Signal transduction is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in various biological activities and processes. It refers to the transmission of signals from the exterior to the interior of a cell, ultimately leading to a specific cellular response. This intricate mechanism ensures that cells can receive and interpret signals from their environment and effectively respond to changes and stimuli.
Signal transduction is a highly dynamic and complex process that involves numerous molecules, receptors, and signaling pathways. Understanding the intricacies of this process is of paramount importance in biology and has vast implications in fields such as medicine and biotechnology.
In this article, we will delve into the realm of signal transduction and explore twenty extraordinary facts that will ignite your curiosity and deepen your understanding of this fascinating biological phenomenon.
Key Takeaways:
- Signal transduction is like a cell’s messaging system, allowing it to communicate with the outside world and respond to different signals. It’s like a complex network of molecular interactions that keeps cells in the know and helps them stay healthy.
- Abnormal signal transduction can lead to diseases like cancer and diabetes, so it’s super important for cells to get their signals right. Scientists are always discovering new things about signal transduction, like how it can be influenced by drugs and environmental factors.
Signal transduction is a crucial process in cells.
Signal transduction is a vital process that allows cells to receive and interpret signals from their environment, enabling them to respond appropriately to various stimuli.
It involves a complex network of molecular interactions.
Signal transduction pathways consist of intricate networks of proteins, receptors, and second messengers that relay signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, triggering specific cellular responses.
Signal transduction plays a crucial role in cell communication.
Through signal transduction, cells can communicate with each other, coordinating their activities, and responding appropriately to changes in the environment.
Hormones are essential signaling molecules in signal transduction.
Hormones act as signaling molecules that initiate and regulate various physiological processes through signal transduction pathways.
Signal transduction can occur through various mechanisms.
There are several mechanisms by which signal transduction can occur, including receptor-mediated signaling, intracellular signaling cascades, and ligand-receptor interactions.
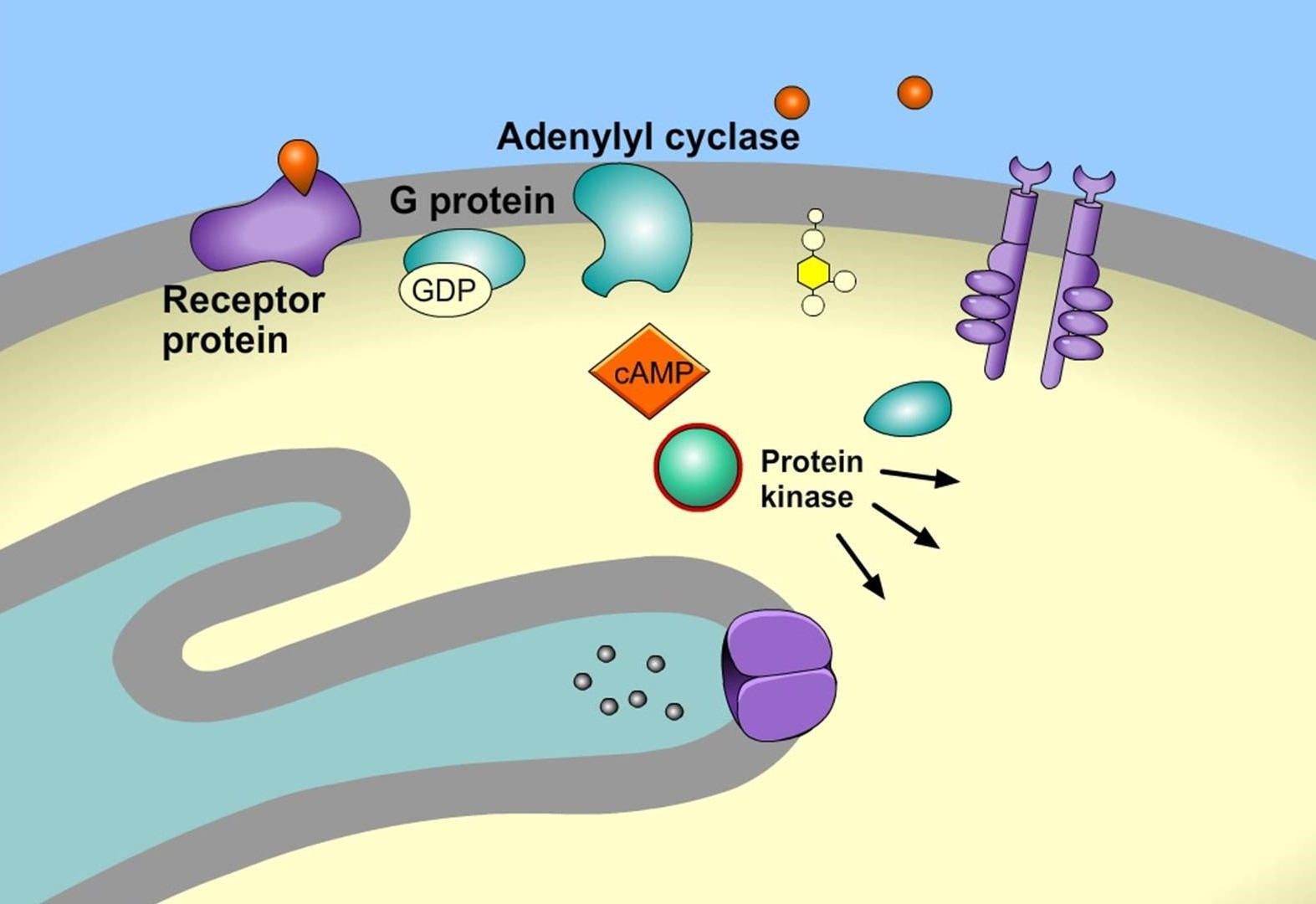
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are key players in signal transduction.
GPCRs are a large family of cell surface receptors that play a crucial role in signal transduction by activating intracellular signaling pathways upon binding to specific ligands.
Protein kinases are important components of signal transduction pathways.
Protein kinases are enzymes that modify other proteins by adding phosphate groups, playing a vital role in transmitting signals through signal transduction pathways.
Signal transduction can occur within seconds.
Some signal transduction pathways can produce rapid cellular responses, with signaling events occurring within seconds of the initial stimulus.
Signal transduction pathways can be highly specific.
Signal transduction pathways can exhibit high specificity, allowing cells to differentiate between various signals and respond accordingly.
Abnormal signal transduction can lead to diseases.
Disruptions or abnormalities in signal transduction pathways can contribute to the development of various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
Signal transduction can be altered by environmental factors.
Environmental factors, such as toxins or pollutants, can interfere with signal transduction pathways, disrupting normal cellular responses and potentially leading to diseases.
Signal transduction is central to the immune system.
The immune system relies on signal transduction to detect and respond to pathogens, initiating an immune response to protect the body from infections.
Signal transduction influences cell growth and development.
Signal transduction pathways play a crucial role in regulating cell growth, development, and differentiation, ensuring proper tissue formation and organogenesis.
Signal transduction can be modulated by drugs and therapeutic interventions.
Understanding signal transduction pathways has paved the way for the development of targeted therapies and drugs that can modulate specific signaling events to treat diseases.
Signal transduction involves the activation of transcription factors.
Upon receiving the signal, transcription factors can be activated in the nucleus, influencing gene expression and leading to specific cellular responses.
Signal transduction can occur in both single-celled organisms and complex multicellular organisms.
Signal transduction is observed across a wide range of organisms, from simple bacteria to complex multicellular organisms like humans.
Signal transduction can result in changes in cellular metabolism.
Signal transduction pathways can regulate cellular metabolism, controlling energy production, nutrient uptake, and other metabolic processes.
Signal transduction can be modified by post-translational modifications.
Post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation or acetylation, can alter the activity of signaling proteins, modulating signal transduction processes.
Signal transduction can involve both positive and negative feedback loops.
Feedback loops are common in signal transduction, where the output of the pathway can either amplify or dampen the initial signal, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Signal transduction is a rapidly evolving field of research.
Scientists are continuously uncovering new insights into signal transduction, deepening our understanding of this complex and fascinating biological process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, signal transduction is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in various biological functions. From allowing cells to communicate and adapt to their environment to regulating numerous physiological processes, signal transduction is truly extraordinary. Through the complex interplay of signaling molecules, receptors, and signaling pathways, cells are able to receive and respond to various external cues, ultimately ensuring their survival and proper functioning.Understanding signal transduction is not only important for advancing our knowledge in biology, but it also has significant implications in medicine and drug development. By studying the intricacies of signal transduction, scientists and researchers can identify potential targets for therapeutic interventions, paving the way for the development of new drugs and treatments for various diseases.The 20 extraordinary facts about signal transduction discussed in this article offer a glimpse into the incredible complexity and versatility of this biological process. Whether it’s the role of G protein-coupled receptors, the involvement of second messengers, or the intricate cross-talk between signaling pathways, signal transduction continues to captivate scientists and researchers alike.Signal transduction is truly a marvel of nature, and further exploration of its mechanisms will undoubtedly help uncover new insights and pave the way for future breakthroughs in the field of biology.
FAQs
1. What is signal transduction?
Signal transduction is the process by which cells receive and respond to external signals or stimuli, such as hormones, growth factors, or neurotransmitters. It involves a series of molecular events that transmit information from the cell surface to the interior of the cell, where specific cellular responses are triggered.
2. How does signal transduction occur?
Signal transduction occurs through a series of steps. It begins with the binding of a signaling molecule to a specific receptor on the cell surface. This binding event initiates a cascade of intracellular events, including the activation of second messengers, the activation of protein kinases, and the subsequent modulation of cellular activities.
3. What are second messengers?
Second messengers are small molecules that amplify and transmit signals from the cell surface to the interior of the cell. Examples of second messengers include cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), inositol trisphosphate (IP3), and diacylglycerol (DAG). They often act as intermediaries between the receptor and the cellular response.
4. What are the key components involved in signal transduction?
Signal transduction involves several key components, including receptors, ligands or signaling molecules, second messengers, protein kinases, and transcription factors. Each of these components plays a critical role in transmitting and translating signals into specific cellular responses.
5. Why is understanding signal transduction important?
Understanding signal transduction is important because it provides insights into how cells communicate and respond to their environment. It has implications in various fields, including medicine and drug development, as targeting specific components of signal transduction pathways can lead to the development of new therapies for diseases.
Signal transduction is a complex and fascinating process, but there's still much to learn. Delve deeper into the intricacies of signal transduction pathways, explore the captivating world of protein trafficking, and unravel the enigmatic nature of kinases. Each topic offers a wealth of knowledge and potential for groundbreaking discoveries. Whether you're a curious student, a seasoned researcher, or simply someone eager to expand their understanding of cellular processes, these articles promise to provide valuable insights and spark your scientific curiosity. Embark on a journey of exploration and let these extraordinary facts guide you through the wonders of cellular communication.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
