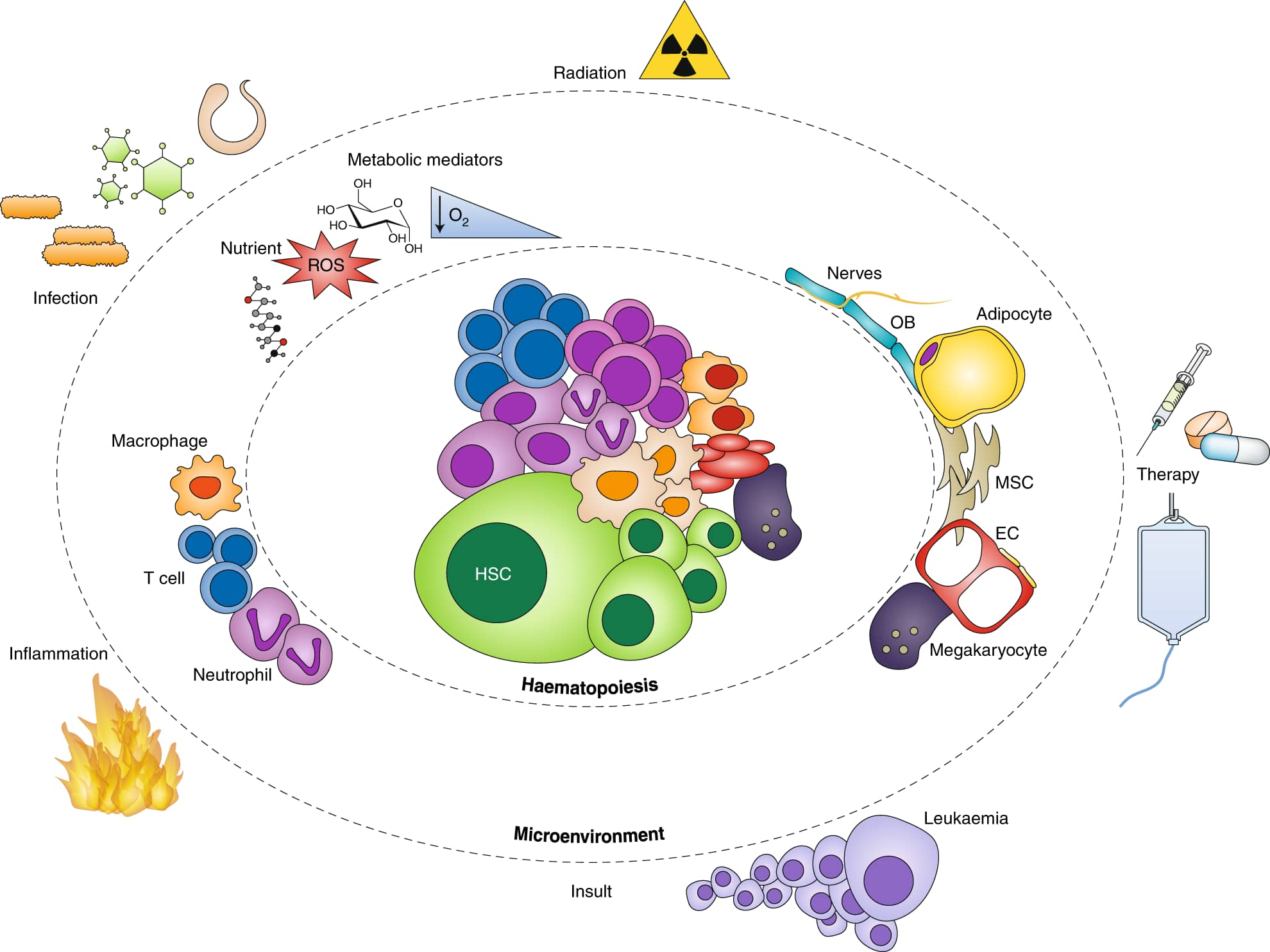
Stem cells have long been a topic of fascination and scientific research. These remarkable cells have the ability to differentiate into various specialized cell types, making them a valuable tool in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. But have you ever wondered where these wondrous cells reside within our bodies? Enter the concept of stem cell niches.
Stem cell niches are microenvironments that provide the necessary signals and support for stem cells to thrive and self-renew. These niches can be found in different organs and tissues throughout the body, and they play a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and promoting regeneration.
In this article, we will dive into the world of stem cell niches and explore 19 intriguing facts about them. From the diverse locations where they can be found to the mechanisms that regulate their function, we will unravel the secrets of these specialized microenvironments and gain a deeper understanding of their importance in the field of stem cell biology.
Key Takeaways:
- Stem cell niches are special places in the body where stem cells live and interact with other cells. They help the body make new cells and repair damaged tissue.
- Scientists study stem cell niches to learn how they work and how they can be used to help people with diseases and injuries. They are like little repair shops inside our bodies!
Stem cell niches are specialized microenvironments.
Stem cell niches provide the necessary conditions for stem cells to self-renew and differentiate into specialized cell types.
Stem cell niches exist in various tissues and organs.
These niches can be found in bone marrow, skin, brain, liver, and many other tissues, ensuring the continuous regeneration and repair of cells in the body.
Stem cell niches maintain the balance between self-renewal and differentiation.
The molecular and cellular components within the niche regulate the delicate balance between stem cell division and the production of specialized cells.
Stem cell niches provide physical support.
The extracellular matrix within the niche provides a physical framework for stem cells to anchor and interact with neighboring cells.
Stem cell niches regulate stem cell behavior.
The niche influences stem cell proliferation, quiescence, migration, and fate determination through complex signaling pathways.
Stem cell niches can be influenced by external factors.
Environmental cues, such as injury or disease, can impact the functionality of stem cell niches and alter stem cell behavior.
Stem cell niches can undergo remodeling.
In response to tissue regeneration or repair, the structure and composition of stem cell niches can be dynamically modified.
Stem cell niches house both active and quiescent stem cells.
While active stem cells are continuously dividing, quiescent stem cells are in a dormant state until activated by specific signals.
Stem cell niches play a vital role in tissue regeneration.
By providing a reservoir of stem cells, niches contribute to the replenishment of damaged or lost tissue.
Stem cell niches are influenced by age.
As we age, the functionality of stem cell niches can decline, leading to reduced regenerative capacity.
Stem cell niches can be artificially engineered.
Scientists can recreate stem cell niches in the laboratory to study stem cell behavior and develop regenerative medicine approaches.
Stem cell niches are involved in cancer progression.
Abnormalities within stem cell niches can contribute to the initiation and growth of cancerous cells.
Stem cell niches can be targeted for therapeutic interventions.
By manipulating the components of stem cell niches, it is possible to enhance tissue repair and regeneration.
Stem cell niches are influenced by hormonal signals.
Hormones can modulate the behavior of stem cells within their niches, affecting their self-renewal and differentiation abilities.
Stem cell niches can exhibit spatial organization.
Within certain tissues, stem cell niches are organized in specific patterns, ensuring the proper distribution and function of stem cells.
Stem cell niches communicate with the immune system.
Immune cells within the niche can either promote or inhibit stem cell activity depending on the immune response required.
Stem cell niches can be influenced by nutrition.
The availability of nutrients and metabolic factors can impact the function and maintenance of stem cell niches.
Stem cell niches can be protective against DNA damage.
The microenvironment of the niche can provide a protective shield for stem cells, preventing DNA damage and maintaining their integrity.
Stem cell niches hold potential for regenerative therapies.
By understanding the intricacies of stem cell niches, researchers aim to harness their power for developing novel regenerative therapies for various diseases and injuries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stem cell niches are fascinating and vital components of the body that play a crucial role in stem cell maintenance and regulation. These specialized microenvironments provide a nurturing and supportive environment for stem cells, allowing them to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types as needed. Through a complex interplay of signaling molecules and physical cues, stem cell niches ensure the balance between stem cell proliferation and differentiation, ultimately contributing to tissue homeostasis and regeneration.Studying stem cell niches and understanding their intricate mechanisms can have significant implications in regenerative medicine and disease treatment. By harnessing the power of these niches, scientists can potentially manipulate stem cells to replenish damaged or diseased tissues, offering hope for conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and heart disease.As research in stem cell biology progresses, it is becoming increasingly clear that unraveling the mysteries of stem cell niches will lead to groundbreaking advancements in medicine and healthcare. By harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells and optimizing their niche environments, we hold the key to unlocking the full therapeutic potential of these remarkable cells.
FAQs
Q: What is a stem cell niche?
A stem cell niche is a specialized microenvironment in the body that supports and regulates the behavior of stem cells. It provides the necessary signals and physical cues for stem cells to self-renew or differentiate into specific cell types.
Q: Where are stem cell niches found in the body?
Stem cell niches are found in various locations throughout the body, including the bone marrow, skin, intestines, brain, and hair follicles. Each organ or tissue has its own unique niche that is tailored to the specific needs of the resident stem cells.
Q: How do stem cell niches regulate stem cell behavior?
Stem cell niches regulate stem cell behavior through a combination of chemical signals and physical interactions. These cues can include growth factors, extracellular matrix components, cell-cell adhesion molecules, and neighboring cells. The niche creates a microenvironment that directs stem cell fate, determining whether they will self-renew or differentiate.
Q: Why are stem cell niches important in regenerative medicine?
Stem cell niches are essential in regenerative medicine because they provide the ideal conditions for stem cells to thrive and function optimally. By understanding and manipulating the niche environment, scientists can enhance stem cell-based therapies and potentially regenerate damaged or diseased tissues.
Q: Can stem cell niches be artificially created?
While creating an exact replica of a natural stem cell niche is challenging, scientists are making progress in artificially recreating certain aspects of these microenvironments. By studying the key components of stem cell niches and mimicking their signaling cues and physical properties, researchers aim to develop synthetic niches that can support stem cell growth and differentiation in the laboratory.
Stem cell niches offer a fascinating glimpse into the intricate world of cellular biology. Exploring their role in maintaining and regulating stem cells opens doors to groundbreaking discoveries. Unraveling mysteries of cellular differentiation could lead to a deeper understanding of how cells specialize and develop. Regenerative medicine holds immense potential for treating various diseases and injuries by harnessing the power of stem cells. Stem cell therapy is a promising field that aims to replace damaged or diseased cells, offering hope for patients with previously incurable conditions. Embark on a journey through these captivating topics and expand your knowledge of the incredible advancements in stem cell research.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
