The biogeochemical cycle is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of life on Earth. It refers to the flow and recycling of essential elements, such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, through biological, geological, and chemical processes. Understanding these cycles is essential in comprehending the intricate relationship between living organisms and their surrounding environment.
In this article, we will explore 20 astounding facts about the biogeochemical cycle that will leave you in awe of the intricate and dynamic nature of our planet’s ecosystems. From the significance of these cycles in sustaining life to the impact of human activities on their disruption, we will delve into the depths of this captivating subject.
Key Takeaways:
- The biogeochemical cycle is a natural process that moves essential nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus through the environment, helping plants and animals grow and thrive.
- Human activities can disrupt the biogeochemical cycle, leading to environmental issues like climate change and nutrient pollution. Understanding and protecting this cycle is crucial for our planet’s health.
The biogeochemical cycle involves the movement of nutrients.
The biogeochemical cycle facilitates the movement of essential nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur among the atmosphere, living organisms, and the Earth’s geosphere.
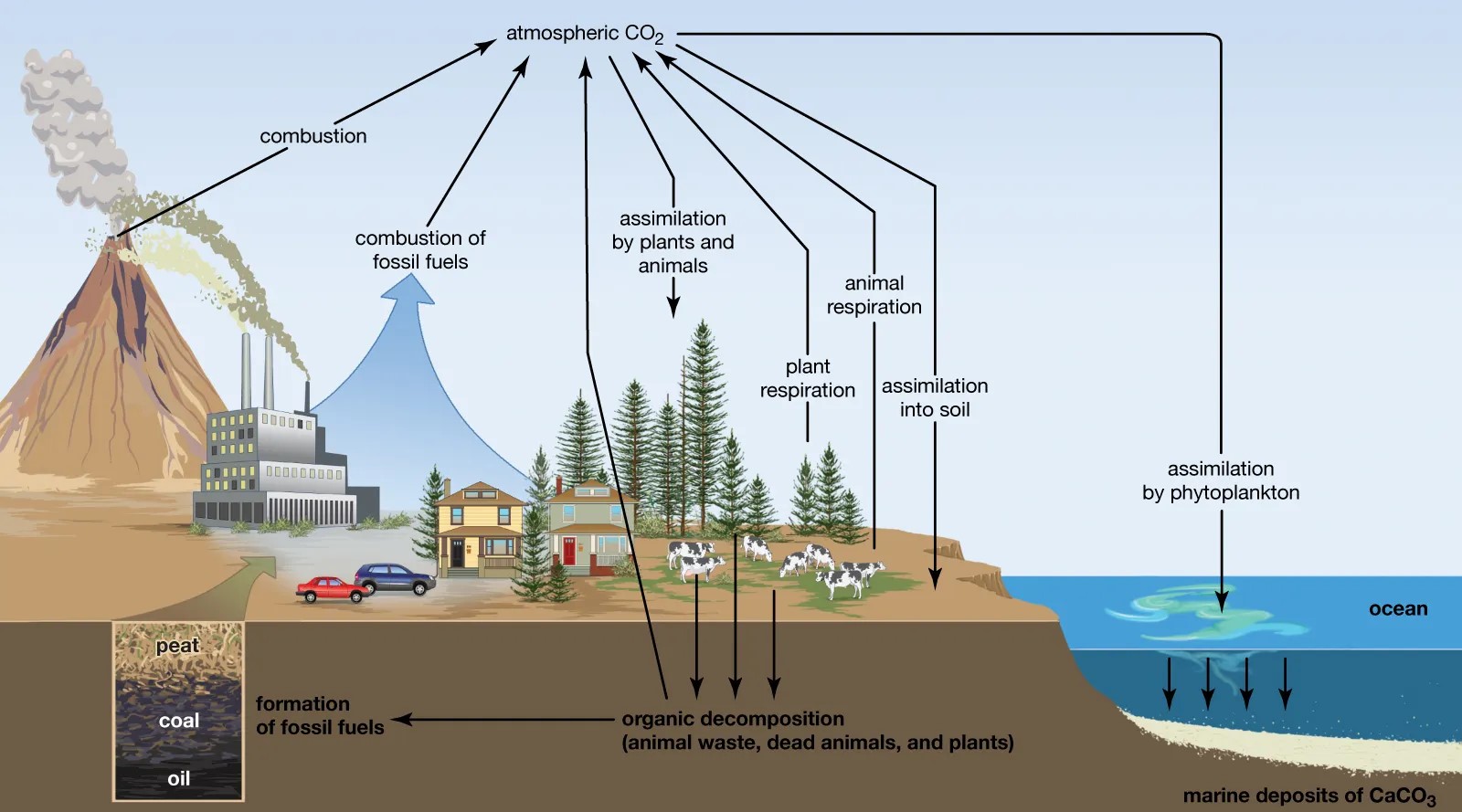
The carbon cycle is a vital part of the biogeochemical cycle.
The carbon cycle involves the exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and plants through photosynthesis, as well as the release of carbon dioxide through respiration and decomposition.
The nitrogen cycle helps convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms.
Nitrogen fixation is a key process in the biogeochemical cycle, where specialized bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that can be utilized by plants and other organisms.
The phosphorus cycle is essential for plant growth.
Phosphorus, a crucial nutrient for plants, is cycled through soil, water, and living organisms, enabling its uptake by plants for growth and development.
The sulfur cycle plays a role in atmospheric processes.
Sulfur compounds are released through volcanic eruptions and industrial activities, with some being converted into sulfate and incorporated into the soil or released back into the atmosphere.
The water cycle is closely connected to the biogeochemical cycle.
The water cycle involves the movement of water through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, enabling the transport of dissolved nutrients in the form of runoff or groundwater.
Human activities can disrupt the biogeochemical cycle.
Activities such as deforestation, burning of fossil fuels, and excessive fertilizer use can alter the natural balance of the biogeochemical cycle, leading to environmental issues such as climate change and nutrient pollution.
The biogeochemical cycle helps regulate Earth’s climate.
The exchange of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, within the biogeochemical cycle has a significant impact on Earth’s climate by influencing the planet’s temperature and weather patterns.
Organisms play a crucial role in the biogeochemical cycle.
From bacteria that fix nitrogen to decomposers that break down organic matter, organisms of all sizes contribute to the cycling of nutrients in various habitats and ecosystems.
The biogeochemical cycle is a dynamic, interconnected system.
All the different cycles within the biogeochemical cycle interact with and depend on one another, creating a complex web of interconnections and feedback mechanisms.
The biogeochemical cycle operates on multiple time scales.
The cycle can occur over short time scales, such as the rapid uptake and release of carbon dioxide by plants, or over longer time scales, such as the slow weathering of rocks and minerals.
Microorganisms play a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
Bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms are responsible for various processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, and decomposition, which are essential for nutrient cycling.
The biogeochemical cycle is impacted by climate change.
Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and carbon dioxide levels due to climate change can alter the rates and patterns of nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
The biogeochemical cycle supports biodiversity.
By providing essential nutrients to different organisms, the biogeochemical cycle supports the diverse array of species found in various ecosystems around the world.
The biogeochemical cycle influences ocean chemistry.
The exchange of carbon and other elements between the atmosphere and the oceans affects the pH and chemical composition of seawater, which in turn impacts marine life.
Human intervention can help restore or enhance the biogeochemical cycle.
Efforts such as reforestation, sustainable farming practices, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions can help restore and preserve the balance of the biogeochemical cycle.
The biogeochemical cycle has geological implications.
Over long periods, the movement of elements through the biogeochemical cycle can result in the formation of minerals, rocks, and even fossil fuels that have significant geological importance.
The biogeochemical cycle is influenced by weathering processes.
Chemical and physical weathering of rocks release essential elements, such as phosphorus, into the soil, where they can be taken up by plants and contribute to the cycle.
The biogeochemical cycle is a fundamental aspect of Earth’s biosphere.
From the microscopic to the global scale, the biogeochemical cycle shapes the dynamics and functioning of ecosystems, making it a critical component of the Earth’s biosphere.
Understanding the biogeochemical cycle is crucial for environmental stewardship.
By studying and comprehending the intricacies of the biogeochemical cycle, we can make informed decisions and take actions to protect and sustain our planet’s delicate balance of nutrients and resources.
Conclusion
The biogeochemical cycle is an incredible process that plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our planet’s ecosystems. From the cycling of essential elements and nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, to the intricate dance between living organisms and their environment, the biogeochemical cycle highlights the interconnectedness of all life forms on Earth.
By understanding the biogeochemical cycle, scientists and researchers can gain insights into the impacts of human activities, such as deforestation and pollution, on these delicate processes. This knowledge is vital for developing sustainable solutions to combat climate change, protect biodiversity, and ensure the well-being of both present and future generations.
As we continue to explore and study the biogeochemical cycle, it is clear that the more we know about this remarkable system, the better equipped we will be to address the environmental challenges facing our world.
FAQs
1. What is the biogeochemical cycle?
The biogeochemical cycle refers to the flow and recycling of essential elements and nutrients between living organisms, the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, and the lithosphere.
2. Why is the biogeochemical cycle important?
The biogeochemical cycle is vital as it controls the availability of essential elements and nutrients, regulates climate patterns, supports ecosystem functions, and sustains life on Earth.
3. What are the main components of the biogeochemical cycle?
The main components of the biogeochemical cycle include the atmosphere, lithosphere (earth’s crust), hydrosphere (water bodies), living organisms, and the processes that enable the cycling of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and oxygen.
4. How do human activities affect the biogeochemical cycle?
Human activities such as deforestation, burning fossil fuels, and excessive use of fertilizers can disrupt the biogeochemical cycle, leading to imbalances in nutrient cycles, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and environmental degradation.
5. How can we promote a healthier biogeochemical cycle?
We can promote a healthier biogeochemical cycle by practicing sustainable land and water management, reducing pollution and waste, conserving natural resources, and adopting eco-friendly practices in agriculture, industry, and transportation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
