Signal transduction pathways are a vital component of biological processes, allowing cells to communicate and respond to external signals. These pathways play a crucial role in the regulation of numerous physiological functions, ranging from embryonic development to immune response. Understanding how these pathways work is fundamental to unraveling the complexities of cellular signaling and uncovering the underlying mechanisms of various diseases.
In this article, we will delve into 11 extraordinary facts about signal transduction pathways. We will explore the intricate signaling cascades that occur within cells, highlighting the key players and their roles in transmitting signals. From ligand-receptor interactions to the activation of downstream effectors, these facts will provide fascinating insights into the remarkable ways in which cells interpret and respond to external cues. So, let’s embark on a journey through the fascinating world of signal transduction pathways and uncover some intriguing secrets along the way.
Key Takeaways:
- Signal transduction pathways are like cellular messengers, helping cells communicate and respond to their environment. They can be targeted by drugs for treating diseases.
- Protein phosphorylation and second messengers are key players in signal transduction, influencing gene expression and cellular processes. Dysregulation can lead to diseases.
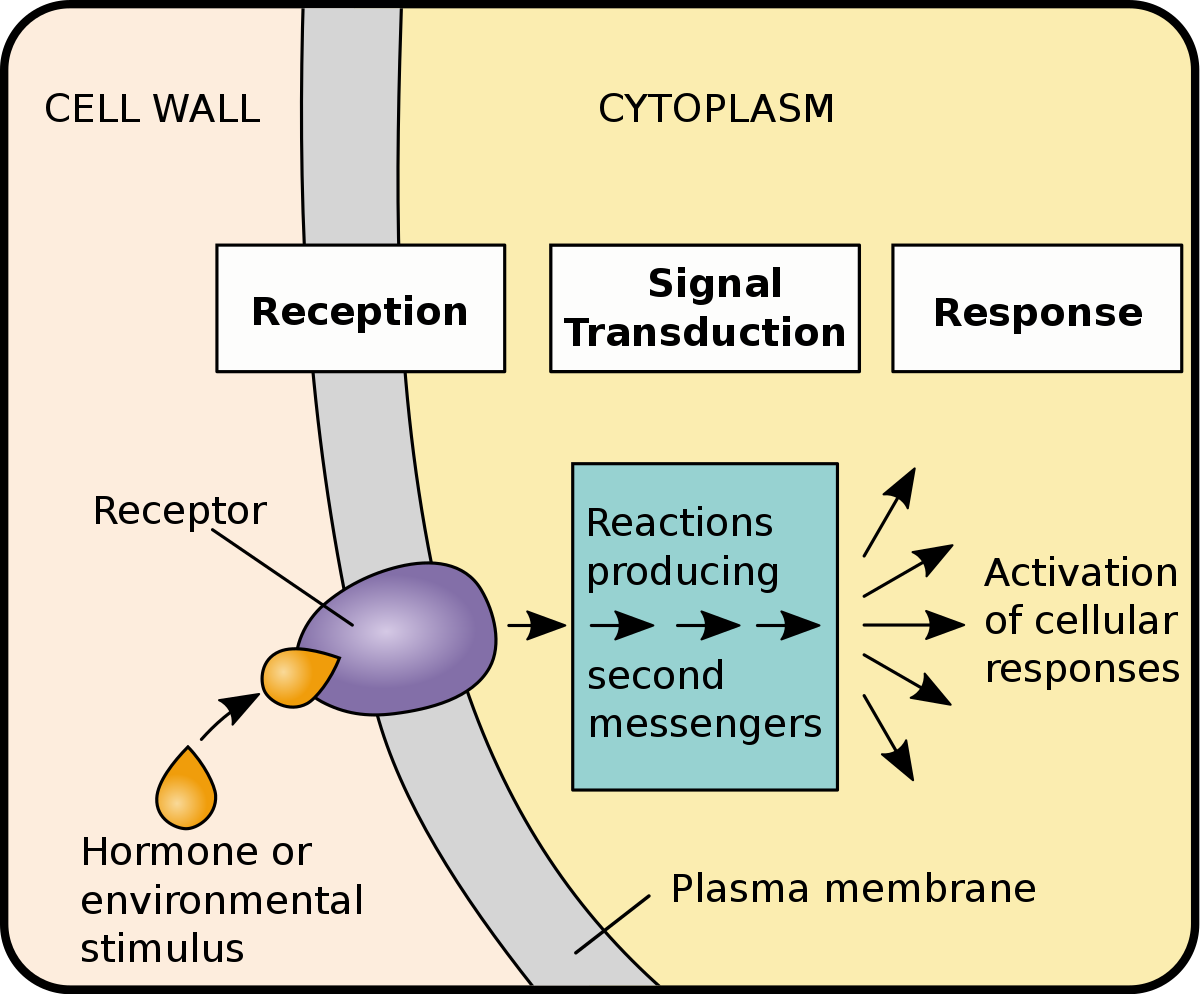
Signal transduction pathways are crucial for cellular communication.
Signal transduction pathways play a fundamental role in transmitting signals from the external environment to the cell’s nucleus, enabling cells to respond to various stimuli.
There are multiple types of signal transduction pathways.
Signal transduction pathways can be categorized into several types, including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) pathways, and intracellular signaling pathways.
Protein phosphorylation is a key event in signal transduction.
Phosphorylation, the addition of a phosphate group to a protein, is a common modification that occurs in signal transduction pathways and is crucial for relaying signals within the cell.
Signal transduction pathways regulate gene expression.
Signal transduction pathways often lead to changes in gene expression, which can ultimately impact cellular processes, development, and even disease progression.
Crosstalk between signal transduction pathways is common.
Signal transduction pathways often interact with one another, allowing for intricate communication and regulation within the cell.
Abnormal signal transduction can lead to various diseases.
Dysregulation of signal transduction pathways has been implicated in numerous diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and autoimmune conditions.
Second messengers play a vital role in signal transduction.
Second messengers, such as cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium ions, serve as intermediaries in signal transduction pathways, amplifying and propagating the signal within the cell.
Signal transduction pathways can be activated by ligand-receptor interactions.
Binding of specific ligands to cell surface receptors triggers signal transduction pathways, initiating a cascade of events that lead to cellular responses.
Signal transduction pathways can exhibit feedback regulation.
Feedback loops within signal transduction pathways allow for precise control and adjustment of cellular responses to changing conditions.
Some signal transduction pathways are involved in developmental processes.
Signal transduction pathways play critical roles in embryogenesis, tissue differentiation, and organ development, ensuring proper growth and morphogenesis.
Signal transduction pathways can be modulated by drugs.
Pharmaceutical agents can be designed to target specific components of signal transduction pathways, making them potential therapeutic interventions for various diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, signal transduction pathways play a crucial role in cellular communication and regulation. Understanding the various components and mechanisms involved in these pathways is essential for unraveling the complexities of biological processes. From the intricate networks of protein interactions to the diverse array of molecules involved, signal transduction pathways provide a fascinating area of study for biologists.
By uncovering the extraordinary facts about signal transduction pathways, we gain valuable insights into the inner workings of cells. From the role of second messengers and protein kinases to the importance of feedback loops and crosstalk, these pathways demonstrate the intricate nature of cellular communication.
As researchers continue to delve deeper into the complexities of signal transduction pathways, we can expect to uncover even more extraordinary facts that will expand our understanding of these fundamental biological processes.
FAQs
1. What is a signal transduction pathway?
A signal transduction pathway is a series of molecular events that allows cells to receive, process, and respond to extracellular signals. These signals can come from various sources, such as hormones, growth factors, or neurotransmitters.
2. What are some common components of signal transduction pathways?
Some common components of signal transduction pathways include receptors, which bind to the signaling molecules; second messengers, such as cyclic AMP or calcium ions; and protein kinases, which modify proteins by adding phosphate groups.
3. How do signal transduction pathways regulate cellular processes?
Signal transduction pathways regulate cellular processes by activating or inhibiting specific genes, enzymes, or other proteins. This can lead to changes in cell proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, or other essential functions.
4. Are signal transduction pathways involved in diseases?
Yes, signal transduction pathways play a significant role in various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Dysregulation of these pathways can disrupt normal cell signaling and contribute to the development of disease.
5. How can studying signal transduction pathways benefit medical research?
Studying signal transduction pathways can provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of diseases. This knowledge can help in the development of targeted therapies that specifically modulate the activity of these pathways, leading to more effective treatments for various diseases.
Signal transduction pathways are truly extraordinary, but there's more to explore in the world of cellular communication. Unravel the captivating process of receptor-mediated endocytosis, where cells selectively internalize molecules from their environment. Dive into the intriguing realm of cGMP, a cyclic nucleotide that plays crucial roles in various physiological processes. Continue your journey through the fascinating landscape of cellular signaling and discover the marvels that await you.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
