It is easy to miss this tiny stuff, but there are things about them that you just could not miss. A few knowledge of bacteria facts would not cost you anything, and could even be helpful in your daily life. Read on these bacteria facts that you could keep in mind for a safer and cleaner daily living.
- Bacteria (singular: bacterium) hails from the kingdom monera and is the simplest unicellular organism.
- Only with powerful microscopes are the bacteria visible to the human eyes as they are the smallest among cells.
- Bacteria are known as the most abundant forms of life.
- Bacteria live everywhere: on land, in water, in the air, and inside the bodies of other living organisms.
- While there are useful bacteria, some could cause diseases.
- A fever is your body’s defense mechanism against infections caused by bacteria.
- Collected bacteria from all over your body could weigh up to 4 pounds.
- Bacteria could enter your body through the mouth, nose or broken skin.
- Some bacteria are useful in making antibiotics.
- Bacteria holds credit for the production of half the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- A baby’s body contains zero (0) bacteria upon delivery.
- Antibacterial components form earwax which is the reason why bacteria or fungus growing inside the ear canal is not possible.
- Due to their complex sugars content, breast milk is more for the enrichment of bacterial growth in the intestines rather than food for the infant.
- Live and dead bacteria make up a big part of human stools.
- The presence of bacteria in the mouth makes a human being’s bite one of the most poisonous in the world.
- Mobile phones contain more bacteria than a toilet’s handles.
- A single dollar bill could be home to at least 300 different types of bacteria.
- Each tooth in the mouth could still have bacteria exceeding 10,000 even after cleaning.
- The number of bacteria present in your mouth is higher than the number of living humans in the world.
- A toilet contains 400 times fewer viruses than your ordinary office desk.
Bacteria are older than dinosaurs.
Research shows that bacteria are already present more than 3 and a half billion years past. As per the researchers, those bacterial particles would still be on Earth even long after the annihilation of the human race.
Bacteria reproduce quickly through binary fission.
This process, also known as “division in half,” is a kind of asexual reproduction and is the most common form among prokaryotes. However, it also transpires in a few single-celled eukaryotes.
The types of bacteria are determined according to their shape, structure, and feeding mechanisms.
Shapes vary from rod-shaped, spiral or spherical ones which are called cocci bacteria. Bacteria found in plants are different from those found in animals. Some are heterotrophic, meaning they feed on organic carbon. Otherwise, they are parasites that either kill or help their host.
Humans were not able to catch sight of them until 1674.
While studying pond water and human mouth scrapings under the newly-invented microscope, Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek detected the tiny floating “animacules”.
Life on Earth could not last without bacteria.
The cycle starts with the release of nitrates from bacteria found in soil. Every single plant needs that substance to be able to produce essential elements called amino acids. From there, the rest follows and the cycle repeats.
A single human cell contains 10 cells of bacteria.
With that 1:10 ratio and the fact that your intestine has more bacteria than the earth has people, therefore, your body is full of bacteria.
Apart from the 99% of good bacteria, the 1% bad bacteria are called “pathogens”.
This type is harmful to the human body and could cause diseases like tuberculosis, pneumonia, cholera, rickets, and plague. Escherichia coli (E.coli), for instance, is a common gastrointestinal tract bacteria and is very much part of the normal bacterial flora. However, some of its strains could produce toxins that could cause serious infections.
In the 1920s, Alexander Fleming warned about the possible resistance of bacteria to antibiotics.
Many doctors and healthcare professionals have been warning us for years now about over use of antibiotics to treat conditions that would be better left alone. The misuse of these drugs leads to the creation of bacteria which become resistant to treatment. We call them superbugs, and cases of them are on the increase. However, the Scottish biologist made the marvelous discovery of penicillin in the 20th century and has served the warning which could be caused by improper overuse.
Bacteria do not cause colds or sore throats; viruses do.
Hence, taking antibiotics could not cure these conditions and could actually cause real harm to your health.
Aside from having individual fingerprints, every single human also has a unique belly button ecosystem.
Different bacteria combinations dwell in each person, as scientists discovered at least 1,458 new bacteria species by only using belly button material. A volunteer was even found to carry Japanese soil bacteria in its belly button despite never being to Japan prior to the experiment.
The bacteria staphylococcus epidermidis is responsible for the body odor associated with sweating.
Human sweat is originally odorless. However, this bacteria which resides on human skin combine with other microorganisms and produce essences from sweat, thus, the smell. These bacteria inhabit mainly sweaty parts like armpits, but they could also be in your nostrils and your back.
A gene could prevent the production of sweat, therefore the absence of the body odor bacteria.
If you live in the Far East, particularly in East Asia, you may have a particular gene mutation called ABCC11 which will mean that you do not sweat, or produce sweat that attracts bacteria. Therefore you won’t suffer from body odour. Other people across the world have this gene too, but it is most prevalent in East Asia.
Gonorrhea bacteria is a type of bacteria that could lift up to 100,000 times their own weight.
For comparison, ants are considered as the strongest creatures for their ability to carry things that are 100 times greater than their own body weight.
Chocolate is an antibacterial food.
Contrary to popular belief that this sweet stuff ruins your teeth, chocolate protects your teeth and helps fight against germs that make tooth decay.
Australian physician Barry Marshall proved that bacteria is the cause of stomach ulcers.
For his experiment, he downed a beakerful of bacterial culture to show that stress is not the culprit for stomach ulcers. This research won him the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 2005 after developing stomach ulcers from the deliberate culture consumption.
Bacterial strains have a role in a lesser-known treatment method for cancer.
It is a given that chemotherapy is the most famous method, but there are also other alternatives. One is where depleted bacterial strains of bovine tuberculosis undergo urethral delivery and eradicate cancer cells, thanks to the immune response as a result. The method is also known to be safer than that of chemo.
Bacteria from worms have healing benefits.
Wounded soldiers during the civil war were exposed to infection by worms. Bioluminescent bacteria springs from these worms. They could not only glow in the dark, but they could also eliminate pathogens. Therefore, soldiers gain an increase in life expectancy.
Adults are immune to C. botulinum, a bacteria that produces toxic poison.
However, the immune system of infants is yet to be resistant to the bacteria. These bacteria, which flourishes in honey, are the cause for botulism and could annihilate the entire population of the United States with as little as a properly-distributed spoonful.
Those morning mouth chunks are bacteria.
No, those white bits of foul smells that you find in your mouth in the morning are not pieces of any food. They are formed by bacteria and sweat from the tonsils which have hardened overnight.
Bacteria are also used in the creation of many foods.

Research promotes the benefits of having good bacteria in foods and how their presence aids digestion. Examples of bacteria-rich common snacks are selected cheeses, yogurt, sourdough bread, and pickles. Other foods that are just rising into fame are tempeh, miso, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir.
Bacteria could enter and grow inside an egg.
A thin organic layer protects eggs that have not yet been washed. This cover allows for a safe shelf-storage for them. However, washing the eggs removes the protective layer. The egg is then exposed to bacteria that could enter through the surface’s tiny pores.
A particular bacteria species travels in its environment through magnetic fields.
Called the magnetospirillum magneticum, this species embodies the free iron radicals present in its surroundings. It then converts the elements into active magnetite, aligning it in its body like a spine that could be used in traveling.
Bacteria found in our guts aid in food digestion.
Moreover, further research shows that such microbial diversity has the ability to either cause or prevent obesity. Hopes are up that science could one day solve how bacteria could keep bodies slim through studies of human bacteria in mice guts.
Store-bought mayonnaise was once suspected of causing food poisoning.
This claim was later proven false, given the fact that mayo prevents bacteria from growing in food. Other ingredients for the picnic could be the real cause, though, like meat.
One of the most numerous living organisms on Earth is the eubacteria, or "true" bacteria.
These unicellular species belong to the domain bacteria and exist at 40 million per single soil gram. All over the world, 4,000 different species of bacteria exist even in the extremities of volcanoes, radioactive waste, and deep layers of the Earth’s crust.
A certain type of bacteria is responsible for the scent that you smell when it rains.
It is called actinomycetes, and it could be found on the soil. As much as it causes the smell that emanates after the rain, it is also the cause behind the earthy taste in water.
Using a paper towel is safer than using a hand dryer, in contrast to what many believe.
The hand dryer-over-paper towel thought follows the idea that there is no contact involved with the machine. The truth is that paper towels could help decrease the number of bacteria by 45-60%. On the other hand, the hand dryer procreates moist and warm environments that are perfect growing places for bacteria. Hence, bacteria count rises up to 255% with the hand dryer.
Kangeroo bacteria might hold the key to stop greenhouse gas emissions.
Kangaroos don’t break wind! In fact they don’t produce any methane at all in their stomachs. Scientists are intrigued by this and are now trying to harvest the bacteria they have in their colons to see if there is anything in there that could potentially help with reducing greenhouse gases. The worst offenders for producing methane in the animal world are cows – and researchers are hopeful that whatever they discover in the tummies of kangaroos can somehow be transferred into cows to reduce the emissions they produce.
Scientists have used bacteria from cows to treat bladder cancer.

Cattle which suffer from bovine tuberculosis have samples taken from them, which are then cultured and weakened in a laboratory. The resultant bacteria is then injected into the urethra of people who have bladder cancer. This treatment has shown itself to be very effective and has even outperformed chemotherapy in terms of its ability to manage the disease.
Bacteria could survive without food.
In cases where they ran out of resources, they deliberately stop meddling with the mechanisms inside them. This action is in confidence that beneficial changes could equip their survival under such conditions, and is a classic example of something called active evolution.
Scientists have found 8-million-year-old bacteria in ice.
This ice was found in a glacier in Antarctica about 16 feet below ground in 2007. Scientists isolated and resuscitated some of the bacteria and organisms in it, and found they were up to 8 million years old. Some of these are now being grown in laboratories, but would cause little to no harm to humans now. When ice melts because of global warming, these bacterial colonies will come back to life, so scientists are keen to find out what they are and how they will develop.
Bacteria may be able to clean up serious oil spills in the future.
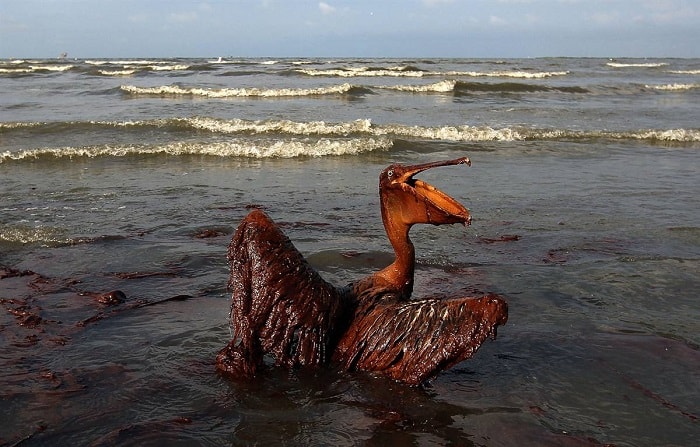

Over the last few years we have seen some terrible and destructive oil spills – one of the worst in memory was the spill caused by BP in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010. The damage to plant and marine life is incalculable. Scientists in the USA are working on developing strains of bacteria that want to eat oil. In the future, if such disasters occur again, they can release colonies of these organisms into the water and earth, destroying the oil without detriment to the environment.
The US Navy once undertook a mission involving bacteria.
Operation Seaspray took place during the 1950s in San Francisco. The US Navy took balloons and filled them with various pathogens. These were then released and burst into the air over the city. A short while after this occurred, doctors in the city reported that there was a sharp increase in the number of people reporting to them with pneumonia and urinary infections.
The experiment was set up to see how, if the USA underwent a biological attack with nuclear weapons, the wind would carry the released particles, and how they might possibly affect people’s health.
Listening to music can create bacteria.
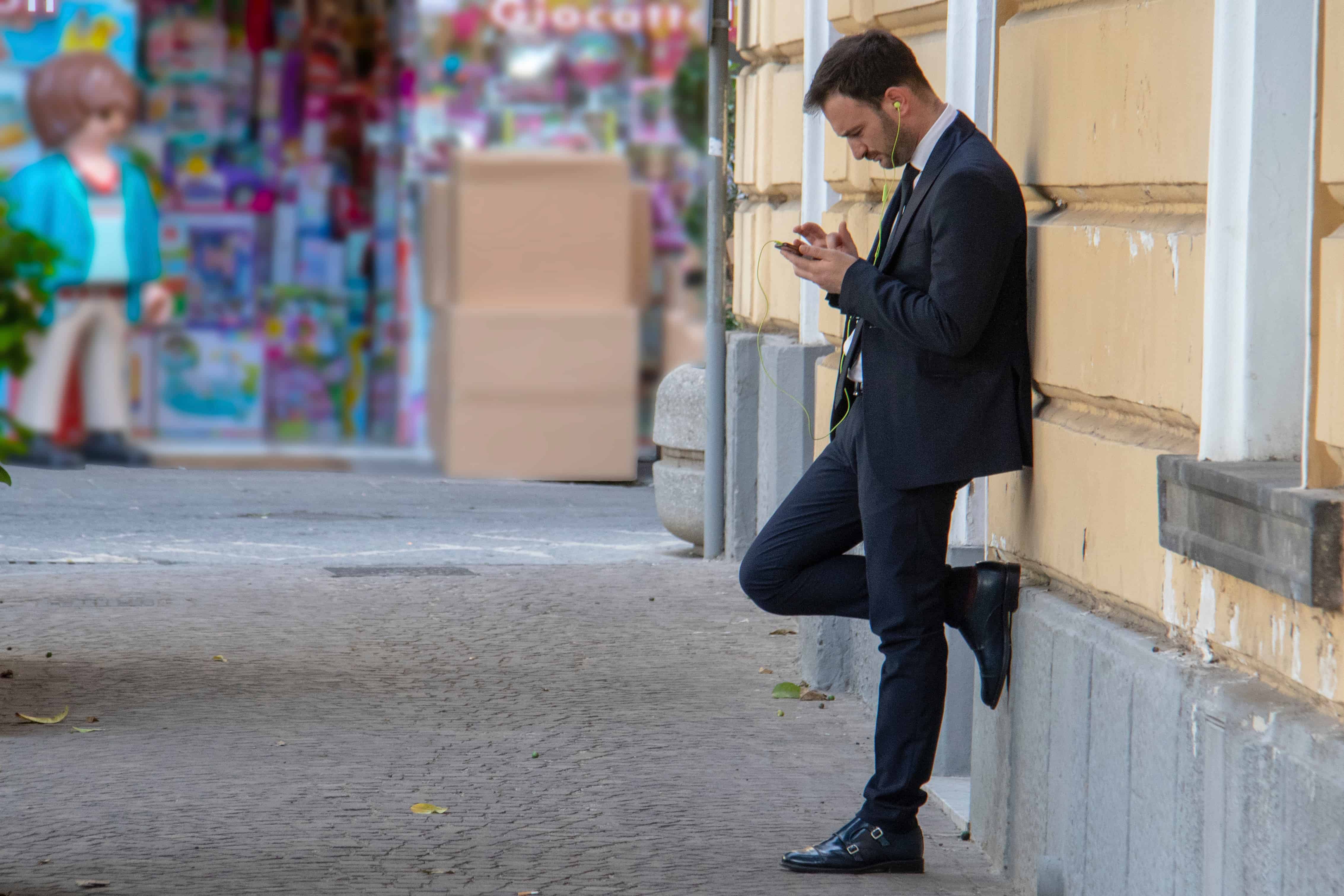

Strange but true: you might not think about this, but every time you put your headphones on to listen to your favourite tunes, you’re exposing yourself to millions of bacteria that mutate. Listening to music through earphones or headphones for just one hour a day can multiply the amount of bacteria in your ears 700 times over!
Warner Brothers promoted bacteria through their film “Contagion.”
In the movie, they used fungi and bacteria contained in two big Petri dishes. The setting was a Toronto storefront, with the story following the growth of the organisms in the vessels and how they formed the biohazard symbols as well as the film name.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


