Camp (Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate) is a crucial molecule that plays a central role in various biological processes within the human body. This second messenger is involved in signal transduction, which enables cells to communicate and respond to external stimuli. Camp is an essential regulator of cellular functions and is responsible for processes such as hormone secretion, gene expression, metabolism, and cell growth.In this article, we will explore 14 fascinating facts about Camp, shedding light on its role in different aspects of biology. From its discovery and structure to its significance in various physiological processes, we will delve into the intricacies of this remarkable molecule. So, let’s dive into the world of Camp and uncover the intriguing facts that make it such a crucial component of our biological systems.
Key Takeaways:
- cAMP is like a cell messenger that helps cells talk to each other and control important jobs like breaking down sugar and getting ready for action when we’re stressed.
- Scientists are studying cAMP to make new medicines for things like asthma and memory problems because it’s super important for how our bodies work and stay healthy.
Camp is a crucial component in cell signaling.
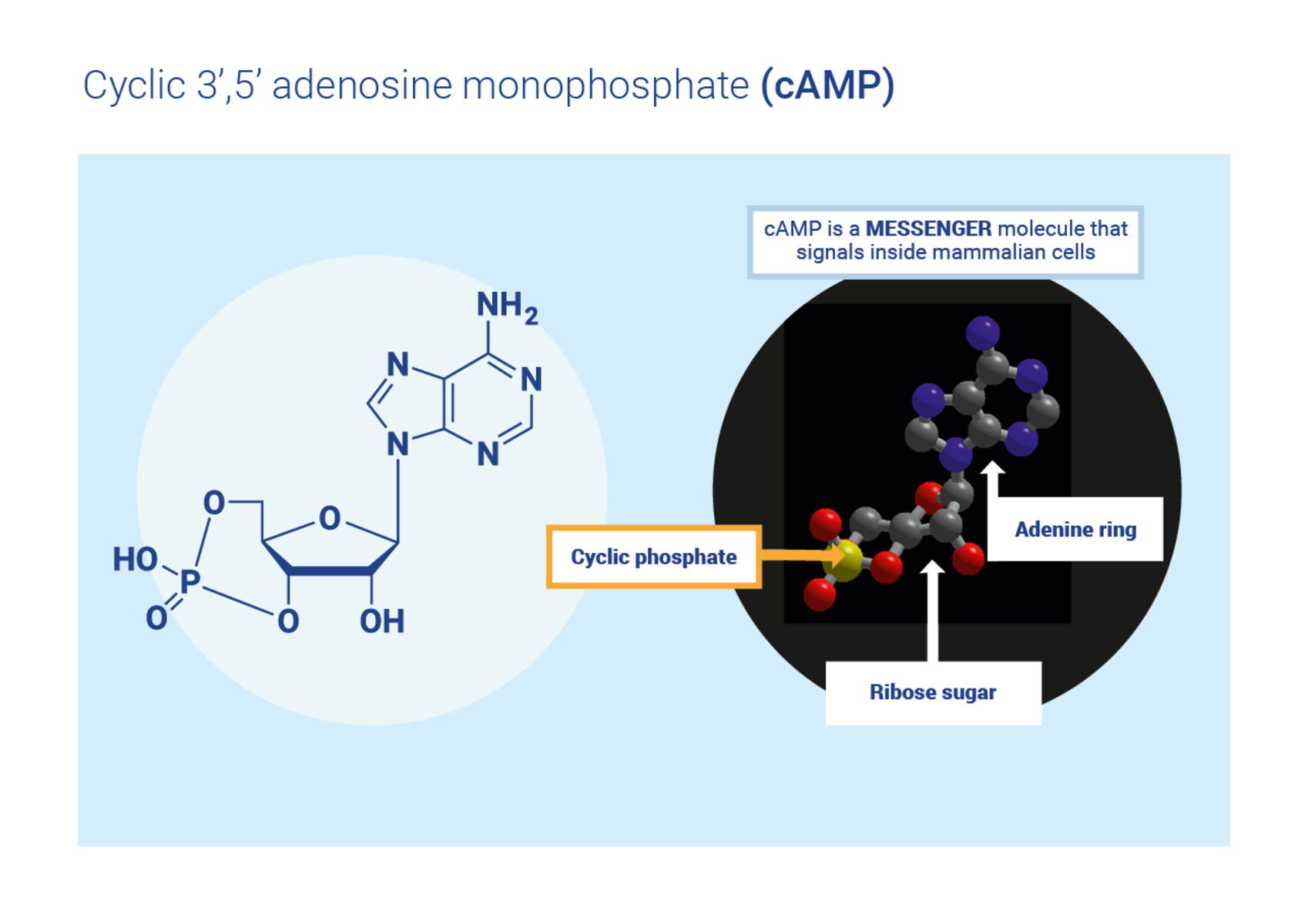
Also known as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, Camp plays a significant role in transmitting signals within cells. It acts as a secondary messenger, relaying information from the cell surface to regulate various cellular processes.
Camp is derived from adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Camp is formed through the enzymatic action of adenylyl cyclase on adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is converted into Camp by the removal of two phosphate groups, resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide.
Camp is involved in the activation of protein kinase A (PKA).
Upon binding Camp, PKA is activated, leading to phosphorylation of target proteins. This phosphorylation process regulates a wide range of cellular functions, including metabolism, gene expression, and cell growth.
Camp regulates glycogen breakdown in the liver.
When blood glucose levels decrease, Camp stimulates the breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver, releasing glucose into the bloodstream. This process helps maintain a steady supply of glucose for energy production.
Camp plays a role in the fight or flight response.
During stressful situations, Camp is released, triggering the fight or flight response. This response prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate, dilating blood vessels, and releasing energy stores.
Camp is involved in neurotransmitter release.
Neurons use Camp as a signaling molecule to regulate the release of neurotransmitters. It plays a critical role in synaptic transmission, modulating communication between neurons in the central nervous system.
Camp is important for learning and memory formation.
Studies have shown that Camp is vital for synaptic plasticity, a process involved in learning and memory formation. It plays a crucial role in strengthening neuronal connections and facilitating long-term potentiation.
Camp is linked to the regulation of circadian rhythms.
Camp has been found to influence the timing of biological processes, including sleep-wake cycles. It interacts with various clock genes and proteins to regulate the body’s internal clock.
Camp is involved in the regulation of gene expression.
Camp, along with PKA, can modulate gene expression by phosphorylating specific transcription factors. This process affects the transcription of genes involved in various cellular processes and can have significant impacts on cell function.
Camp is essential for proper functioning of the immune system.
Camp plays a role in regulating immune responses, including the activation and proliferation of immune cells. It also modulates the production of inflammatory mediators and cytokines.
Camp is used in medical research and drug development.
The study of Camp has led to the development of various drugs for the treatment of diseases such as asthma, inflammation, and cancer. Researchers continue to explore Camp-related pathways for potential therapeutic interventions.
Camp is involved in taste bud signaling.
Signal transduction pathways involving Camp play a role in taste bud activation and perception. Camp is released upon stimulation by tastants, triggering a cascade of events leading to the perception of taste.
Camp levels can be altered by various factors.
Several factors, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and stress, can influence Camp levels within cells. Dysregulation of Camp signaling has been implicated in various diseases and disorders.
Camp is a promising target for therapeutic interventions.
Given its crucial role in cellular signaling, Camp-based therapies are being explored for the treatment of various conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, and cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Camp (Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate) is a fascinating molecule that plays a crucial role in various biological processes. From its involvement in cellular signaling to its impact on metabolism and gene expression, Camp has captured the attention of scientists and researchers around the world.Understanding Camp and its functions not only provides valuable insights into fundamental aspects of biology but also opens doors to new possibilities in fields such as medicine and drug development. Its ability to regulate processes like cell growth, immune response, and memory formation highlights the significance of Camp in maintaining the homeostasis of organisms.As we continue to unravel the complexities of Camp, one thing is for certain – its importance in biological systems cannot be overstated. By diving deeper into the world of Camp, we can gain a deeper understanding of life and discover innovative ways to improve human health and well-being.
FAQs
1. What is Camp (Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate)?
Camp, also known as Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate, is a crucial molecule involved in cellular signaling and the regulation of various biological processes.
2. How is Camp produced in cells?
Camp is synthesized from Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) by the enzyme adenylyl cyclase. It is then broken down by the enzyme phosphodiesterase.
3. What role does Camp play in metabolism?
Camp acts as a secondary messenger in metabolic pathways, regulating processes such as glucose and lipid metabolism, energy production, and adipose tissue breakdown.
4. How does Camp influence gene expression?
Camp modulates gene expression by activating protein kinases, which then phosphorylate transcription factors that regulate the expression of specific genes.
5. Can Camp be targeted for therapeutic purposes?
Yes, researchers are exploring the potential of targeting Camp in the development of drugs to treat various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic disorders.
6. Are there any diseases associated with Camp dysregulation?
Imbalances in Camp levels have been linked to diseases like obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and certain psychiatric conditions.
7. Is there any natural way to increase Camp levels?
Several lifestyle factors, such as exercise, fasting, and certain dietary components, have been shown to increase Camp levels naturally.
8. Can Camp be used in anti-aging research?
There is ongoing research investigating the role of Camp in the aging process, and whether manipulating Camp levels can have anti-aging effects.
9. How does Camp impact memory and learning?
Camp plays a crucial role in synaptic plasticity, which is the basis of learning and memory formation in the brain.
10. Does Camp have any other functions apart from cellular signaling?
Yes, Camp is also involved in the regulation of immune responses, cell growth and differentiation, and hormonal signaling.
Dive deeper into the captivating world of cellular communication and explore more fascinating facts! Unravel the mysteries of signal transduction and discover how cells transmit information. Delve into the intricacies of cell signaling and learn how cells coordinate their activities. Embark on a journey through the complex networks of intracellular signaling cascades and uncover the secrets of cellular decision-making. Get ready to be amazed by the incredible world of cellular communication!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
