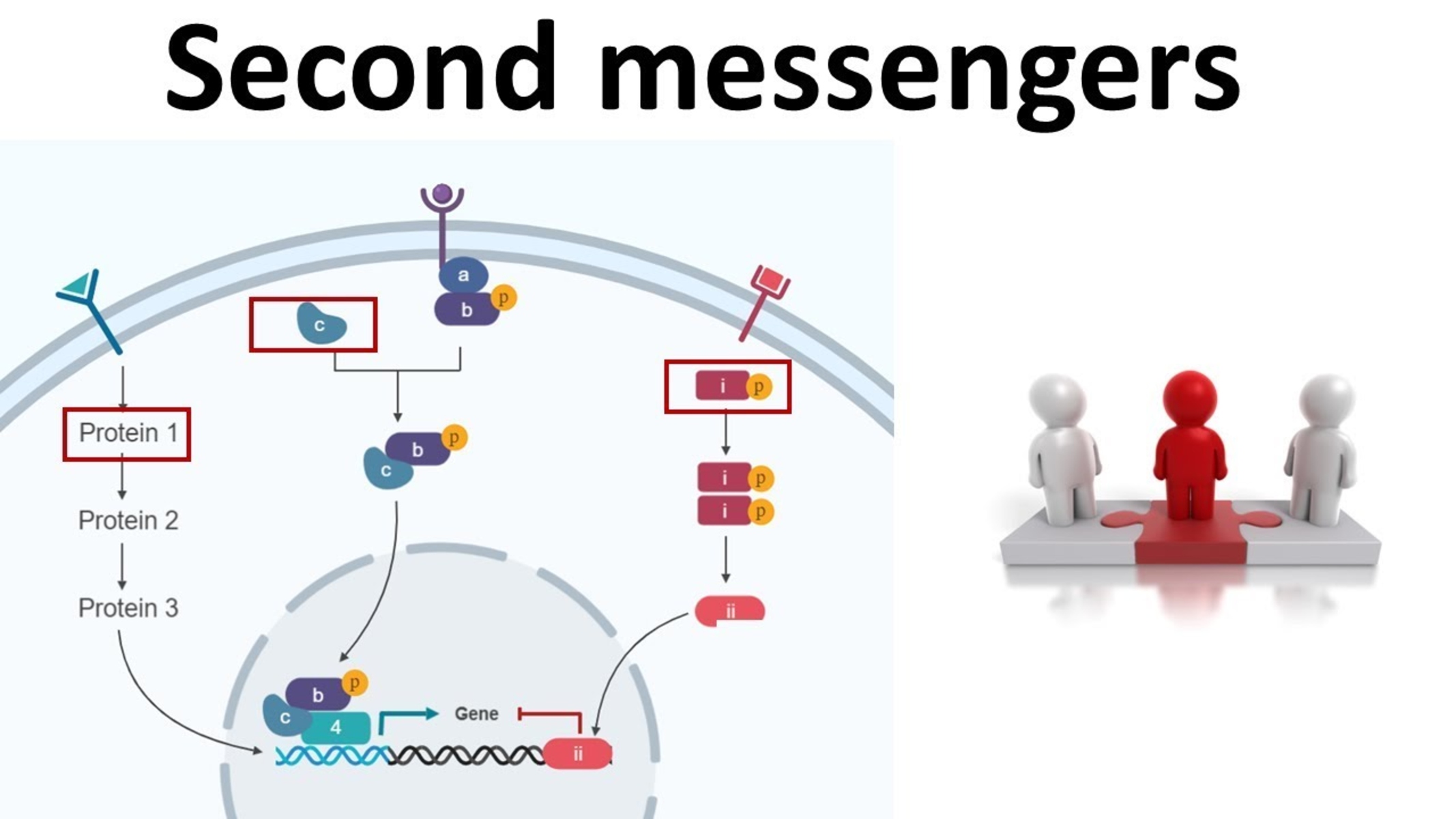
When it comes to the intricate world of cellular signaling, second messengers play a vital role in relaying information from the cell surface to the interior. These small molecules are like messengers, transmitting signals from one part of the cell to another, triggering a cascade of events that ultimately lead to various cellular responses. Second messengers act as intermediaries between extracellular signals, such as hormones or neurotransmitters, and the intracellular signaling pathways that govern cellular processes.
While second messengers have been extensively studied and are well-known among biologists, there are still some mind-blowing facts about these molecules that might surprise you. In this article, we will delve into 13 fascinating facts about second messengers that will leave you in awe of the intricacies of cellular communication.
Key Takeaways:
- Second messengers are like cellular messengers that help cells communicate and control important processes like muscle contraction, gene expression, and even heart rate.
- Understanding second messengers can lead to new medicines and treatments for diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, offering hope for better health in the future.
Second messengers are essential components of cell signaling pathways
Second messengers play a crucial role in transmitting signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, allowing for a wide variety of cellular processes to occur.
The most well-known second messenger is cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
cAMP acts as a signaling molecule in many biological systems, including the regulation of metabolism, gene expression, and neurotransmitter release.
Calcium ions serve as second messengers in numerous cellular processes
Calcium plays a vital role in muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, cell division, and gene expression, among many other functions.
Second messengers can be produced through various signaling pathways
Depending on the specific signaling event, second messengers can be generated by enzymatic reactions, ion channels, or G protein-coupled receptors.
Multiple second messengers can act in synergy to regulate cellular processes
Second messengers such as cAMP, calcium, and diacylglycerol (DAG) can work together to modulate the activity of specific proteins and influence cellular responses.
Second messengers can amplify signals
Due to their ability to activate or inhibit multiple downstream targets, second messengers can greatly amplify signaling cascades, resulting in a more robust cellular response.
Second messengers can have both short-term and long-term effects
While some second messengers mediate immediate cellular responses, others can modulate gene expression, leading to long-lasting changes in cell behavior.
Nitric oxide (NO) acts as a unique second messenger
Unlike other second messengers, NO is a gas that diffuses freely across cell membranes, allowing it to influence neighboring cells and regulate diverse processes.
Second messengers are involved in numerous physiological processes
From regulating heart rate to mediating synaptic plasticity, second messengers are critical for maintaining proper cellular function in various organ systems.
Second messengers can be targeted by drugs for therapeutic purposes
Understanding the role of second messengers in disease pathways has allowed for the development of specific drugs that target these cellular signaling molecules.
Second messengers play a role in cell growth and development
By influencing processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, second messengers contribute to the overall growth and development of an organism.
Dysregulation of second messengers can lead to disease
Imbalances in second messenger signaling have been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular conditions.
Second messengers continue to be a focus of research and discovery
Scientists are constantly uncovering new insights into the complexity of second messenger signaling, paving the way for potential therapeutic interventions in the future.
Conclusion
The 13 mind-blowing facts about second messengers highlight their crucial role in cellular communication and their impact on various physiological processes. From their role in signal amplification to their involvement in disease pathways, the study of second messengers continues to captivate researchers and opens up new possibilities for understanding and treating human health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, second messengers play a fascinating role in cellular communication and signal transduction. These small molecules act as intermediaries, relaying messages from the cell surface to the cell interior, and triggering various biological responses. From their discovery to their diverse functions in different signaling pathways, second messengers continue to captivate scientists and researchers around the world.We have explored 13 mind-blowing facts about second messengers that shed light on their significance in cellular processes. From cAMP and calcium ions to cyclic guanosine monophosphate and inositol trisphosphate, these molecules are the key players in regulating cellular functions such as metabolism, gene expression, and neurotransmitter release.Understanding the intricacies of second messenger signaling not only deepens our knowledge of fundamental biological processes but also holds promise for potential therapeutic interventions. As research in this field continues to advance, we can look forward to unlocking even more astonishing discoveries about the role of second messengers in human health and disease.
FAQs
1. What are second messengers?
Second messengers are small molecules that relay signals from the cell surface to the cell interior, triggering various cellular responses.
2. What are some examples of second messengers?
Examples of second messengers include cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), calcium ions (Ca2+), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), inositol trisphosphate (IP3), and diacylglycerol (DAG).
3. How do second messengers work?
Second messengers typically bind to specific proteins or enzymes, initiating a series of biochemical reactions that ultimately lead to changes in cell function or gene expression.
4. What is the importance of second messengers in cellular processes?
Second messengers are crucial for regulating various cellular processes such as metabolism, cell growth, differentiation, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression.
5. How are second messengers involved in signal transduction?
Second messengers act as intermediaries in signal transduction pathways, relaying signals from cell surface receptors to intracellular targets, amplifying the signal, and influencing cellular responses.
6. Can abnormalities in second messenger signaling lead to diseases?
Yes, disruptions in second messenger signaling have been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, neurological disorders, and metabolic diseases.
7. Are there any drugs that target second messenger signaling?
Yes, several drugs that target second messenger signaling pathways have been developed for therapeutic purposes, such as calcium channel blockers for hypertension and phosphodiesterase inhibitors for erectile dysfunction.
8. How is research on second messengers advancing?
Ongoing research focuses on unraveling the intricate mechanisms of second messenger signaling, identifying new second messengers, and developing innovative strategies to modulate their activity for improved therapeutic interventions.
Intrigued by the captivating world of second messengers? Continue your exploration of cellular communication with our next article, "14 Fascinating Facts About cAMP Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate." Delve deeper into the intricacies of this essential signaling molecule and its pivotal role in various physiological processes. From regulating metabolism to influencing memory formation, cAMP's impact on our bodies is truly remarkable. Prepare to be amazed as we unravel more mind-blowing facts about the incredible world of intracellular signaling!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
