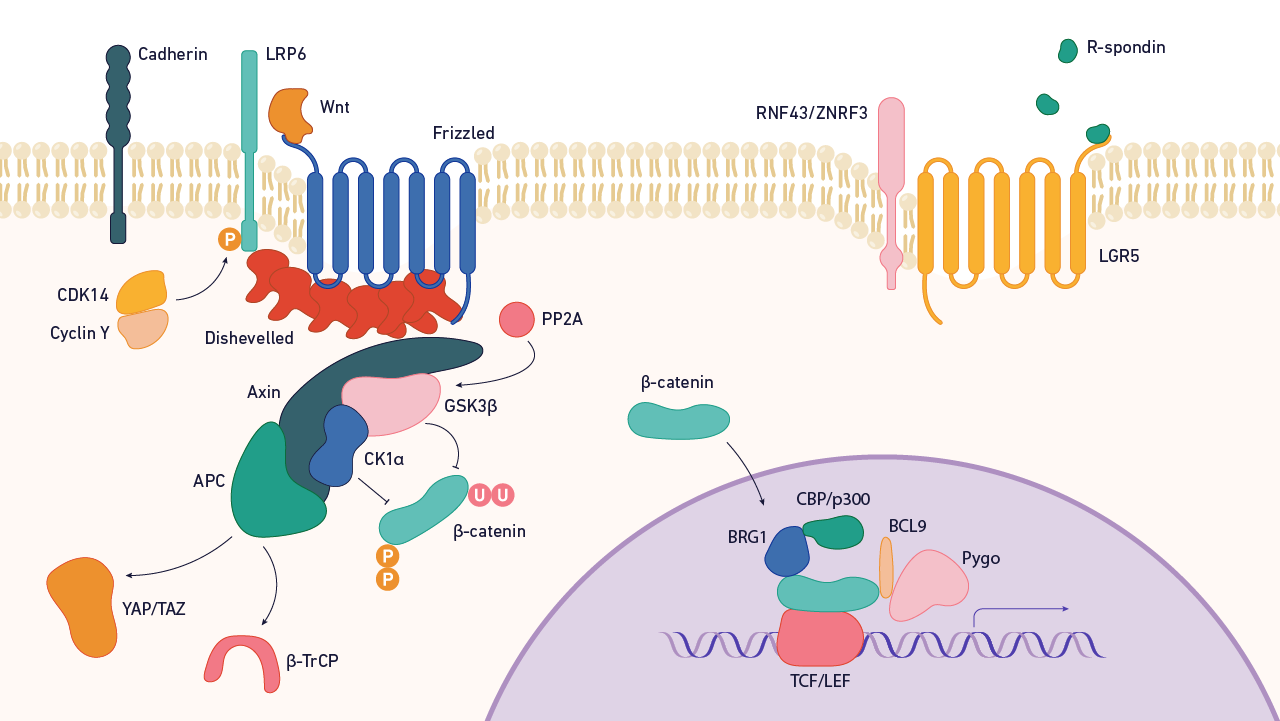
The Wnt signaling pathway is a remarkable and complex network of cell-to-cell communication that plays a crucial role in the development and functioning of organisms. Named after the Wnt family of secreted signaling proteins, this pathway is highly conserved across species, from worms to humans. It regulates various biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and embryo development.
The discovery and study of the Wnt pathway have revolutionized our understanding of developmental biology and the mechanisms that drive diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Wnt signaling pathway and uncover 20 astounding facts that showcase its importance and impact on life as we know it.
Key Takeaways:
- The Wnt signaling pathway is like a conductor orchestrating the symphony of life, from building organs to regulating immune responses and even controlling hair growth.
- Dysregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway can lead to serious consequences, such as cancer and developmental disorders, highlighting its crucial role in maintaining our health and well-being.
The Wnt signaling pathway is essential for embryonic development.
The Wnt signaling pathway plays a crucial role in embryonic development, regulating processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue patterning. This intricate pathway ensures the proper formation of organs and body structures.
It is named after a combination of “wingless” and “int-1.”
The name “Wnt” was derived from the combination of the Drosophila gene “wingless” and the oncogene “int-1” found in mice. This reflects the pathway’s importance in both developmental processes and cancer progression.
Wnt signaling pathway is highly conserved across species.
This signaling pathway is conserved throughout evolution, meaning its components and functions are similar in a wide range of organisms, from fruit flies and worms to humans. This emphasizes its fundamental role in biological processes.
There are 19 known Wnt proteins.
The Wnt family consists of 19 different proteins that bind to specific receptors to initiate the signaling cascade. Each Wnt protein has unique functions and spatial-temporal expression patterns.
Dysregulation of Wnt signaling can lead to cancer.
Aberrant activation or inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway has been linked to the development and progression of various types of cancer, including colorectal, breast, and liver cancer. Understanding the intricacies of this pathway is crucial for developing targeted cancer therapies.
Wnt signaling is involved in stem cell maintenance and self-renewal.
The Wnt pathway plays a vital role in maintaining the pluripotency and self-renewal capacity of stem cells. It regulates the balance between proliferation and differentiation, ensuring the continuous supply of undifferentiated cells.
Wnt signaling is necessary for bone formation and remodeling.
Activation of the Wnt pathway is crucial for bone development and remodeling. It stimulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation.
Wnt signaling is involved in the control of hair growth.
Wnt signaling plays a role in regulating the hair follicle cycle, including the growth and maintenance of hair. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to hair disorders such as alopecia.
Wnt signaling is essential for tissue regeneration.
The Wnt pathway is closely involved in tissue regeneration and wound healing. It promotes cell proliferation and migration to aid in the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues.
Wnt signaling is critical for neuronal development and synapse formation.
During brain development, Wnt signaling controls the proliferation and differentiation of neuronal progenitor cells. It also regulates the formation and remodeling of synapses, the junctions between nerve cells.
Wnt signaling is involved in heart development and function.
The Wnt pathway plays a crucial role in heart development, ensuring proper cardiac tissue formation and function. Dysregulation of Wnt signaling can lead to congenital heart defects.
Wnt signaling is implicated in the regulation of immune responses.
The Wnt pathway has been found to modulate immune responses, including the activation of immune cells and the regulation of inflammatory processes. This highlights its role in maintaining immune homeostasis.
Wnt signaling can be regulated by secreted inhibitors.
To maintain precise control over the Wnt signaling pathway, secreted inhibitors such as Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF-1) and Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) can bind to Wnt proteins or their receptors, modulating their activity.
Wnt signaling pathway can cross-talk with other signaling pathways.
The Wnt pathway interacts with various other signaling pathways, such as Notch, Hedgehog, and TGF-beta, creating a complex network of cross-talk. This integration allows for intricate regulation of developmental processes and cellular functions.
Wnt signaling can regulate cell polarity and tissue organization.
Through its role in regulating cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization, the Wnt pathway influences cell polarity and tissue organization. It ensures proper alignment and arrangement of cells within tissues and organs.
Wnt signaling is involved in regulating intestinal crypt stem cells.
In the intestine, Wnt signaling maintains the population of stem cells in the crypts, which are responsible for continuous epithelial cell renewal. Disruption of this pathway can impair intestinal homeostasis.
Wnt signaling plays a role in kidney development and regeneration.
The Wnt pathway is crucial for kidney development, regulating processes such as nephron formation and branching morphogenesis. It also contributes to kidney regeneration after injury.
Wnt signaling is important for lung development and repair.
During lung development, Wnt signaling influences branching morphogenesis and cell fate determination. It is also involved in the repair of lung tissue after injury.
Wnt signaling is implicated in the regulation of adipogenesis.
The Wnt pathway plays a role in controlling the differentiation of adipocytes (fat cells) from precursor cells. Dysregulation of this pathway can contribute to obesity and metabolic disorders.
Wnt signaling is involved in the regulation of reproductive processes.
Wnt signaling has been found to play a role in various reproductive processes, including ovarian development, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis. It is crucial for maintaining fertility and reproductive function.
Conclusion
The Wnt signaling pathway is a fascinating area of study in biology, with numerous implications for development, disease, and regeneration. The pathway plays a vital role in embryogenesis, tissue homeostasis, stem cell maintenance, and cell fate determination. Through the activation or inhibition of various components, the Wnt pathway regulates a wide range of cellular processes and helps control complex biological events.
Understanding the intricate mechanisms of Wnt signaling has the potential to revolutionize our approach to medical treatments, including the development of novel therapies for diseases such as cancer, bone disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. Researchers continue to explore and unveil the many astonishing facts about this pathway, shedding light on its multiple facets and unveiling new possibilities for intervention.
As we delve deeper into the complexities of the Wnt signaling pathway, we are poised to unlock new discoveries and transform the way we perceive and treat human health. With each revelation, we inch closer to unraveling the mysteries of biology and paving the way for future advancements.
FAQs
1. What is the Wnt signaling pathway?
The Wnt signaling pathway is a highly conserved pathway that regulates numerous cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
2. How does the Wnt pathway influence development?
The Wnt pathway plays a critical role in embryonic development by controlling cell fate determination and tissue patterning.
3. What happens when the Wnt pathway malfunctions?
Dysregulation of the Wnt pathway has been associated with various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and developmental abnormalities.
4. How is the Wnt pathway linked to cancer?
In many cancers, the Wnt pathway is hyperactivated, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation.
5. Are there any drugs targeting the Wnt pathway?
Researchers are actively developing drugs that target different components of the Wnt pathway, with the aim of developing more effective treatments for diseases.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
