and signaling molecules. It’s crucial for organ development and has implications for regenerative medicine.
- Genetic and environmental factors influence organogenesis, and disruptions can lead to birth defects. Understanding this process is key for developing new treatments and approaches in regenerative medicine.
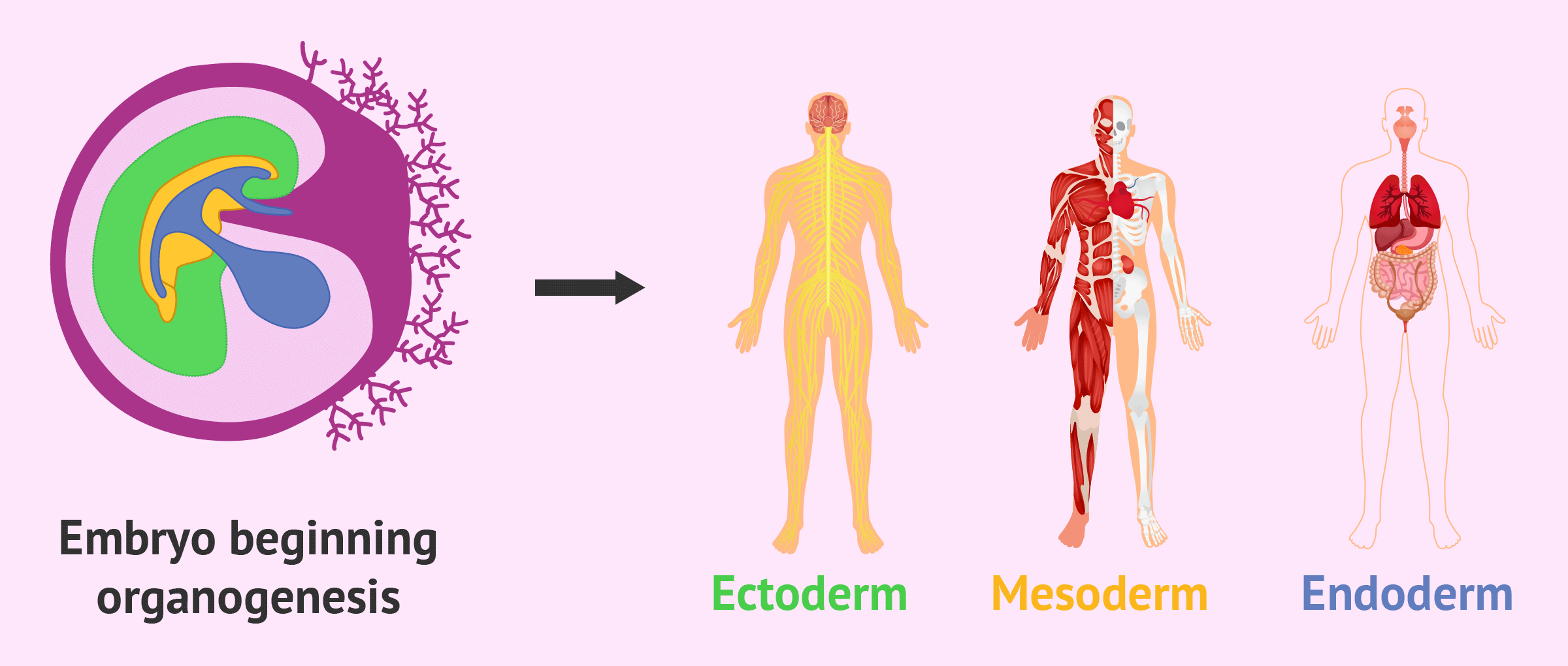
Organogenesis is the process of organ formation in living organisms.
During organogenesis, the cells undergo complex and coordinated interactions to develop into functional organs.
It begins during early embryonic development.
Organogenesis starts when the embryo is just a few weeks old, and continues throughout the gestation period.
The major organs are formed through organogenesis.
Organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and brain all develop through this process.
Organogenesis is regulated by various signaling molecules.
Growth factors and transcription factors play a crucial role in guiding the development of different organs.
It involves the differentiation of stem cells into specialized cell types.
During organogenesis, stem cells differentiate into specific cell types that are required for the structure and function of organs.
Organogenesis is a tightly regulated process.
Precise timing and spatial organization are essential for the proper formation of organs.
Developmental abnormalities can occur during organogenesis.
Disruptions in the process can lead to congenital malformations and birth defects.
Organogenesis continues throughout postnatal development.
While the major organs form during embryonic development, growth and refinement of organs continue after birth.
The process of organogenesis requires intricate cellular communication.
Cells within developing organs communicate through various signaling pathways to ensure proper development.
Organogenesis involves the growth and shaping of tissues.
Tissues expand and undergo morphological changes to form the complex three-dimensional structures of organs.
Regenerative medicine aims to harness the principles of organogenesis.
Scientists are studying organogenesis to develop new approaches for tissue engineering and organ transplantation.
Different organs have distinct patterns of organogenesis.
The process of organ formation varies depending on the specific organ and its function.
Genetic factors influence organogenesis.
Genes play a crucial role in determining the timing and progression of organ development.
Environmental factors can impact organogenesis.
Exposure to certain substances or conditions during pregnancy can disrupt the normal process of organ formation.
Organogenesis is a fascinating area of research.
Scientists are continually uncovering new insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying organ development.
Organogenesis is essential for the survival and function of organisms.
Without proper development of organs, organisms would not be able to carry out vital physiological processes.
The study of organogenesis has significant implications for regenerative medicine.
Understanding the intricate process of organ formation can help guide the development of innovative approaches to treat organ damage and disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organogenesis is a fascinating biological process that plays a crucial role in the development of organisms. Through a series of intricate cellular and molecular events, organs are formed and take on their specific functions.During organogenesis, cells undergo various stages of differentiation and specialization. They organize themselves into specific tissue types and shapes, ultimately forming complex structures like the human heart, brain, and lungs. This process is tightly regulated by genetic programs and signaling pathways.Through organogenesis, the human body and other organisms are able to grow and adapt to their environment. Understanding the mechanisms behind this process is not only of scientific interest but also holds great potential for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.Overall, exploring the astonishing facts about organogenesis reveals the incredible precision and complexity of nature’s design. It reminds us of the wonders of life and the intricacies of our own existence.
FAQs
1. What is organogenesis?
Organogenesis is the process by which organs develop and form during embryonic development. It involves intricate cellular events and molecular signaling to create the specific structures and functions of various organs.
2. How does organogenesis occur?
Organogenesis occurs through a series of steps involving cell differentiation, migration, and morphogenesis. Cellular interactions, genetic programs, and signaling pathways guide the process, ensuring the precise formation of organs.
3. What are some examples of organs formed during organogenesis?
Some examples of organs formed during organogenesis include the heart, lungs, brain, liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs. These organs play vital roles in the functioning of an organism.
4. Can organogenesis be studied in adults?
While organogenesis primarily occurs during embryonic development, certain forms of organogenesis can also happen in adult organisms. For example, the liver has the ability to regenerate and restore its functionality.
5. What is the significance of studying organogenesis?
Studying organogenesis provides valuable insights into the mechanisms that govern organ formation. It has implications for understanding birth defects, tissue regeneration, and the development of therapeutic approaches for various diseases.
6. Are there any disorders or conditions related to organogenesis?
Yes, disruptions in organogenesis can lead to various congenital disorders or birth defects. These conditions can range from mild to severe and may affect the structure or functionality of organs.
Organogenesis is a remarkable process that shapes living organisms. From the intricate signaling pathways to the differentiation of stem cells, this field holds countless wonders waiting to be explored. If you found these facts about organogenesis captivating, why not delve into the extraordinary world of hedgehog signaling? This pathway plays a crucial role in embryonic development and tissue regeneration, offering fascinating insights into the complexities of life.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.